Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2021 Dec;26(4):252-258. 10.6065/apem.2040266.133.
Identification of sphingosine 1-phosphate level and MAPK/ERK signaling in pancreatic β cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2523831
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2040266.133
Abstract
- Purpose
Sphingosine kinase is a lipid kinase that phosphorylates sphingosine to generate sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). S1P regulates pancreatic islet β-cell endoplasmic reticulum stress and proliferation. Type 1 and type 2 diabetes share some key pathogenic processes. In this study, we investigated whether secretion of insulin and production of S1P is altered in alloxan and glucose-treated cells from the rat pancreatic β-cell line RIN-5F.
Methods
RIN-5F cells were treated with 2 mM alloxan and 20 mM glucose for 6 hours or 24 hours before being evaluated by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blotting.
Results
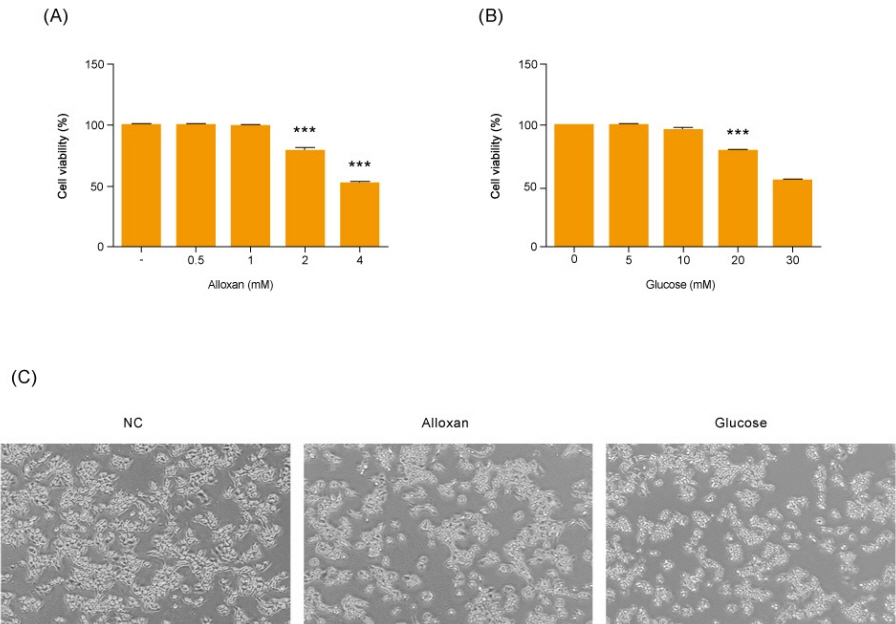
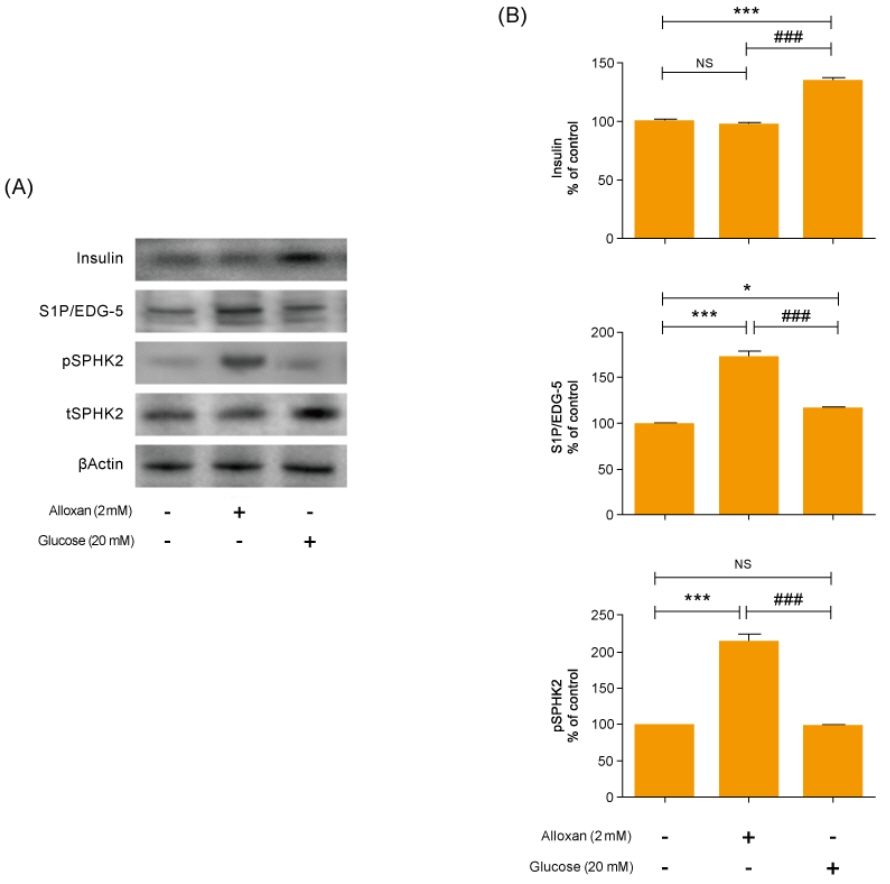
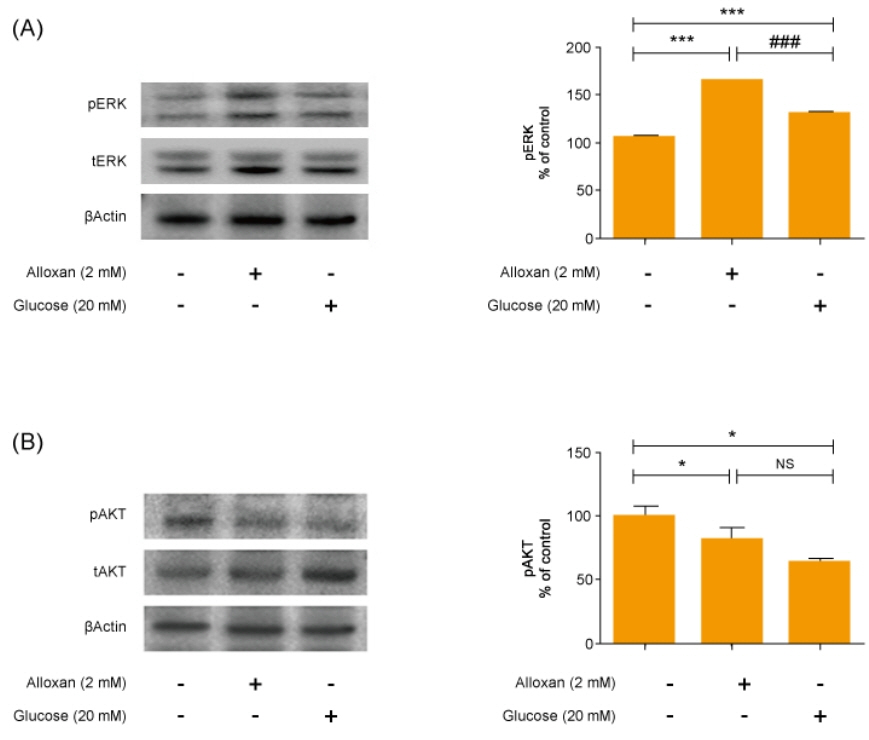
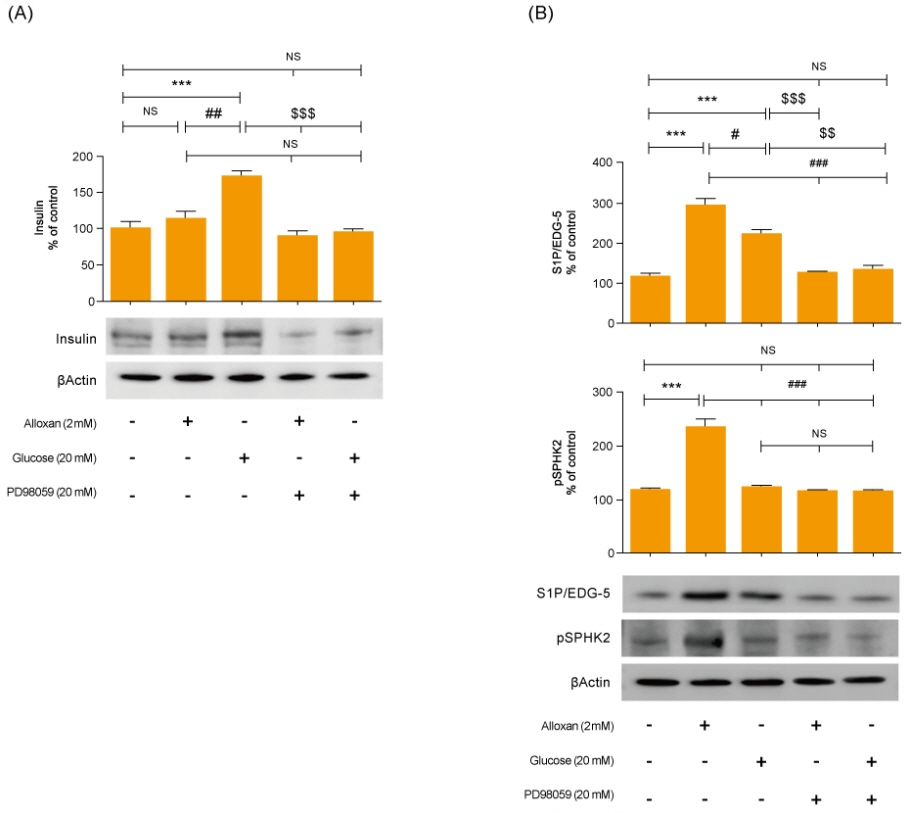
