J Korean Soc Transplant.
2013 Sep;27(3):132-137. 10.4285/jkstn.2013.27.3.132.
Disseminated Cryptococcosis with Cutaneous Manifestation in a Renal Transplant Recipient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kangjm@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1495871
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2013.27.3.132
Abstract
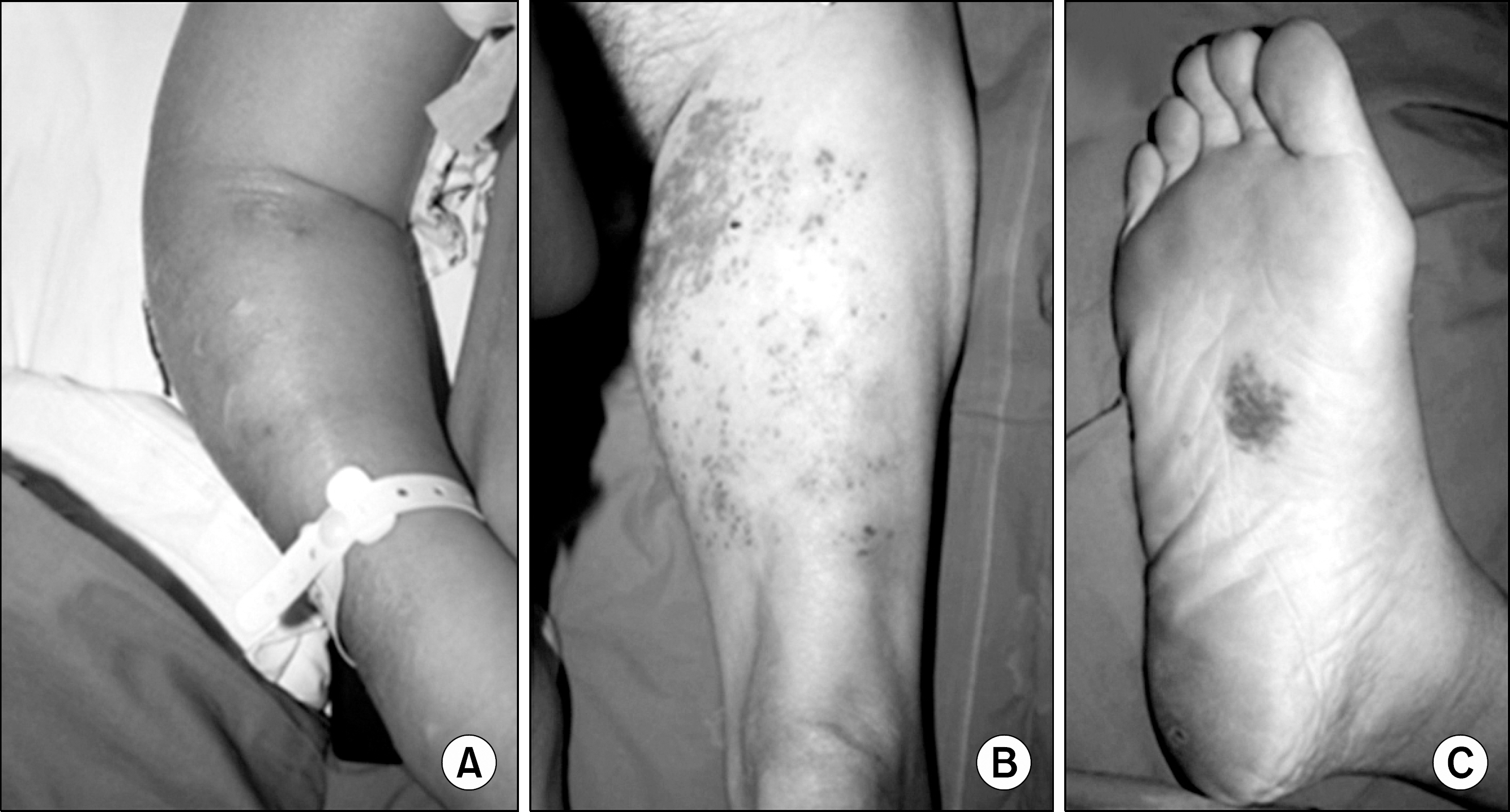
- Cryptococcosis commonly affects patients with immune dysfunction, as in the case of immunosuppression in organ transplant patients or as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in patients afflicted with human immunodeficiency virus. The varied appearance of cryptococcal skin lesion makes clinical diagnosis of cutaneous cryptococcosis difficult. Cryptococcosis proves to be a fatal fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient. Therefore, diagnosis and early treatment of cryptococcosis become vital. A 56-year-old renal transplant recipient, with an ongoing immunosuppression regimen of cyclosporine, prednisolone, and mycophenolate mofetil, was admitted with a 2-week history of pain and edema of right arm without respiratory symptoms. Despite empiric antibiotic therapy, the patient continued to complain of severe tenderness of the involved arm and fever persisted as well. On the third day of hospital stay, a biopsy of the erythematous skin lesion was acquired. On the eighth day of hospital stay, results of both skin biopsy and blood cultures showed the presence of Cryptococcus neoformans. The treatment was begun with intravenous fluconazole (400 mg/day). After 4 days of antifungal treatment, the patient developed fever along with cough with purulent sputum. As the new developing symptoms were suggestive of pneumonia, especially of pulmonary cryptococcosis, the antifungal agent was changed from fluconazole to amphotericin B treatment (0.8 mg/kg, 50 mg/day). Chest computer tomography showed improvement in the pneumonic infiltration and consolidation after 4 weeks of amphotericin B treatment. In conclusion, cellulitis in immunocompromised patients should be suspected in case of highly atypical infectious etiology, and skin biopsy should not be delayed if empiric antibiotic therapy does not control the inflammatory response. Additionally, the patient should be treated with intravenous amphotericin B treatment in case of severe cryptococcosis.
