Tuberc Respir Dis.
2007 Sep;63(3):278-282. 10.4046/trd.2007.63.3.278.
A Case of Pseudomembranous Necrotizing Bronchial Aspergillosis in An Old Age Host
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea. medics27@cau.ac.kr
- 2Division of Pathology, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1518420
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2007.63.3.278
Abstract
- Invasive aspergillus tracheobronchitis is uncommon manifestation of infection due to Aspergillus species, occurring in severely immunocompromised patients who are generally neutropenic with haematological diseases, AIDS, or after heart and lung transplantation. The pseudomembranous form is the most severe condition and is usually fatal despite treatment with antifungal agents. However, there are a few cases reported with no apparent severe compromise in the host defences. We encountered a pseudomembranous necrotizing bronchial aspergillosis in a 73-year old male patient, who was treated successfully with antifungal agents.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
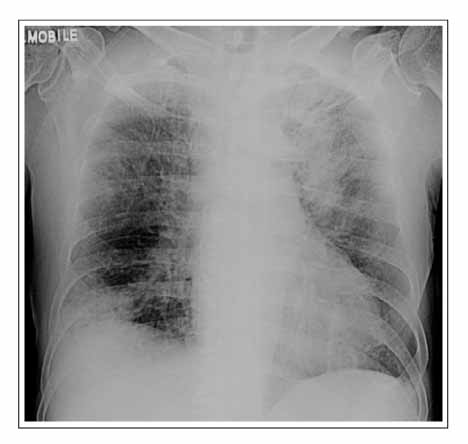
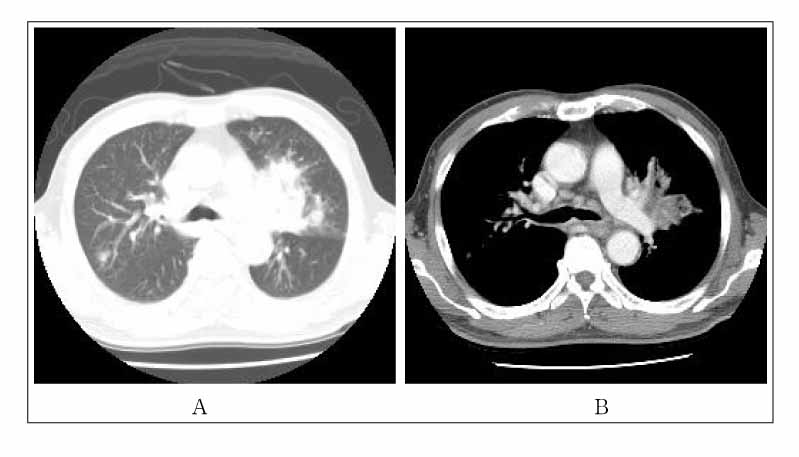
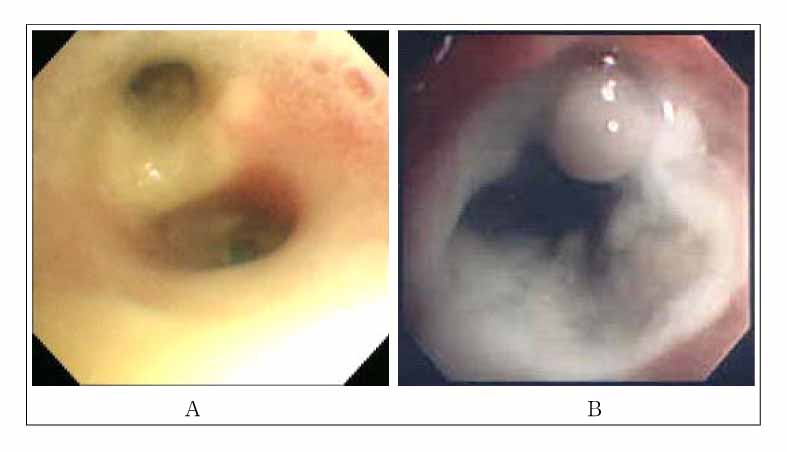
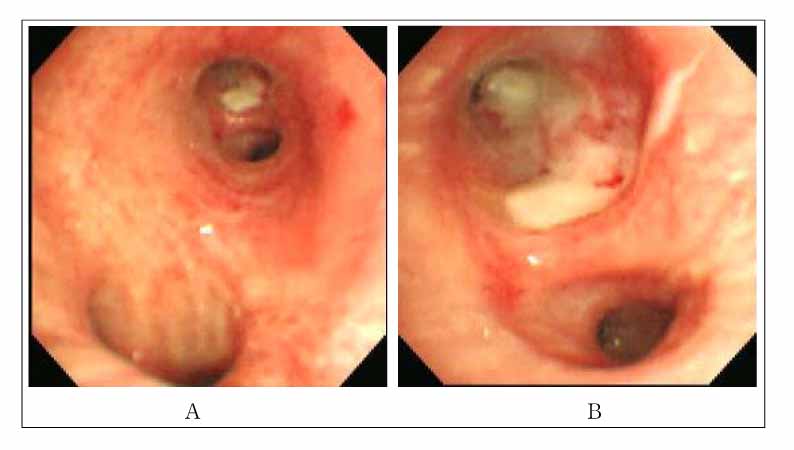
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Invasive Tracheobronchial Aspergillosis : Case Reports and a Literature Review
Jae-Ki Choi, Jin-Hee No, Bo-Hee Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Si-Hyun Kim, Jae-Cheol Kwon, Ji-Hyung Hong, Guk-Jin Lee, Sun Hee Park, Su-Mi Choi, Dong-Gun Lee, Jung-Hyun Choi, Jin-Hong Yoo
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(1):76-81. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.1.76.
Reference
-
1. Oh HJ, Kim HR, Hwang KE, Kim SY, Ahn SH, Yang SH, et al. Case of pseudomembranous necrotizing tracheobronchial aspergillosis in an immunocompetent host. Korean J Intern Med. 2006. 21:279–282.2. Soubani AO, Chandrasekar PH. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Chest. 2002. 121:1988–1999.3. Ahn MI, Park SH, Kim JA, Kwon MS, Park YH. Pseudomembranous necrotizing bronchial aspergillosis. Br J Radiol. 2000. 