J Breast Cancer.
2008 Sep;11(3):116-124. 10.4048/jbc.2008.11.3.116.
Correlation between the Her-2/neu Status as Determined by Immunohistochemical Analysis and the Serum Her-2/neu Concentration as Determined by the Use of ADVIA Cencaur(R) Automated Immunoassay in Breast Cancer Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ahnsh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Oncology, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1485104
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2008.11.3.116
Abstract
- PURPOSE
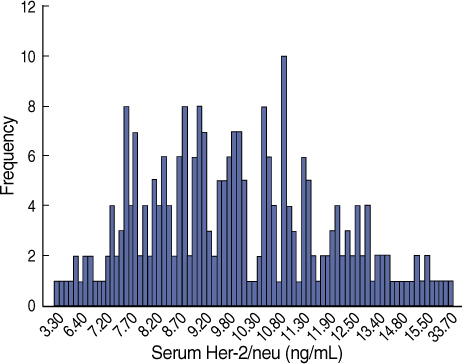
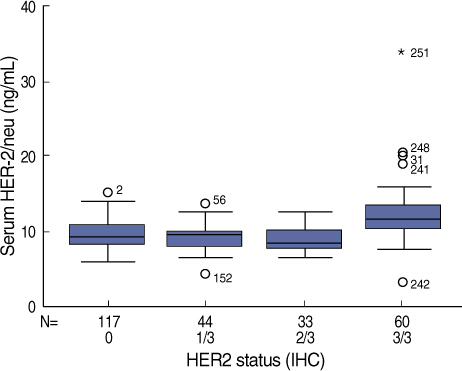
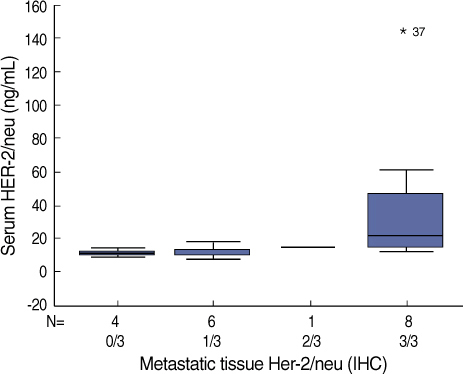
Serum Her-2/neu is extracted from the extracelluar domain of the Her-2/neu tyrosine kinase to serum. We evaluated the correlation between the Her-2/neu status as determined by immunohistochemical analysis (IHC) and the serum Her-2/neu concentration in a population of Korean women with breast cancer. METHODS: Serum Her-2/neu levels were examined from 254 female patients with primary breast cancer and 38 patients with metastatic breast cancer. Serum Her-2/neu levels were measured by the use of a chemiluminescence immunoassay (ADVIA centaur(R) system) during the preoperative period. The level of Her-2/neu in all of the breast cancer tissue samples was determined by IHC, and samples with an IHC grade +2 were subject to fluorescence in situ (FISH). When tissue samples exhibited IHC grade +3 or showed amplification of Her-2/neu as determined by FISH analysis, Her-2/neu was considered overexpressed. The cut-off value for serum Her-2/neu level was 10.2 ng/mL. RESULTS: The mean serum Her-2/neu level was 10.1 ng/mL in primary breast cancer samples. The serum Her-2/neu concentration significantly correlated with expression of Her-2/neu as determined by tissue IHC analysis (grade 1/3, 9.33+/-1.7 ng/mL; grade 2/3, 8.89+/-1.6 ng/mL; grade 3/3, 12.37+/-4.0 ng/mL, p<0.001). Increased serum HER-2/neu levels were associated with the lymph node status (p=0.003) and hormone unresponsiveness (p<0.001), tumor size (p<0.01) and age group (p<0.001). In metastatic breast cancer samples, the mean serum Her-2/neu level was 13.6 ng/mL. Elevated serum Her-2/neu levels were seen in 71.7% of metastatic breast cancer samples. The serum Her-2/neu level correlated with expression of Her-2/neu in metastatic tissue as determined by IHC analysis (p<0.001) rather than with the Her-2/neu status of the primary breast cancer (p=0.16) CONCLUSION: Serum Her-2/neu appears to be correlate with tissue Her-2/neu expression in primary and metastatic breast cancer where Her-2/neu is overexpressed. Further studies to determine levels of serum Her-2/neu are required to determine cuttoff values and the clinical application of the finding for breast cancer patients in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Impact of Serum HER2 Levels on Survival and Its Correlation with Clinicopathological Parameters in Women with Breast Cancer
Dong Won Ryu, Chung Han Lee
J Breast Cancer. 2012;15(1):71-78. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.1.71.
Reference
-
1. Ross JS, Fletcher JA. The Her-2/neu oncogene in breast cancer: prognostic factor, predicitve factor, and target for therapy. Stem Cell. 1998. 16:413–428.
Article2. Lal P, Salazar PA, Hudis CA, Ladanyi M, Chen B. Her-2 testing in breast cancer using immunohistochemical analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004. 121:631–636.
Article3. Schaller G, Evers K, Papadopoulos S, Ebert A, Buhler H. Current use of Her2 test. Ann Oncol. 2001. 12:S97–S100.4. Narita T, Funahashi H, Satoh Y, Takashi H. C-erbB2 protein in sera of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1992. 24:97–102.5. Ali SA, Leitzel K, Chinchilli VM, Engle L, Demers L, Harvey HA, et al. Relationship of serum Her-2/neu and serum CA 15-3 in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2002. 48:1314–1320.
Article6. Harris LN, Liotcheva V, Broadwater G, Ramirez MJ, Maimonis P, Anderson S, et al. Comparison of methods of measuring HER-2 in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:1698–1706.
Article7. Hayes DF, Yamauchi H, Broadwater G, Cirrincione CT, Rodrigue SP, Berry DA, et al. Circulating HER-2/erbB-2/c-neu (HER-2) extracellular domain as a prognostic factor in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. 7:2703–2711.8. Yamauchi H, O'Neil A, Gelman R, Carney W, Tenny D, Hosch S, et al. Prediction of response to antiestrogen therapy in advanced breast cancer patients by pretreatment circulating levels of extracelluar domain of the HER-2/c-neu protein. J Clin Oncol. 1997. 15:2518–2525.
Article9. Classen S, Kopp R, Possinger K, Weidenhagen R, Eiermann W, Wilmanns W. Clinical relevance of soluble c-erbB2 for patients with metastatic breast cancer predicting the response to second line hormone or chemotherapy. Tumor Biol. 2002. 23:70–75.
Article10. Muller V, Witzel I, Pantel K, Krenkel S, Luck HJ, Neumann R, et al. Prognostic and predictive impact of soluble epidermal growth factor receptor (sEGFR) protein in the serum of patients treated with chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2006. 26:1479–1487.11. Mehta RR, McDermott JH, Heiken TJ, Marler KC, Patel MK, Wild LD, et al. Plasma c-erbB2 levels in breast cancer patients: Prognostic significance in predicting response to chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:2409–2491.
Article12. Schoendorf T, Hoopmann M, Warm M, Neumann R, Thomas A, Gohring UJ, et al. Serologic concentrations of HER-2/neu in breast cancer patients with visceral metastasis receiving trastuzumab therapy predict the clinical course. Clin Chem. 2002. 48:1360–1362.13. Hoopmann M, Neumann R, Tanasale T, Schondorf T. HER-2/neu determination in blood plasma of patients with HER-2/neu overexpressing metastatic breast cancer; a longitudinal study. Anticancer Res. 2003. 23:1031–1034.14. Isola JJ, Holli K, Oksa H, Teramato Y, Kallioniemi OP. Elevated erbB2 oncoprotein levels in preoperative and follow-up serum samples define an aggressive disease course in patients with breast cancer. Cancer. 1994. 73:652–658.
Article15. Kim JW, Kim SY, Lee HS, Woo HD, Son DM, Lim CW, et al. Establishment for reference range of serum Her-2/neu in Korean healthy women. J Breast Cancer. 2006. 9:301–308.
Article16. Kong SY, Kang JH, Kwon Y, Kang HS, Chung KW, Kang SH, et al. Serum Her-3 concentration in patient with primary breast cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2006. 59:373–376.17. Watanabe N, Miyamoto Y, Tokuda Y, Kubota M, Ando Y, Tajima T, et al. Serum c-erbB2 in breast cancer patients. Acta Oncol. 1994. 33:901–904.18. Carney WP, Neumann DR, Lipton A, Leitzel K, Ali S, Price CP. Potential clinical utility of serum Her-2/neu oncoprotein concentrations in patients with breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2003. 49:1579–1598.
Article19. Cook GB, Neaman IE, Goldblatt JL, Cambetas DR, Hussain M, Luftner D, et al. Clinial utility of serum Her-2/neu testing on the Bayer Immuno 1 automated system in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2001. 21:1465–1470.20. Brandt-Rauf PW, Pincus MR, Carney WP. The c-erbB2 protein in oncogenesis: molecular structure to molecular epidemiology. Crit Rev Oncog. 1994. 5:313–329.
Article21. Isola JJ, Holli K, Okasa H, Teramoto Y, Kallioniemi OP. Elevated erbB-2 oncoprotein levels in preoperative and follow-up serum samples define an aggressive disease course in patients with breast cancer. Cancer. 1994. 73:652–658.
Article22. Willsher PC, Beaver J, Pinder S, Bell JA, Ellis EO, Blamey RW, et al. Prognostic significance of serum c-erbB2 protein in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996. 40:251–255.
Article23. Kostler WJ, Schwab B, Singer CF, Neumann R, Rucklinger E, Brodowicz T, et al. Monitoring of serum HER-2/neu predicts response and progression-free survival to trastuzumab-based treatment in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:1618–1624.
Article24. Molina R, Jo J, Zanon G, Filella X, Farrus B, Munoz M, et al. Utility of C-erbB2 in tissue and in serum in the early diagnosis of recurrence in breast cancer patients: comparison with carcinoembryonic antigen and CA15.3. Br J Cancer. 1996. 74:1126–1131.
Article25. Anderson TI, Paus E, Nesland JM, McKenzie SJ, Borresen AL. Detection of c-erbB2 related protein in sera from breast cancer patients. Acta Oncologica. 1995. 34:499–504.
Article26. Imoto S, Kitoh T, Hasebe T. Serum c-erbB2 levels in monitoring operable breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1999. 29:336–339.27. Molina R, Jo J, Filella X, Zanon G, Pahisa J, Munoz M, et al. C-erb B2 oncoprotein in the sera and tissue of patients with breast cancer. Utility in prognosis. Anticancer Res. 1996. 16:2295–2300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Correlation of Serum HER-2/neu and CA15-3 in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer
- The Predictive Value of Serum HER2/neu for Response to Anthracycline-Based and Trastuzumab-Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
- Establishment for Reference Range of Serum HER-2/neu in Korean Healthy Women
- An Expression of HER-2/neu Oncoprotein in Endometrial Cancer
- The Analysis of HER-2/neu Gene Status and Correlation with Other Clinico-Pathologic Factors for Breast Cancer Using Tissue Microarray