Tuberc Respir Dis.
2008 Mar;64(3):200-205. 10.4046/trd.2008.64.3.200.
Prognostic Value of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (bFGF) Expression in Resected Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. youngkim@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1478181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2008.64.3.200
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Tumor angiogenesis plays an important role in tumor growth, maintenance and metastatic potential. Tumor tissue produces many types of angiogenic growth factors. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) have both been implicated to have roles in tumor angiogenesis. In this study, the expression of tissue VEGF and bFGF from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients were analyzed.
METHODS
We retrospectively investigated 35 patients with a histologically confirmed adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, where the primary curative approach was surgery. An ELISA was employed to determine the expression of VEGF and bFGF in extracts prepared from 35 frozen tissue samples taken from the cancer patients.
RESULTS
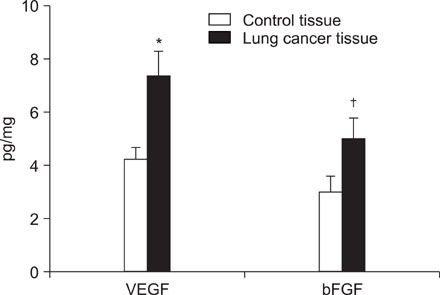
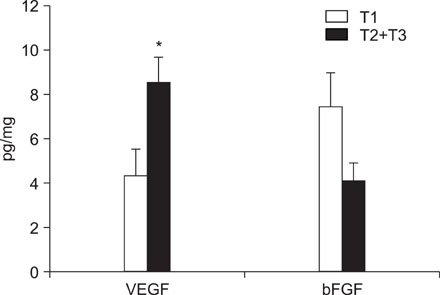
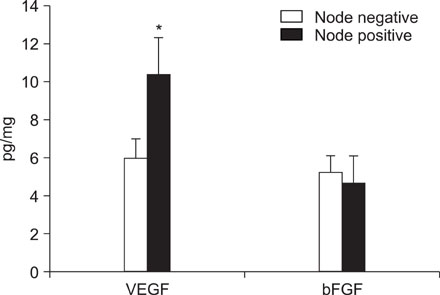
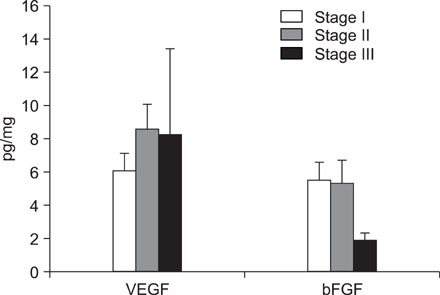
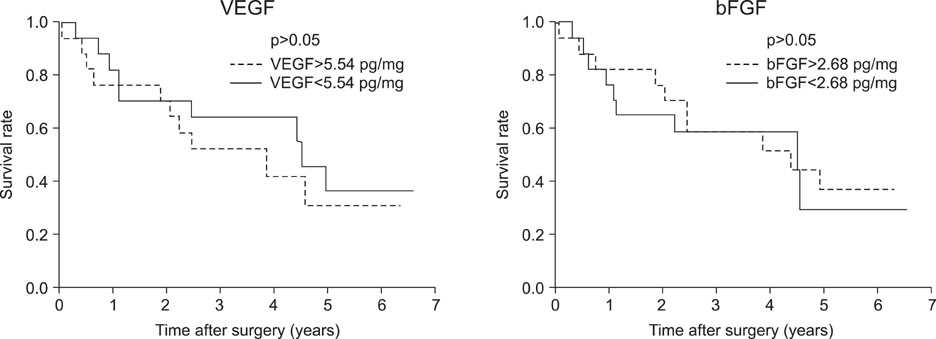
VEGF and bFGF concentrations were significantly increased in lung cancer tissue as compared with control (non-cancerous) tissue. The VEGF concentration was significantly increased in T2 and T3 cancers as compared with T1 cancer. Expression of VEGF was increased in node-positive lung cancer tissue as compared with node-negative lung cancer tissue (p=0.06). VEGF and bFGF expression were not directly related to the stage of lung cancer and patient survival.