73:73–75.4. Kramer MR, Denning DW, Marshall SE, Ross DJ, Berry G, Lewiston NJ, et al. Ulcerative tracheobronchitis after lung transplantation. A new form of invasive aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. 144:552–556.5. Nusair S, Amir G, Or R, Breuer R. Invasive airway aspergillosis with new airflow obstruction mimicking post-BMT bronchiolitis obliterans. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002. 29:711–713.6. Cook DJ, Achong MR, King DE. Disseminated aspergillosis in an apparently healthy patient. Am J Med. 1990. 88:74–76.7. Polat G, Urpek G, Yilmaz U, Buyuksirin M, Karadag Polat S, Uluer S, et al. Successful treatment of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in an immunocompetent host. Respirology. 2005. 10:393–395.8. Pervez NK, Kleinerman J, Kattan M, Freed JA, Harris MB, Rosen MJ, et al. Pseudomembranous necrotizing bronchial aspergillosis. A variant of invasive aspergillosis in a patient with hemophilia and acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985. 131:961–963.9. Hines DW, Haber MH, Yaremko L, Britton C, McLawhon RW, Harris AA. Pseudomembranous tracheobronchitis caused by Aspergillus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. 143:1408–1411.10. Denning DW. Invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1998. 26:781–803. quiz 804-5.11. Ducreux D, Chevallier P, Perrin C, Jourdan J, Hofman P, Raffaelli C, et al. Pseudomembranous aspergillus bronchitis in a double-lung transplanted patient: unusual radiographic and CT features. Eur Radiol. 2000. 10:1547–1549.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Case of Pseudomembranous Necrotizing Tracheobronchial Aspergillosis in an Immunocompetent Host
- Sudden Atelectasis and Respiratory Failure in a Neutropenic Patient: Atypical Presentation of Pseudomembranous Necrotizing Bronchial Aspergillosis
- Necrotizing Bronchial Aspergillosis: A case report
- A Case of chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis with pulmonary artery aneurysm
- A Case of Invasive Aspergillosis Characterized by the Formation of Large Bronchial Cast in Patient with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia