Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2008 Oct;12(5):245-251. 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.5.245.
Single-Channel Recording of TASK-3-like K+ Channel and Up- Regulation of TASK-3 mRNA Expression after Spinal Cord Injury in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medical Research Center for Neural Dysfunction and Department of Physiology, Jinju, Korea. dawon@gnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, College of Medicine and Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, College of Medicine and Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Yeungnam University Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1486106
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.5.245
Abstract
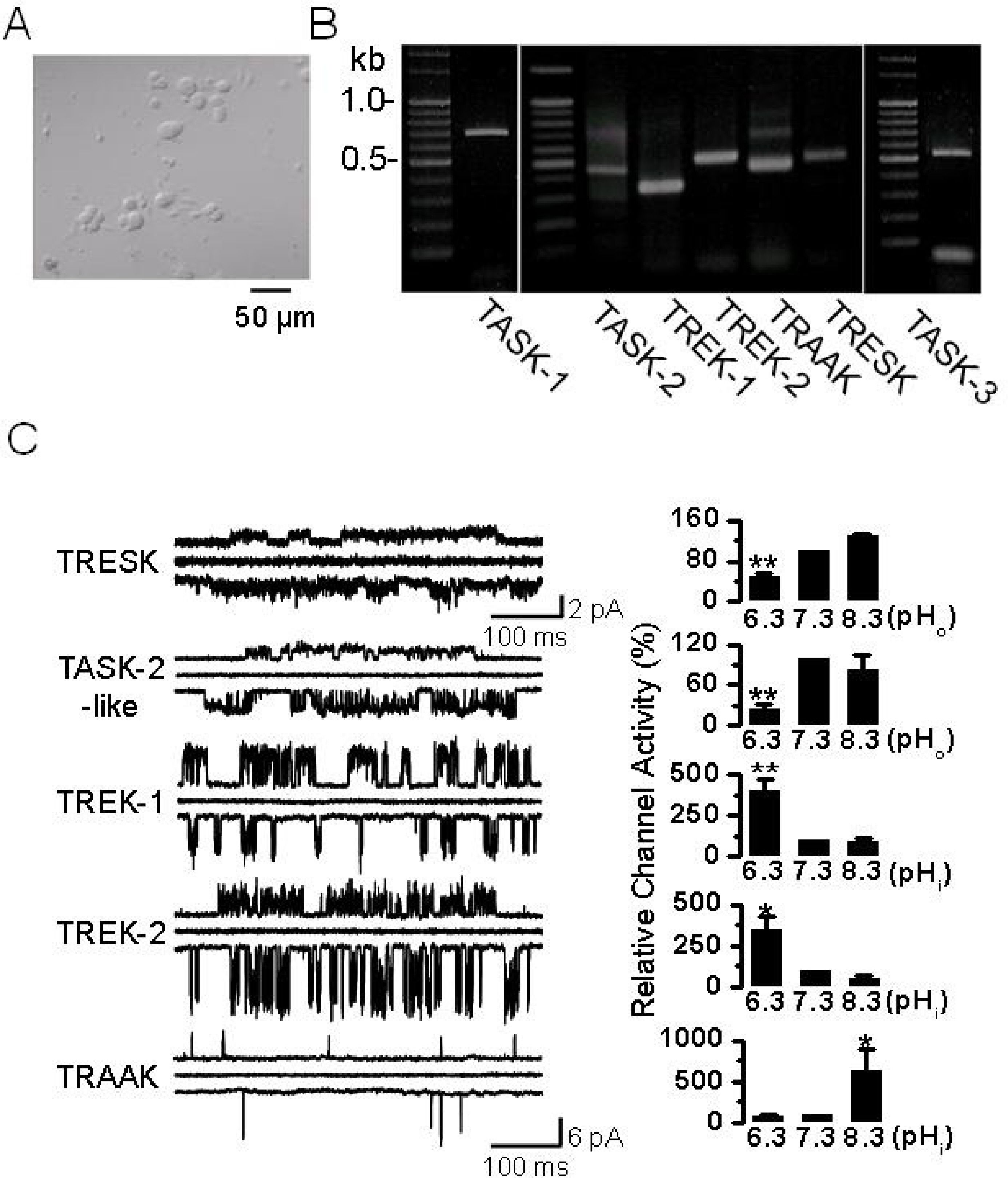
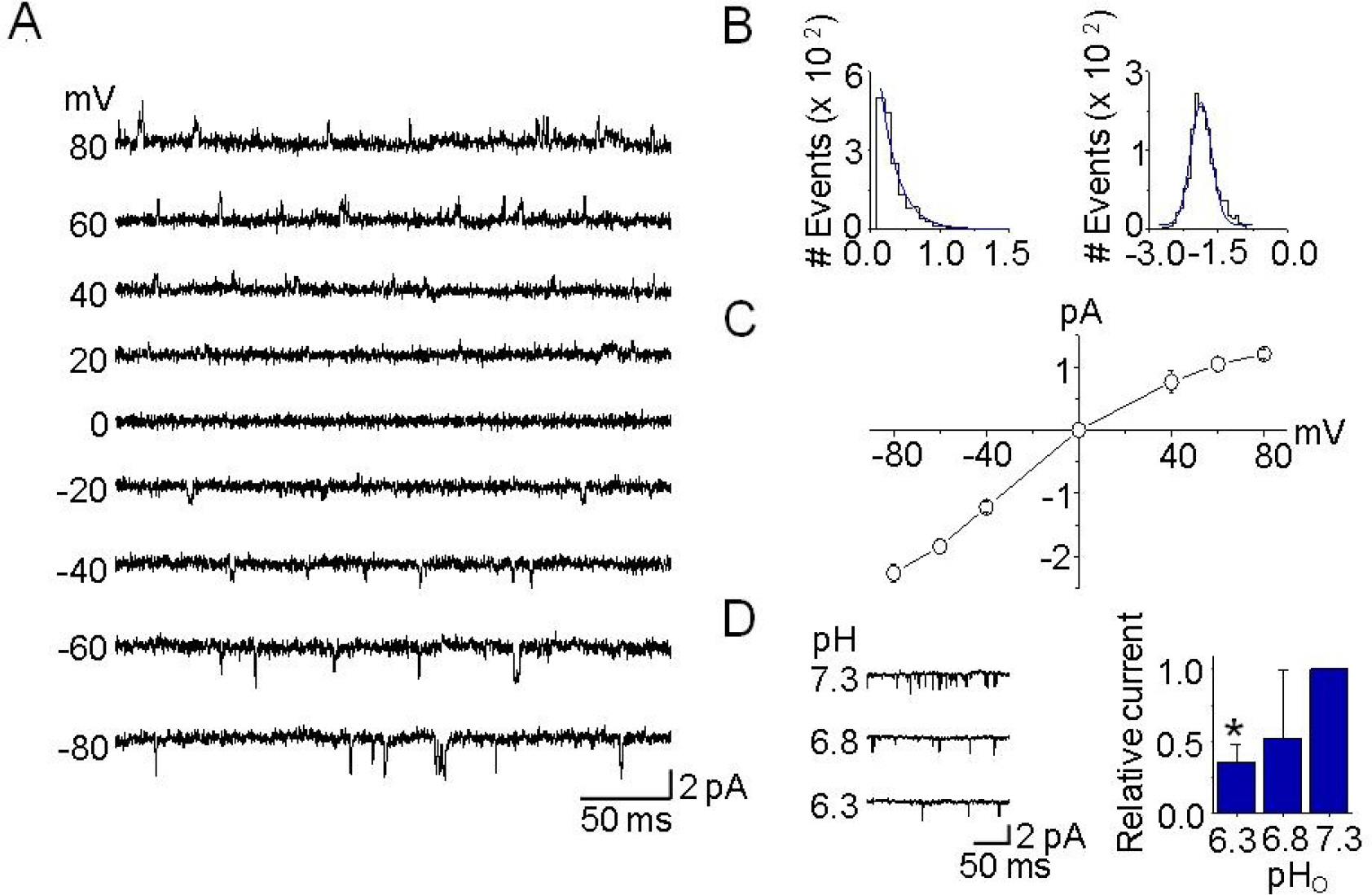
- Single-channel recordings of TASK-1 and TASK-3, members of two-pore domain K+ channel family, have not yet been reported in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, even though their mRNA and activity in whole-cell currents have been detected in these neurons. Here, we report single-channel kinetics of the TASK-3-like K+ channel in DRG neurons and up-regulation of TASK-3 mRNA expression in tissues isolated from animals with spinal cord injury (SCI). In DRG neurons, the single-channel conductance of TASK-3-like K+ channel was 33.0+/-0.1 pS at -60 mV, and TASK-3 activity fell by 65+/-5% when the extracellular pH was changed from 7.3 to 6.3, indicating that the DRG K+ channel is similar to cloned TASK-3 channel. TASK-3 mRNA and protein levels in brain, spinal cord, and DRG were significantly higher in injured animals than in sham-operated ones. These results indicate that TASK-3 channels are expressed and functional in DRG neurons and the expression level is up-regulated following SCI, and suggest that TASK-3 channel could act as a potential background K+ channel under SCI-induced acidic condition.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
Basso DM., Beattie MS., Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995.
