J Korean Acad Nurs.
2013 Dec;43(6):746-759. 10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.746.
Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Diagnostic Accuracy of Infrared Thermometer when Identifying Fever in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2School of Nursing, Pai Chai University, Daejeon, Korea. shpark@pcu.ac.kr
- 3Research Development Team, Korea Health Promotion Foundation, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1711266
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.6.746
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Infrared thermometers are increasingly used as a convenient, non-invasive assessment method for febrile children. However, the diagnostic accuracy of the infrared thermometer for children has been questioned, particularly in relation to sensitivity and specificity. The aim of this study was to evaluate diagnostic accuracy of infrared thermometers in febrile children.
METHODS
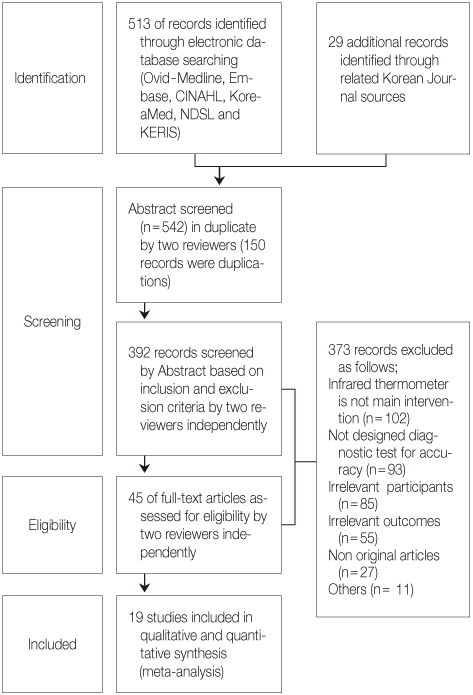
Articles published between 1966 and 2012 from periodicals indexed in the Ovid Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, KoreaMed, NDSL, KERIS and other databases were selected, using the following keywords: 'infrared thermometer'. The QUADAS-II was applied to assess the internal validity of the diagnostic studies. Selected studies were analyzed using meta-analysis with MetaDisc 1.4.
RESULTS
Nineteen diagnostic studies with high methodological quality, involving 4,304 children, were included. The results of meta-analysis showed that the pooled sensitivity, specificity and AUC (Area Under the Curve) of infrared tympanic thermometers in children over 1 year were 0.80 (95% CI 0.78, 0.81), 0.94 (95% CI 0.93, 0.95) and 0.95 respectively. However the diagnostic accuracy of infrared tympanic thermometers in children with hyperthermia was low.
CONCLUSION
The diagnostic accuracy of infrared tympanic thermometer was similar to axillary and rectal thermometers indicating a need for further research to substantiate these findings in children with hyperthermia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brennan DF, Falk JL, Rothrock SG, Kerr RB. Reliability of infrared tympanic thermometry in the detection of rectal fever in children. Ann Emerg Med. 1995; 25(1):21–30.2. Burke K. The tympanic membrane thermometer in paediatrics: A review of the literature. Accid Emerg Nurs. 1996; 4(4):190–193.3. Chamberlain JM, Grandner J, Rubinoff JL, Klein BL, Waisman Y, Huey M. Comparison of a tympanic thermometer to rectal and oral thermometers in a pediatric emergency department. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1991; 30:4 Suppl. 24–29.4. Chiappini E, Sollai S, Longhi R, Morandini L, Laghi A, Osio CE, et al. Performance of non-contact infrared thermometer for detecting febrile children in hospital and ambulatory settings. J Clin Nurs. 2011; 20(9-10):1311–1318. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2010.03565.x.5. Childs C, Harrison R, Hodkinson C. Tympanic membrane temperature as a measure of core temperature. Arch Dis Child. 1999; 80(3):262–266.6. Craig JV, Lancaster GA, Taylor S, Williamson PR, Smyth RL. Infrared ear thermometry compared with rectal thermometry in children: A systematic review. Lancet. 2002; 360(9333):603–609. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(02)09783-0.7. Devrim I, Kara A, Ceyhan M, Tezer H, Uludağ AK, Cengiz AB, et al. Measurement accuracy of fever by tympanic and axillary thermometry. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2007; 23(1):16–19. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0b013e31802c61e6.8. Dodd SR, Lancaster GA, Craig JV, Smyth RL, Williamson PR. In a systematic review, infrared ear thermometry for fever diagnosis in children finds poor sensitivity. J Clin Epidemiol. 2006; 59(4):354–357. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.10.004.9. Edelu BO, Ojinnaka NC, Ikefuna AN. Fever detection in under 5 children in a tertiary health facility using the infrared tympanic thermometer in the oral mode. Ital J Pediatr. 2011; 37:8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1824-7288-37-8.10. El-Radhi AS, Barry W. Thermometry in paediatric practice. Arch Dis Child. 2006; 91(4):351–356.11. El-Radhi AS, Patel SP. Temperature measurement in children with cancer: An evaluation. Br J Nurs. 2007; 16(21):1313–1316.12. Erickson RS, Woo TM. Accuracy of infrared ear thermometry and traditional temperature methods in young children. Heart Lung. 1994; 23(3):181–195.13. Greenes DS, Fleisher GR. Accuracy of a noninvasive temporal artery thermometer for use in infants. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2001; 155(3):376–381.14. Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith RD. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med. 2000; 45(1-2):23–41.15. Hay AD, Peters TJ, Wilson A, Fahey T. The use of infrared thermometry for the detection of fever. Br J Gen Pract. 2004; 54(503):448–450.16. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002; 21(11):1539–1558. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186.17. Hong YS, Lee SO. An experimental study on the shortest optimum time for body temperature measurement. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1975; 5(2):38–50.18. Hwang JS, Sohng KY. Comparison of rectal temperature with axillary and tympanic temperature. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 1997; 4(2):351–358.19. Jean-Mary MB, Dicanzio J, Shaw J, Bernstein HH. Limited accuracy and reliability of infrared axillary and aural thermometers ina pediatric outpatient population. J Pediatr. 2002; 141(5):671–676. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mpd.2002.127664.20. Jeong IS, Yoo EJ. Study on the body temperature measuring time and accuracy and reliability of tympanic thermometer. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 1997; 4(1):19–30.21. Jeong YS, Kim JS. Fever and fever management in children: A literature review. J Korean Acad Child Health Nurs. 2010; 16(1):30–40. http://dx.doi.org/10.4094/jkachn.2010.16.1.30.22. Kim JS. Anesthesia and temperature. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2004; 47(5):609–616.23. Kozier B, Erb G, Blais K, Wilkinson JM. Fundamentals of nursing: Concepts, process, and practice. 5th ed. Redwood City, CA: Addison-Wesley;1997.24. Lee G, Flannery-Bergey D, Randall-Rollins K, Curry D, Rowe S, Teague M, et al. Accuracy of temporal artery thermometry in neonatal intensive care infants. Adv Neonatal Care. 2011; 11(1):62–70. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/ANC.0b013e3182087d2b.25. Lee JK, Kim EJ, Lee HK, Yu YH, Lee HS. The effect of bundling on neonatal body temperature. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1998; 41(1):26–32.26. Lee TJ, Kim DS. Fever. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50(2):121–126. http://dx.doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2007.50.2.121.27. Lee YK, Lee SM. Clinical trials and accuracy of diagnostic tests. J Genet Med. 2011; 8(1):28–34. http://dx.doi.org/10.5734/jgm.2011.8.1.28.28. Liu CC, Chang RE, Chang WC. Limitations of forehead infrared body temperature detection for fever screening for severe acute respiratory syndrome. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2004; 25(12):1109–1111. http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/502351.29. Macaskill P, Gatsonis C, Deeks JJ, Harbord RM, Takwoingi Y. Chapter 10: Analysing and presenting results. In : Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy version 1.0. Oxford, UK: The Cochrane Collaboration;2010. p. 1–47.30. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151(4):264–269. W26431. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Feverish illness in children: NICE guideline. London, UK: Author;2007.32. Nimah MM, Bshesh K, Callahan JD, Jacobs BR. Infrared tympanic thermometry in comparison with other temperature measurement techniques in febrile children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2006; 7(1):48–55.33. Robinson JL, Seal RF, Spady DW, Joffres MR. Comparison of esophageal, rectal, axillary, bladder, tympanic, and pulmonary artery temperatures in children. J Pediatr. 1998; 133(4):553–556.34. Royal College of Nursing. Standards for assessing, measuring and monitoring vital signs in infants, children and young people: RCN guidance for children's nurses and nurses working with children. London, UK: Author;2011.35. Selfridge J, Shea SS. The accuracy of the tympanic membrane thermometer in detecting fever in infants aged 3 months and younger in the emergency department setting. J Emerg Nurs. 1993; 19(2):127–130.36. Shenep JL, Adair JR, Hughes WT, Roberson PK, Flynn PM, Brodkey TO, et al. Infrared, thermistor, and glass-mercury thermometry for measurement of body temperature in children with cancer. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1991; 30:4 Suppl. 36–41. discussion 49.37. Sohng KY, Kang SS, Hwang JS, Kim MJ. Accuracy of temperature measurements, nursing time for measuring temperature and the validity of fever detection. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 1998; 5(1):33–45.38. Sohng KY, Park HS, Hong YH, Yoon EJ, Lee KY, Cho BH, et al. Fundamentals of nursing. 2nd ed. Paju: Soomoonsa;2009.39. van Staaij BK, Rovers MM, Schilder AG, Hoes AW. Accuracy and feasibility of daily infrared tympanic membrane temperature measurements in the identification of fever in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2003; 67(10):1091–1097.40. Walter SD. Properties of the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for diagnostic test data. Stat Med. 2002; 21(9):1237–1256. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/sim.1099.41. Wells N, King J, Hedstrom C, Youngkins J. Does tympanic temperature measure up? MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. 1995; 20(2):95–100.42. Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011; 155(8):529–536. http://dx.doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009.43. Wilshaw R, Beckstrand R, Waid D, Schaalje GB. A comparison of the use of tympanic, axillary, and rectal thermometers in infants. J Pediatr Nurs. 1999; 14(2):88–93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0882-5963(99)80042-6.44. Yun KW, Lim IS. A study for accuracy and usefulness of tympanic membrane and forehead thermometers. Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48(8):820–825.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reliability and Accuracy of Infrared Temperature: A Systematic Review
- A Study for Accuracy and Usefulness of Tympanic Membrane and Forehead Thermometers
- Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part I. General Guidance and Tips
- Overview of the Process of Conducting Meta-analyses of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy
- Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part II. Statistical Methods of Meta-Analysis