MeSH Terms
-
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Amphotericin B
Arm
Biopsy
Cellulitis
Cough
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcus neoformans
Cyclosporine
Edema
Fever
Fluconazole
HIV
Humans
Immunocompromised Host
Immunosuppression
Kidney Transplantation
Length of Stay
Middle Aged
Mycophenolic Acid
Pneumonia
Prednisolone
Skin
Sputum
Thorax
Transplants
Amphotericin B
Cyclosporine
Fluconazole
Mycophenolic Acid
Prednisolone
Figure
Reference
-
1). Chuang YM, Ho YC, Chang HT, Yu CJ, Yang PC, Hsueh PR. Disseminated cryptococcosis in HIV-unin-fected patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008; 27:307–10.
Article2). Silveira FP, Husain S. Fungal infections in solid organ transplantation. Med Mycol. 2007; 45:305–20.
Article3). Singh N, Alexander BD, Lortholary O, Dromer F, Gupta KL, John GT, et al. Cryptococcus neoformans in organ transplant recipients: impact of calcineurin-inhibitor agents on mortality. J Infect Dis. 2007; 195:756–64.4). Probst C, Pongratz G, Capellino S, Szeimies RM, Schölmerich J, Fleck M, et al. Cryptococcosis mimicking cutaneous cellulitis in a patient suffering from rheuma-toid arthritis: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. 2010; 10:239.
Article5). Singh N, Dromer F, Perfect JR, Lortholary O. Cryptococcosis in solid organ transplant recipients: current state of the science. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 47:1321–7.6). Husain S, Wagener MM, Singh N. Cryptococcus neoformans infection in organ transplant recipients: variables influencing clinical characteristics and outcome. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001; 7:375–81.7). Prevost-Smith E, Hutton N. Improved detection of Cryptococcus neoformans in the BACTEC NR 660 blood culture system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994; 102:741–5.8). Ruiz V, Barnadas MA, Matas L, Bagué S, Alomar A. Disseminated cryptococcosis presenting as skin nodules resembling erythema nodosum. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2011; 102:221–3.
Article9). Neuville S, Dromer F, Morin O, Dupont B, Ronin O, Lortholary O. French Cryptococcosis Study Group. Pri-mary cutaneous cryptococcosis: a distinct clinical entity. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:337–47.
Article10). Baer S, Baddley JW, Gnann JW, Pappas PG. Cryptoco-ccal disease presenting as necrotizing cellulitis in transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2009; 11:353–8.
Article11). Sun HY, Alexander BD, Lortholary O, Dromer F, Forrest GN, Lyon GM, et al. Cutaneous cryptococcosis in solid organ transplant recipients. Med Mycol. 2010; 48:785–91.
Article12). Perfect JR, Dismukes WE, Dromer F, Goldman DL, Graybill JR, Hamill RJ, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease: 2010 update by the infectious diseases society of america. Clin Infect Dis. 2010; 50:291–322.
Article13). Dromer F, Mathoulin S, Dupont B, Brugiere O, Leten-neur L. Comparison of the efficacy of amphotericin B and fluconazole in the treatment of cryptococcosis in human immunodeficiency virus-negative patients: retro-spective analysis of 83 cases. French Cryptococcosis Study Group. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 22(Suppl 2):S154–60.14). Singh N, Lortholary O, Alexander BD, Gupta KL, John GT, Pursell KJ, et al. Antifungal management practices and evolution of infection in organ transplant recipients with cryptococcus neoformans infection. Transplantation. 2005; 80:1033–9.
Article15). Pfaller MA, Castanheira M, Diekema DJ, Messer SA, Jones RN. Wild-type MIC distributions and epidemio-logic cutoff values for fluconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole when testing Cryptococcus neoformans as determined by the CLSI broth microdilution method. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011; 71:252–9.
Article16). Cheong JW, McCormack J. Fluconazole resistance in cryptococcal disease: emerging or intrinsic? Med Mycol. 2013; 51:261–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of Cryptococcosis with Cutaneous Manifestations
- A Case of Cutaneous Cryptococcosis Resembling Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- Cutaneous Manifestation of Disseminated Cryptococcosis Mimicking Herpes Zoster
- A Case of Asymptomatic Disseminated Cryptococcosis in a Renal Transplant Patient
- A Case of Cryptococcosis with Skin Involvement in a Liver Transplant Recipient