ArticleBraughler JM., Hall ED. Effects of multi-dose methylprednisolone sodium succinate administration on injured cat spinal cord neurofilament degradation and energy metabolism. J Neurosurg. 61:290–295. 1984.
ArticleCooper BY., Johnson RD., Rau KK. Characterization and function of TWIK-related acid sensing K+ channels in a rat nociceptive cell. Neuroscience. 129:209–224. 2004.Farooque M., Hillered L., Holtz A., Olsson Y. Effects of methylprednisolone on extracellular lactic acidosis and amino acids after severe compression injury of rat spinal cord. J Neurochem. 66:1125–1130. 1996.
ArticleHolzer P. Acid-sensitive ion channels in gastrointestinal function. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 3:618–625. 2003.
ArticleKang D., Choe C., Kim D. Thermosensitivity of the two-pore domain K+ channels TREK-2 and TRAAK. J Physiol. 564:103–116. 2005.Kang D., Han J., Talley EM., Bayliss DA., Kim D. Functional expression of TASK-1/TASK-3 heteromers in cerebellar granule cells. J Physiol. 554:64–77. 2004a.
ArticleKang D., Kim D. Single-channel properties and pH sensitivity of two-pore domain K+ channels of the TALK family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 315:836–844. 2004.Kang D., Kim D. TREK-2 (K2P10.1) and TRESK (K2P18.1) are major background K+ channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 291:C138–146. 2006.Kang D., Mariash E., Kim D. Functional expression of TRESK-2, a new member of the tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem. 279:28063–28070. 2004b.Kim D. Fatty acid-sensitive two-pore domain K+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 24:648–654. 2003.La JH., Kang D., Park JY., Hong SG., Han J. A novel acid-sensitive K (+) channel in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons. Neurosci Lett. 406:244–249. 2006.Lang-Lazdunski L., Bachet J., Rogers C. Repair of the descending thoracic aorta: impact of open distal anastomosis technique on spinal cord perfusion, neurological outcome and spinal cord histopathology. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 26:351–358. 2004.
ArticleMedhurst AD., Rennie G., Chapman CG., Meadows H., Duckworth MD., Kelsell RE., Gloger II., Pangalos MN. Distribution analysis of human two pore domain potassium channels in tissues of the central nervous system and periphery. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 86:101–114. 2001.
ArticleOh U., Hwang SW., Kim D. Capsaicin activates a nonselective cation channel in cultured neonatal rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci. 16:1659–1667. 1996.
ArticleRau KK., Cooper BY., Johnson RD. Expression of TWIK-related acid sensitive K+ channels in capsaicin sensitive and insensitive cells of rat dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience. 141:955–963. 2006.Rush AM., Cummins TR., Waxman SG. Multiple sodium channels and their roles in electrogenesis within dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Physiol. 579:1–14. 2007.
ArticleSmith GT. Pharmacological characterization of ionic currents that regulate high-frequency spontaneous activity of electromotor neurons in the weakly electric fish, Apteronotus leptorhynchus. J Neurobiol. 66:1–18. 2006.Zhang XF., Gopalakrishnan M., Shieh CC. Modulation of action potential firing by iberiotoxin and NS1619 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuroscience. 122:1003–1011. 2003.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distribution of Tyrosine Hydroxylse Immunoreactive Structure in the Spinal Cord and Dorsal Root Ganglion of the Rat
- Expression Profile of Tumor Endothelial Marker 7 and a Putative Ligand in the Rat Spinal Cord and Dorsal Root Ganglion
- DAMGO modulates two-pore domain K⺠channels in the substantia gelatinosa neurons of rat spinal cord
- R-type Calcium Channel Isoform in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
- Changes in Osteopontin Expression in the Rat Lumbar Spinal Cord Following the Avulsion of Lumbar Nerve Roots