Korean J Adult Nurs.
2014 Dec;26(6):668-680. 10.7475/kjan.2014.26.6.668.
Reliability and Accuracy of Infrared Temperature: A Systematic Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Nursing, Pai Chai University, Daejeon, Korea. shpark@pcu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2298157
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2014.26.6.668
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to investigate the accuracy of infrared temperature measurements compared to axillary temperature in order to detect fever in patients.
METHODS
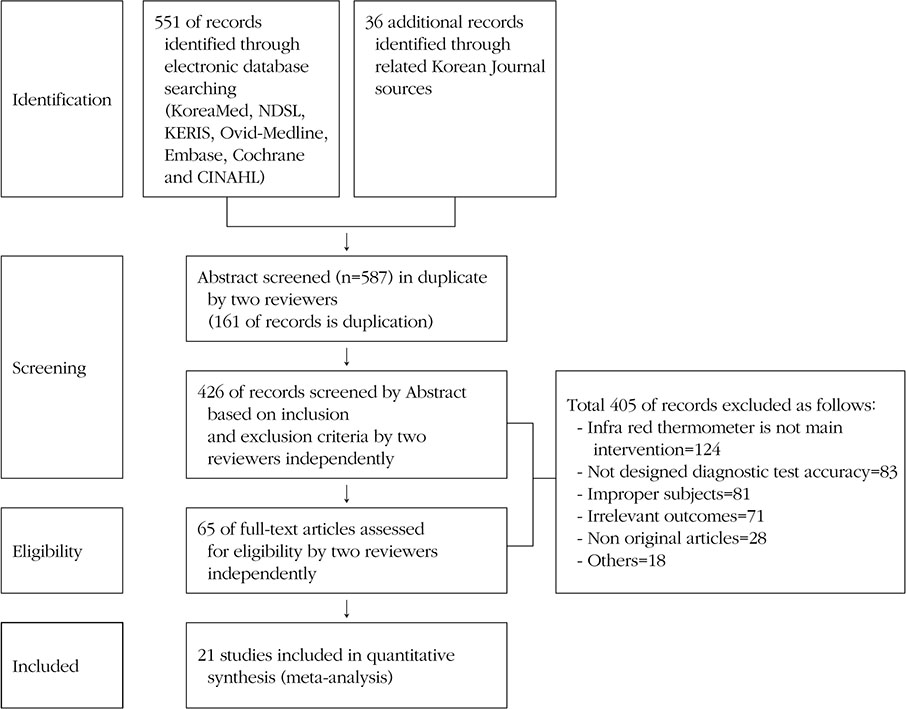
Studies published between 1946 and 2012 from periodicals indexed in Ovid Medline, Embase, CINAHL, Cochrane, KoreaMed, NDSL, KERIS and other databases were selected using the following key words: "infrared thermometer." QUADAS-II was utilized to assess the internal validity of the diagnostic studies. Selected studies were analyzed through a meta-analysis using MetaDisc 1.4.