Insulin secretion and expression was higher in RIN-5F cells treated with glucose compared to control cells. In contrast, alloxan treatment did not affect insulin secretion and expression in RIN-5F cells. Interestingly, compared with normal control levels, S1P/EDG-5 was increased in both alloxan and glucose-treated pancreatic β cell than normal control. Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) inhibition strongly decreased the expression of insulin and S1P in glucose- or alloxan-treated RIN-5F cells.
Conclusion
We observe that production of S1P is increased in both diabetic cell models. In addition, MAPK/ERK signaling regulates secretion of insulin and S1P expression in pancreatic β-cells. Based on the literature and our findings, S1P may be a promising agent for the treatment of insulin-related disorders.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Craig ME, Jefferies C, Dabelea D, Balde N, Seth A, Donaghue KC, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2014. Definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014; 15 Suppl 20:4–17.2. White MF. Insulin signaling in health and disease. Science. 2003; 302:1710–1.
Article3. Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. Acute and chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Lancet. 2007; 369:1823–31.
Article4. Craig ME, Jones TW, Silink M, Ping YJ. Diabetes care, glycemic control, and complications in children with type 1 diabetes from Asia and the Western Pacific Region. J Diabetes Complications. 2007; 21:280–7.
Article5. Saini V. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes. 2010; 1:68–75.
Article6. Arish M, Alaidarous M, Ali R, Akhter Y, Rub A. Implication of sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in diseases: molecular mechanism and therapeutic strategies. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2017; 37:437–46.
Article7. Chen W, Lu H, Yang J, Xiang H, Peng H. Sphingosine 1-phosphate in metabolic syndrome (review). Int J Mol Med. 2016; 38:1030–8.
Article8. Rosen H, Stevens RC, Hanson M, Roberts E, Oldstone MB. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors: structure, signaling, and influence. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013; 82:637–62.
