Hanyang Med Rev.
2010 Aug;30(3):204-212. 10.7599/hmr.2010.30.3.204.
The nfa1 Gene Contributed on the Contact-dependent Pathogenic Mechanisms of Naegleria fowleri
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, and Department of Molecular Science and Technology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hjshin@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 1460255
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2010.30.3.204
Abstract
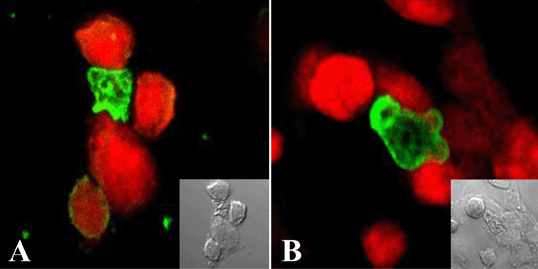
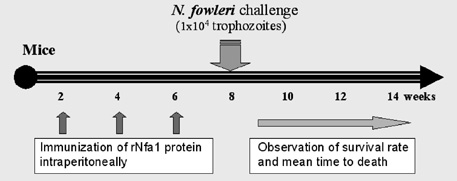
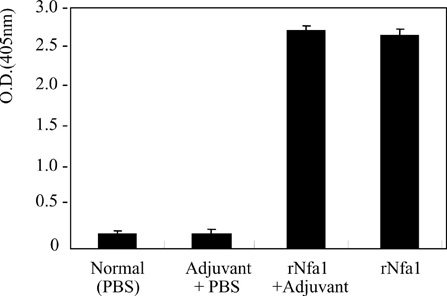
- Free-living Naegleria fowleri is a causal agent of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in mainly children and young adults. An nfa1 gene, encoding 360 bp of nucleotides, was cloned from a N. fowleri cDNA library by SEREX method. By immunohistochemistry and a confocal microscope, Nfa1 protein was found in amoebic pseudopods, especially in food-cups, when amoeba was in contact with target cells. When an anti-Nfa1 antibody was added to the coculture system, the cytotoxicity of N. fowleri trophozoites onto target cells was decreased, and the severe morphological destruction of rat microglial cells cocultured with N. fowleri trophozoites was reduced. In a tansfection system, an expression vector with an nfa1 gene was successful transfected into nonpathogenic N. gruberi, and transgenic N. gruberi showed the increasing in vitro cytotoxicity. The siRNA decreased the expression levels of nfa1 mRNA and Nfa1 protein in transfected N. fowleri trophozoites. On the immunization of mice with the rNfa1 protein, the protective immunity of host was induced. Thus, mice showed the prolonged mean survival times in PAM-developed mice. In final, the nfa1 gene and Nfa1 protein play an important role in the pathogenesis of N. fowleri infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Visvesvara GS, Moura H, Schuster FL. Pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007. 50:1–26.
Article2. De Jonckheere JF. Molecular definition and the ubiquity of species in the genus Naegleria. Protist. 2004. 155:89–103.3. John DT. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis and the biology of Naegleria fowleri. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982. 36:101–123.
Article4. Ma P, Visvesvara GS, Martinez AJ, Theodore FH, Daggett PM, Sawyer TK. Naegleria and Acanthamoeba infections: review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990. 12:490–513.5. Marciano-Cabral F, Cabral GA. The immune response to Naegleria fowleri amebae and pathogenesis of infection. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007. 51:243–259.
Article6. Schuster FL, Visvesvara GS. Free-living amoebae as opportunistic and non-opportunistic pathogens of humans and animals. Int J Parasitol. 2004. 34:1001–1027.
Article7. Shin HJ, Im KI. Pathogenic free-living amoebae in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2004. 42:93–119.
Article8. Page FC. Rosculus ithacus Hawes, 1963 (Amoebida, Flabelluidae) and the amphizoic tendency in amoebae. Acta Protozool. 1974. 13:143–155.9. Marciano-Cabral F. Biology of Naegleria spp. Microbiol Rev. 1988. 52:114–133.10. Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell. 2004. 6:463–477.11. Moon EK, Chung DI, Hong YC, Kong HH. Autophagy protein 8 mediating autophagosome in encysting Acanthamoeba. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2009. 168:43–48.12. Cerva L, Novak K. Epidemic occurrence of amebic meningoencephalitis. Cas Lek Cesk. 1968. 107:873–876.13. Cerva L, Novak K. Amoebic meningoencephalitis: 16 fatalities. Science. 1968. 160:92.14. Cerva L, Novak K. Amebic meningoencephalitis in Czechoslovakia. (Preliminary report on the first 16 detected cases). Cesk Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 1968. 17:65–66.15. Craun GF, Calderon RL, Craun MF. Outbreaks associated with recreational water in the United States. Int J Environ Health Res. 2005. 15:243–262.
Article16. Barnett ND, Kaplan AM, Hopkin RJ, Saubolle MA, Rudinsky MF. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis with Naegleria fowleri: clinical review. Pediatr Neurol. 1996. 15:230–234.
Article17. De Jonckheere JF. Growth characteristics, cytopathic effect in cell culture, and virulence in mice of 36 type strains belonging to 19 different Acanthamoeba spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980. 39:681–685.
Article18. van Klink F, Alizadeh H, Stewart GL, Pidherney MS, Silvany RE, He Y, McCulley JP, Niederkorn JY. Characterization and pathogenic potential of a soil isolate and an ocular isolate of Acanthamoeba castellanii in relation to Acanthamoeba keratitis. Curr Eye Res. 1992. 11:1207–1220.19. Marciano-Cabral F, Zoghby KL, Bradley SG. Cytopathic action of Naegleria fowleri amoebae on rat neuroblastoma target cells. J Protozool. 1990. 37:138–144.
Article20. Kang SY, Song KJ, Jeong SR, Kim JH, Park S, Kim K, Kwon MH, Shin HJ. Role of the Nfa1 protein in pathogenic Naegleria fowleri cocultured with CHO target cells. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2005. 12:873–876.
Article21. Lee YJ, Kim JH, Jeong SR, Song KJ, Kim K, Park S, Park MS, Shin HJ. Production of Nfa1-specific monoclonal antibodies that influences the in vitro cytotoxicity of Naegleria fowleri trophozoites on microglial cells. Parasitol Res. 2007. 101:1191–1196.
Article22. Sohn HJ, Kim JH, Shin MH, Song KJ, Shin HJ. The Nf-actin gene is an important factor for food-cup formation and cytotoxicity of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Parasitol Res. 2010. 106:917–924.
Article23. Han KL, Lee HJ, Shin MH, Shin HJ, Im KI, Park SJ. The involvement of an integrin-like protein and protein kinase C in amoebic adhesion to fibronectin and amoebic cytotoxicity. Parasitol Res. 2004. 94:53–60.
Article24. Cursons RT, Brown TJ. Use of cell cultures as an indicator of pathogenicity of free-living amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1978. 31:1–11.
Article25. Cursons RT, Brown TJ, Keys EA. Virulence of pathogenic free-living amebae. J Parasitol. 1978. 64:744–745.
Article26. Barbour SE, Marciano-Cabral F. Naegleria fowleri amoebae express a membrane-associated calcium-independent phospholipase A(2). Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. 1530:123–133.
Article27. Eisen D, Franson RC. Acid-active neuraminidases in the growth media from cultures of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri and in sonicates of rabbit alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987. 924:369–372.
Article28. Young JD, Lowrey DM. Biochemical and functional characterization of a membrane-associated poreforming protein from the pathogenic ameboflagellate Naegleria fowleri. J Biol Chem. 1989. 264:1077–1083.
Article29. Herbst R, Ott C, Jacobs T, Marti T, Marciano-Cabral F, Leippe M. Pore-forming polypeptides of the pathogenic protozoon Naegleria fowleri. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:22353–22360.30. Herbst R, Marciano-Cabral F, Leippe M. Antimicrobial and pore-forming peptides of free-living and potentially highly pathogenic Naegleria fowleri are released from the same precursor molecule. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:25955–25958.
Article31. Mat Amin N, Najmiah Mustaffa N, Md Arshad N. Detection of Hartmannella sp., a free-living amoeba from Sungai Setiu, Terengganu. Trop Biomed. 2004. 21:77–80.32. Kim JH, Yang AH, Sohn HJ, Kim D, Song KJ, Shin HJ. Immunodominant antigens in Naegleria fowleri excretory-secretory proteins were potential pathogenic factors. Parasitol Res. 2009. 105:1675–1681.
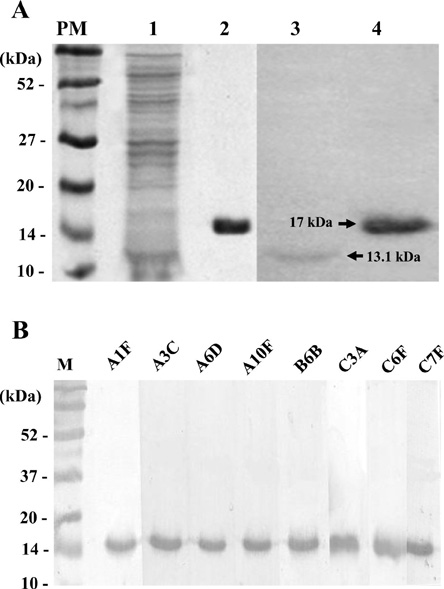
Article33. Shin HJ, Cho MS, Jung SU, Kim HI, Park S, Kim HJ, Im KI. Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene encoding a 13.1 kDa antigenic protein of Naegleria fowleri. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2001. 48:713–717.
Article34. Song KJ, Song KH, Na BK, Kim JH, Kwon D, Park S, Pak JH, Im KI, Shin HJ. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cytosolic heat shock protein 70 from Naegleria fowleri. Parasitol Res. 2007. 100:1083–1089.
Article35. Cho MS, Jung SY, Park S, Kim KH, Kim HI, Sohn S, Kim HJ, Im KI, Shin HJ. Immunological characterizations of a cloned 13.1-kilodalton protein from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003. 10:954–959.
Article36. Jeong SR, Kang SY, Lee SC, Song KJ, Im KI, Shin HJ. Decreasing effect of an anti-Nfa1 polyclonal antibody on the in vitro cytotoxicity of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Korean J Parasitol. 2004. 42:35–40.
Article37. Jung SY, Kim JH, Song KJ, Lee YJ, Kwon MH, Kim K, Park S, Im KI, Shin HJ. Gene silencing of Nfa1 affects the in vitro cytotoxicity of Naegleria fowleri in murine macrophages. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2009. 165:87–93.
Article38. Oh YH, Jeong SR, Kim JH, Song KJ, Kim K, Park S, Sohn S, Shin HJ. Cytopathic changes and pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by Naegleria fowleri trophozoites in rat microglial cells and protective effects of an anti-Nfa1 antibody. Parasite Immunol. 2005. 27:453–459.
Article39. Jeong SR, Lee SC, Song KJ, Park S, Kim K, Kwon MH, Im KI, Shin HJ. Expression of the Nfa1 gene cloned from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri in nonpathogenic N. gruberi enhances cytotoxicity against CHO target cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 2005. 73:4098–4105.
Article40. Song KJ, Jeong SR, Park S, Kim K, Kwon MH, Im KI, Pak JH, Shin HJ. Naegleria fowleri: functional expression of the Nfa1 protein in transfected Naegleria gruberi by promoter modification. Exp Parasitol. 2006. 112:115–120.
Article41. Jung SY, Kim JH, Lee YJ, Song KJ, Kim K, Park S, Im KI, Shin HJ. Naegleria fowleri: Nfa1 gene knock-down by double-stranded RNAs. Exp Parasitol. 2008. 118:208–213.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Decreasing effect of an anti-Nfa1 polyclonal antibody on the in vitro cytotoxicity of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri
- Understanding the pathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in association with N. fowleri antigen-1 (Nfa1)
- Contact-Independent Cell Death of Human Microglial Cells due to Pathogenic Naegleria fowleri Trophozoites
- Pathogenic free-living amoebae
- Experimental meningoencephalitis by Naegleria fowleri in mice