RESULTS
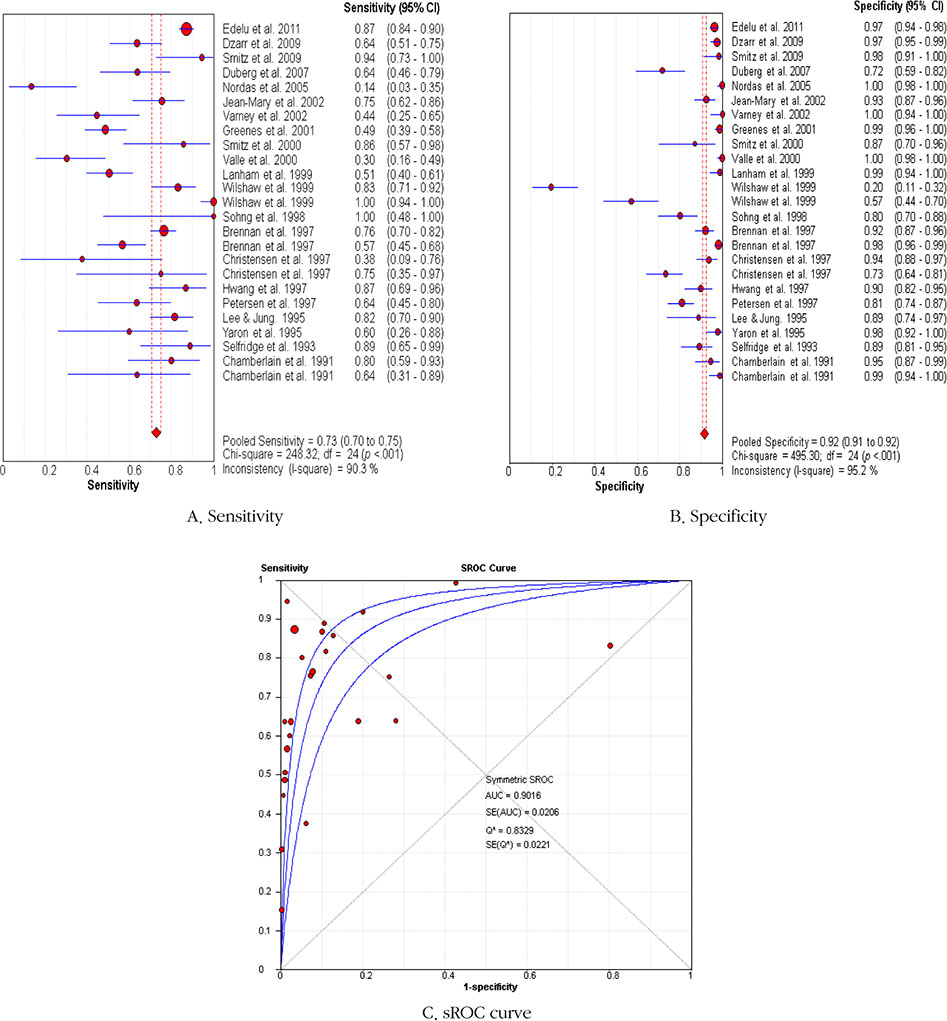
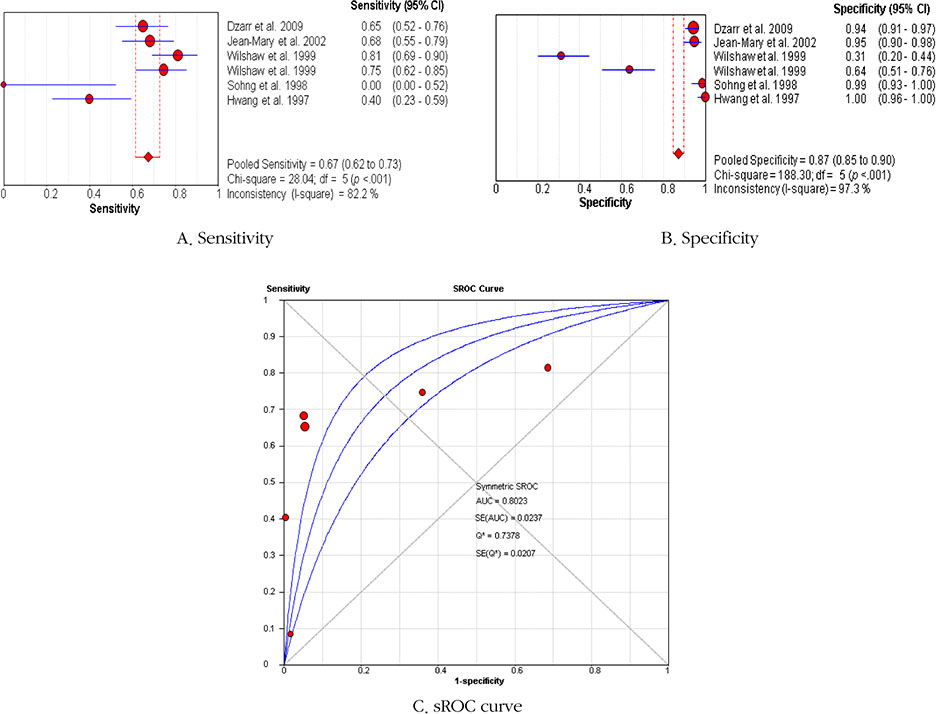
Twenty-one diagnostic studies with high methodological quality were included representing 3,623 subjects in total. Results of the meta-analysis showed that the pooled sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) of infrared tympanic thermometers were 0.73 (95% CI 0.70~0.75), 0.92 (95% CI 0.91~0.92), and 0.90, respectively. For axillary temperature readings, the pooled sensitivity was 0.67 (95% CI 0.62~0.73), the pooled specificity was 0.87 (95% CI 0.85~0.90), and the AUC was 0.80.
CONCLUSION
Infrared tympanic temperature can predict axillary temperature in normothermic and in febrile patients with an acceptable level of diagnostic accuracy. However, further research is necessary to substantiate this finding in patients with hyperthermia.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moran JL, Peter JV, Solomon PJ, Grealy B, Smith T, Ashforth W, et al. Tympanic measurements: are they reliable in the critically ill? A clinical study of measures of agreement. Crit Care Med. 2007; 35(1):155–164.2. Liu CC, Chang RE, Chang WE. Limitations of forehead infrared body temperature detection for fever screening for severe acute respiratory syndrome. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2004; 25(12):1109–1111.
Article3. Lee TJ, Kim DS. Fever. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:121–126.
Article4. Childs C, Harrison R, Hodkinson C. Tympanic membrane temperature as a measure of core temperature. Arch Dis Child. 1999; 80(3):262–266. DOI: 10.1136/adc.80.3.262.
Article5. Park CW, Park SN. Development of standard and improvement of reliability in body temperature measurement. J Korean Soc Precision Eng. 2007; 24(9):32–36.6. Androkites AL, Werger AM, Young ML. Comparison of axillary and infrared tympanic membrane thermometry in a pediatric oncology outpatient setting. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 1998; 15:216–222.
Article7. Yun KW, Lim IS. A study for accuracy and usefulness of tympanic membrane and forehead thermometers. Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48(8):820–825.8. Ministry of Food and Drugs Safety. Medical device regulations revision No. 2014-142. [Internet]. Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drugs Safety;2014. cited 2014 August 11. Available from: http://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do?x=30&searchkey=title:contents&mid=686&searchword=&division=&y=12&pageNo=6&seq=8211&cmd=v.9. Macaskill P, Gatsonis C, Deeks J, Harbord R, Takwoingi T. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy version 1.0. [Internet]. The Cochrane Collaboration;2010. cited 2013 May 30. Available from: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org.10. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Antes G, Atkins D, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151(4):264–269. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135.
Article11. Whitting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011; 155(8):529–536. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009.
Article12. Greiner M, Pfeiffer D, Smith RD. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev Vet Med. 2000; 45(1-2):23–41. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-5877(00)00115-X.
Article13. Walter SD. Properties of the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for diagnostic test data. Stat Med. 2002; 21(9):1237–1256.
Article14. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002; 21(11):1539–1558. DOI: 10.1002/sim.1186.
Article15. Fischer JE, Bachmann LM, Jaeschke R. A readers' guide to the interpretation of diagnostic test properties: clinical example of sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2003; 29(7):1043–1051.
Article16. Zweig MH, Campbell G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem. 1993; 39(4):561–577.
Article17. Wells N, King J, Hedstrom C, Youngkins J. Does tympanic temperature measure up? MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. 1995; 20:95–100.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Diagnostic Accuracy of Infrared Thermometer when Identifying Fever in Children
- A Study of Reliability of Tympanic Temperature Measurement Using Infrared Thermometer ( Home Model ) in Neonates
- Appropriate Body Temperature Measurement Method for Parents of Infants
- Application of infrared thermography in dentistry
- Digital Infrared Thermographic Imaging(D.I.T.I.) in Herniated Lumbar Disc Patients