Article9. Ng ML, Wadham C, Sukocheva OA. The role of sphingolipid signalling in diabetes associated pathologies (review). Int J Mol Med. 2017; 39:243–52.10. R andri amb o avonjy V, B aden ho op K, S chmidt H, Geisslinger G, Fisslthaler B, Fleming I. The S1P(2) receptor expressed in human platelets is linked to the RhoA-Rho kinase pathway and is down regulated in type 2 diabetes. Basic Res Cardiol. 2009; 104:333–40.
Article11. Imasawa T, Koike K, Ishii I, Chun J, Yatomi Y. Blockade of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 signaling attenuates streptozotocin-induced apoptosis of pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010; 392:207–11.12. Alshatwi AA, Subash-Babu P. Aloe-emodin protects RIN-5F (pancreatic β-cell) cell from glucotoxicity via regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine and downregulation of bax and caspase 3. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016; 24:49–56.
Article13. Spiegel S, Milstien S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: signaling inside and out. FEBS Lett. 2000; 476:55–7.
Article14. He Y, Shi B, Zhao X, Sui J. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces islet β-cell proliferation and decreases cell apoptosis in high-fat diet/streptozotocin diabetic mice. Exp Ther Med. 2019; 18:3415–24.
Article15. Hatoum D, Haddadi N, Lin Y, Nassif NT, McGowan EM. Mammalian sphingosine kinase (SphK) isoenzymes and isoform expression: challenges for SphK as an oncotarget. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:36898–929.
Article16. Haass NK, Nassif N, McGowan EM. Switching the sphingolipid rheostat in the treatment of diabetes and cancer comorbidity from a problem to an advantage. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:165105.
Article17. Ighodaro OM, Adeosun AM, Akinloye OA. Alloxan-induced diabetes, a common model for evaluating the glycemic-control potential of therapeutic compounds and plants extracts in experimental studies. Medicina (Kaunas). 2017; 53:365–74.
Article18. Wysham C, Shubrook J. Beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: mechanisms, markers, and clinical implications. Postgrad Med. 2020; 132:676–86.
Article19. Poitout V, Robertson RP. Minireview: secondary beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes--a convergence of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Endocrinology. 2002; 143:339–42.
Article20. Tsubouchi H, Inoguchi T, Sonta T, Sato N, Sekiguchi N, Kobayashi K, et al. Statin attenuates high glucose-induced and diabetes-induced oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo evaluated by electron spin resonance measurement. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005; 39:444–52.
Article21. Rho HW, Lee JN, Kim HR, Park BH, Park JW. Protective mechanism of glucose against alloxan-induced beta-cell damage: pivotal role of ATP. Exp Mol Med. 2000; 32:12–7.
Article22. Lei H, Han J, Wang Q, Guo S, Sun H, Zhang X. Effects of sesamin on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced NIT-1 pancreatic β-cell damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13:16961–70.
Article23. Longuet C, Broca C, Costes S, Hani EH, Bataille D, Dalle S. Extracellularly regulated kinases 1/2 (p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinases) phosphorylate synapsin I and regulate insulin secretion in the MIN6 beta-cell line and islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 2005; 146:643–54.
Article24. Holland WL, Summers SA. Sphingolipids, insulin resistance, and metabolic disease: new insights from in vivo manipulation of sphingolipid metabolism. Endocr Rev. 2008; 29:381–402.
Article25. Maceyka M, Harikumar KB, Milstien S, Spiegel S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and its role in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2012; 22:50–60.
Article26. Holm LJ, Krogvold L, Hasselby JP, Kaur S, Claessens LA, Russell MA, et al. Abnormal islet sphingolipid metabolism in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2018; 61:1650–61.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- HMGB1 increases RAGE expression in vascular smooth muscle cells via ERK and p-38 MAPK-dependent pathways
- Prolonged ERK Activation of S1P on B16 Melanoma Cells
- Hederacoside C Modulates EGF-Induced MUC5AC Mucin Gene Expression by Regulating the MAPK Signaling Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Triggers Apoptotic Signal for B16 Melanoma Cells via ERK and Caspase Activation
- Analysis of a Sphingosine 1-phosphate Receptor hS1P3 in Rat Hepatoma Cells