CONCLUSION
Expression of VEGF and bFGF were increased in lung cancer tissue, and the expression of VEGF concentration in lung cancer tissue was more likely related with tumor size and the presence of a lymph node metastasis than the expression of bFGF. However, in this study, expression of both VEGF and bFGF in tissue were not associated with patient prognosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2
Humans
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Lung
Lung Neoplasms
Lymph Nodes
Neoplasm Metastasis
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2
Intercellular Signaling Peptides and Proteins
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choi Y, Kim Y, Hong YC, Park SK, Yoo KY. Temporal changes of lung cancer mortality in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:524–528.2. Ravdin PM, Davis G. Prognosis of patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer: impact of clinical and pathologic variables. Lung Cancer. 2006. 52:207–212.3. Bremnes RM, Camps C, Sirera R. Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: the prognostic impact of neoangiogenesis and the cytokines VEGF and bFGF in tumours and blood. Lung Cancer. 2006. 51:143–158.4. Onn A, Herbst RS. Angiogenesis and lung cancer: implications for prognosis and treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2007. 8:460–461.5. Anderson IC, Mari SE, Broderick RJ, Mari BP, Shipp MA. The angiogenic factor interleukin 8 is induced in non-small cell lung cancer/pulmonary fibroblast cocultures. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:269–272.6. Iwasaki A, Kuwahara M, Yoshinaga Y, Shirakusa T. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels, as prognostic indicators in NSCLC. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004. 25:443–448.7. Papetti M, Herman IM. Mechanisms of normal and tumor-derived angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. 282:C947–C970.8. Ferrara N. The role of VEGF in the regulation of physiological and pathological angiogenesis. EXS. 2005. 94:209–231.9. Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971. 285:1182–1186.10. Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989. 246:1306–1309.11. Carmeliet P. VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 2005. 69 Suppl 3:4–10.12. Cebe-Suarez S, Zehnder-Fjallman A, Ballmer-Hofer K. The role of VEGF receptors in angiogenesis: complex partnerships. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. 63:601–615.13. Kiselyov A, Balakin KV, Tkachenko SE. VEGF/VEGFR signalling as a target for inhibiting angiogenesis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007. 16:83–107.14. Szebenyi G, Fallon JF. Fibroblast growth factors as multifunctional signaling factors. Int Rev Cytol. 1999. 185:45–106.15. Klagsbrun M. Mediators of angiogenesis: the biological significance of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-heparin and heparan sulfate interactions. Semin Cancer Biol. 1992. 3:81–87.16. Cross MJ, Claesson-Welsh L. FGF and VEGF function in angiogenesis: signalling pathways, biological responses and therapeutic inhibition. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001. 22:201–207.17. Tanaka F, Otake Y, Yanagihara K, Kawano Y, Miyahara R, Li M, et al. Evaluation of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer: comparison between anti-CD34 antibody and anti-CD105 antibody. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. 7:3410–3415.18. Lee SN. The prognostic role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and angiogenesis in curatively resected non-small cell lung cancer. J Korean Cancer Assoc. 1999. 31:1210–1218.19. Ko HJ, Park JH, Shim H, Yang SH, Jeong ET. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2001. 50:676–685.20. Hemmerlein B, Kugler A, Ozisik R, Ringert RH, Radzun HJ, Thelen P. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression, angiogenesis, and necrosis in renal cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2001. 439:645–652.21. Rong Y, Durden DL, Van Meir EG, Brat DJ. 'Pseudopalisading' necrosis in glioblastoma: a familiar morphologic feature that links vascular pathology, hypoxia, and angiogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006. 65:529–539.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Expression in Early Gastric Carcinomas: Correlation with Clinicopathologic Factors
- The Effect of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and basic Fibroblast Growth Factor on the Growth of Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
- The Prognostic Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Expression and Angiogenesis in Curatively Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Clinical Significance of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Expression in Bladder Cancer
- Prognostic Value of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor(VEGF) in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer