Immune Netw.
2010 Feb;10(1):26-34. 10.4110/in.2010.10.1.26.
Fcgamma Receptors Modulate Pulmonary Inflammation by Activating Innate Immune Cells in Murine Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. doohyun@snu.ac.kr
- 2Laboratory of Immune Regulation in Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1456194
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2010.10.1.26
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
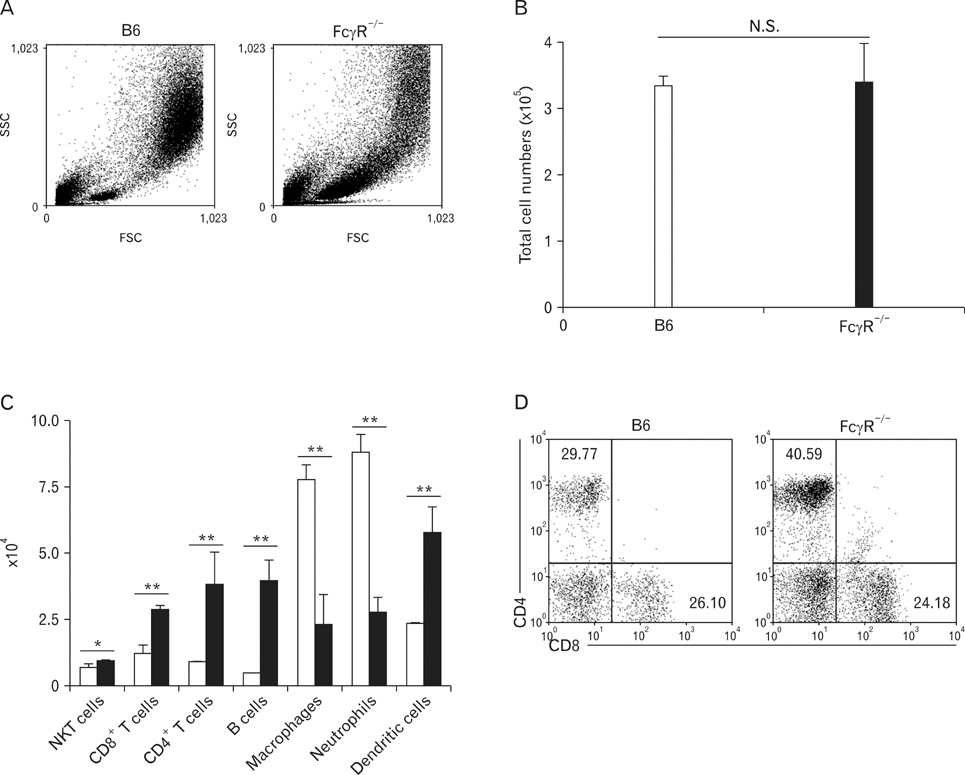
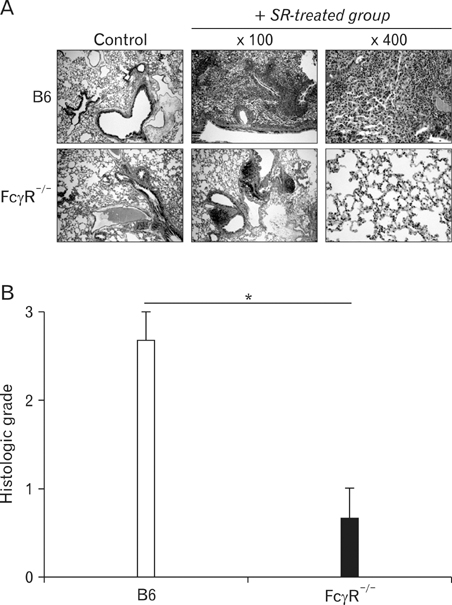
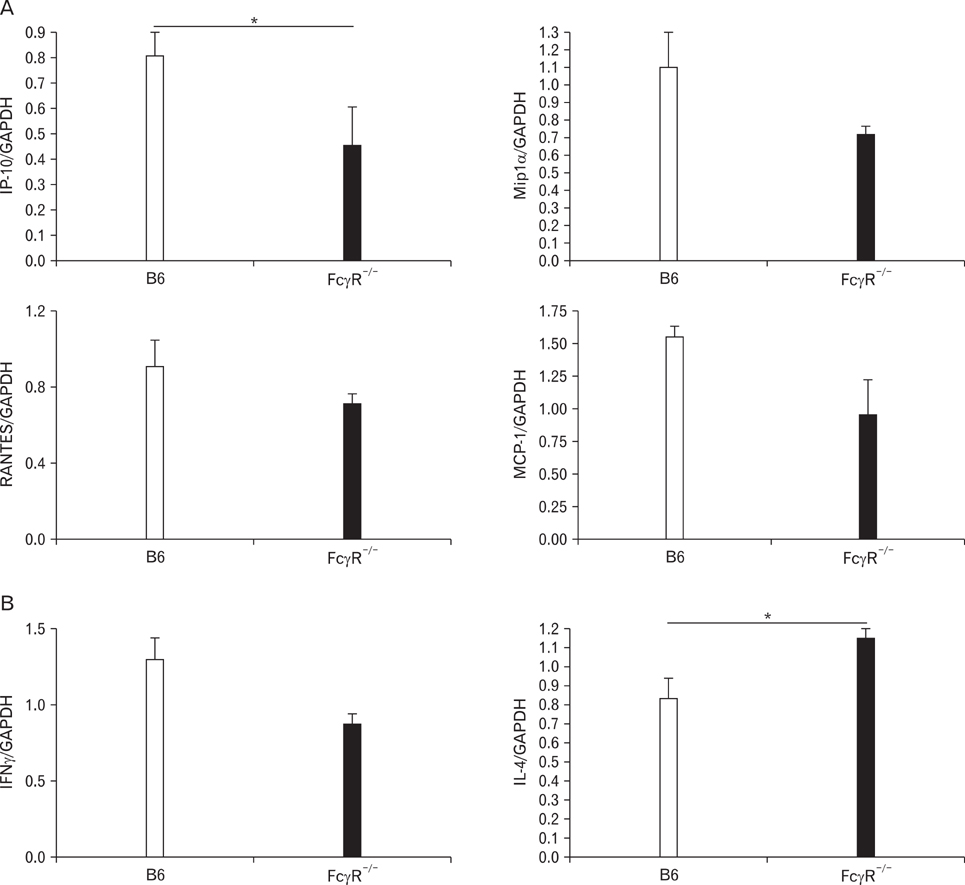
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is an interstitial lung disease that develops following repeated exposure to inhaled particulate antigens. The family of Fcgamma receptors (FcgammaRs) has emerged as central regulators for modulating both pro-and anti-inflammatory responses. However, the role of FcgammaRs in the development of HP has not been investigated yet. METHODS: To explore the functional roles of FcgammaRs in HP, FcgammaR-/- and B6 mice were challenged with Saccharopolyspora rectivirgula (SR) antigen intranasally, and compared these mice in terms of the histological change, infiltrated immune cells in BALF and in vitro immune responses. RESULTS: FcgammaR-/- mice exhibited attenuation of HP in terms of histological alterations, and reduced numbers of neutrophils and macrophages in and the increased CD4:CD8 ratio of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. The lungs of FcgammaR-/- mice showed high production of Th2 cytokine such as IL-4 and slightly low production of Th1 cytokine, INF-gamma compared to those of B6 mice. However, SR-specific adaptive immune responses of FcgammaR-/- mice were similar to those of B6 mice. CONCLUSION: These results demonstrate that activating Fcgamma receptors play an important role in activating neutrophils and macrophages in pulmonary inflammation and inducing Th1 differentiation by regulating cytokine expression in SR-induced HP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schatz M, Patterson R, Fink J. Immunopatholgenesis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977. 60:27–37.2. Patel AM, Ryu JH, Reed CE. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts and future questions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 108:661–670.
Article3. Girard M, Israël-Assayag E, Cormier Y. Pathogenesis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 4:93–98.
Article4. Irifune K, Yokoyama A, Kohno N, Sakai K, Hiwada K. T-helper 1 cells induce alveolitis but do not lead to pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Eur Respir J. 2003. 21:11–18.
Article5. Gudmundsson G, Hunninghake GW. Interferon-gamma is necessary for the expression of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1997. 99:2386–2390.
Article6. Ghadirian E, Denis M. Murine hypersensitivity pneumonitis: interleukin-4 administration partially abrogates the disease process. Microb Pathog. 1992. 12:377–382.
Article7. Mohr LC. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2004. 10:401–411.
Article8. Schuyler M, Gott K, Cherne A. Mediators of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Lab Clin Med. 2000. 136:29–38.
Article9. Denis M. Proinflammatory cytokines in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 151:164–169.
Article10. Nance S, Cross R, Yi AK, Fitzpatrick EA. IFN-gamma production by innate immune cells is sufficient for development of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur J Immunol. 2005. 35:1928–1938.
Article11. Hwang SJ, Kim S, Park WS, Chung DH. IL-4-secreting NKT cells prevent hypersensitivity pneumonitis by suppressing IFN-gamma-producing neutrophils. J Immunol. 2006. 177:5258–5268.
Article12. Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008. 8:34–47.13. Beaven MA, Metzger H. Signal transduction by Fc receptors: the Fc epsilon RI case. Immunol Today. 1993. 14:222–226.14. Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Divergent immunoglobulin g subclass activity through selective Fc receptor binding. Science. 2005. 310:1510–1512.
Article15. Nimmerjahn F. Activating and inhibitory FcgammaRs in autoimmune disorders. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006. 28:305–319.16. Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Fcgamma receptors: old friends and new family members. Immunity. 2006. 24:19–28.17. Ravetch JV, Bolland S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. 19:275–290.
Article18. Uchida J, Hamaguchi Y, Oliver JA, Ravetch JV, Poe JC, Haas KM, Tedder TF. The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy. J Exp Med. 2004. 199:1659–1669.
Article19. Takai T, Li M, Sylvestre D, Clynes R, Ravetch JV. FcR gamma chain deletion results in pleiotrophic effector cell defects. Cell. 1994. 76:519–529.
Article20. Clynes R, Takechi Y, Moroi Y, Houghton A, Ravetch JV. Fc receptors are required in passive and active immunity to melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. 95:652–656.21. Clynes R, Ravetch JV. Cytotoxic antibodies trigger inflammation through Fc receptors. Immunity. 1995. 3:21–26.
Article22. McSharry C, Anderson K, Boyd G. A review of antigen diversity causing lung disease among pigeon breeders. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000. 30:1221–1229.
Article23. Reynolds SP, Edwards JH, Jones KP, Davies BH. Immunoglobulin and antibody levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from symptomatic and asymptomatic pigeon breeders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991. 86:278–285.
Article24. Drent M, van Velzen-Blad H, Diamant M, Wagenaar SS, Hoogsteden HC, van den Bosch JM. Bronchoalveolar lavage in extrinsic allergic alveolitis: effect of time elapsed since antigen exposure. Eur Respir J. 1993. 6:1276–1281.25. Semenzato G, Agostini C, Zambello R, Trentin L, Chilosi M, Pizzolo G, Marcer G, Cipriani A. Lung T cells in hypersensitivity pneumonitis: phenotypic and functional analyses. J Immunol. 1986. 137:1164–1172.26. Oshima M, Maeda A, Ishioka S, Hiyama K, Yamakido M. Expression of C-C chemokines in bronchoalveolar lavage cells from patients with granulomatous lung diseases. Lung. 1999. 177:229–240.
Article27. Nance S, Cross R, Fitzpatrick E. Chemokine production during hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur J Immunol. 2004. 34:677–685.
Article28. Schuyler M, Cormier Y. The diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest. 1997. 111:534–536.
Article29. Hisauchi-Kojima K, Sumi Y, Miyashita Y, Miyake S, Toyoda H, Kurup VP, Yoshizawa Y. Purification of the antigenic components of pigeon dropping extract, the responsible agent for cellular immunity in pigeon breeder's disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 103:1158–1165.
Article30. Woda BA. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: an immunopathology review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008. 132:204–205.
Article31. Ravetch JV, Clynes RA. Divergent roles for Fc receptors and complement in vivo. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998. 16:21–132.32. Suga M, Yamasaki H, Nakagawa K, Kohrogi H, Ando M. Mechanisms accounting for granulomatous responses in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1997. 14:131–138.33. Schuyler M, Gott K, Edwards B. Th1 cells that adoptively transfer experimental hypersensitivity pneumonitis are activated memory cells. Lung. 1999. 177:377–389.
Article34. Takai T. Roles of Fc receptors in autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002. 2:580–592.
Article35. Koyasu S. CD3+CD16+NK1.1+B220+ large granular lymphocytes arise from both alpha-beta TCR+CD4-CD- and gamma-delta TCR+CD4-CD8- cells. J Exp Med. 1994. 179:1957–1972.
Article36. Bendelac A. CD1: presenting unusual antigens to unusual T lymphocytes. Science. 1995. 269:185–186.
Article37. Kim HY, Kim S, Chung DH. FcgammaRIII engagement provides activating signals to NKT cells in antibody-induced joint inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:2484–2492.38. Israël-Assayag E, Fournier E, Cormier Y. Blockade of T cell costimulation by CTLA4-Ig inhibits lung inflammation in murine hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Immunol. 1999. 163:6794–6799.39. Gudmundsson G, Monick MM, Hunninghake GW. Viral infection modulates expression of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Immunol. 1999. 162:7397–7401.40. Park Y, Oh SJ, Chung DH. CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells attenuate hypersensitivity pneumonitis by suppressing IFN-gamma production by CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2009. 86:1427–1437.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Autophagy as an Innate Immune Modulator
- Regulation of Immune Responses by the Activating and Inhibitory Myeloid-Associate Immunoglobuline-Like Receptors (MAIR) (CD300)
- The Innate Immune Responses in Pathogenesis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- The Role of Inflammasome-Associated Innate Immune Receptors in Cancer
- The Innate Immune Response in House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Inflammation