Korean Circ J.
2012 Jun;42(6):406-413. 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.6.406.
Rho-Associated Kinase 2 Polymorphism in Patients With Vasospastic Angina
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, Gangneung, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, Gangneung, Korea. jukim@gnah.co.kr
- 3Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1433860
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.6.406
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
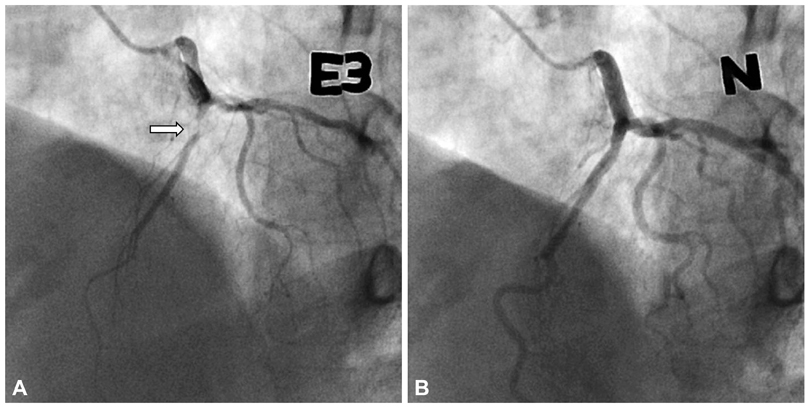
Recent studies indicate that in response to vasoconstrictor stimuli, the small GTPase RhoA and its down-stream effector, Rho-associated kinase 2 (ROCK)/Rho-kinase, are associated with hypercontraction of the vascular smooth muscle of coronary arteries through augmentation of myosin light chain phosphorylation and Ca2+ sensitization. Expression of ROCK/Rho-kinase mRNA was significantly increased and up-regulated in the spastic coronary artery in a porcine model, and a specific inhibitor of ROCK/Rho-kinase inhibited coronary artery spasm in humans. We therefore explored the role of ROCK2 polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of vasospastic angina (VA).
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
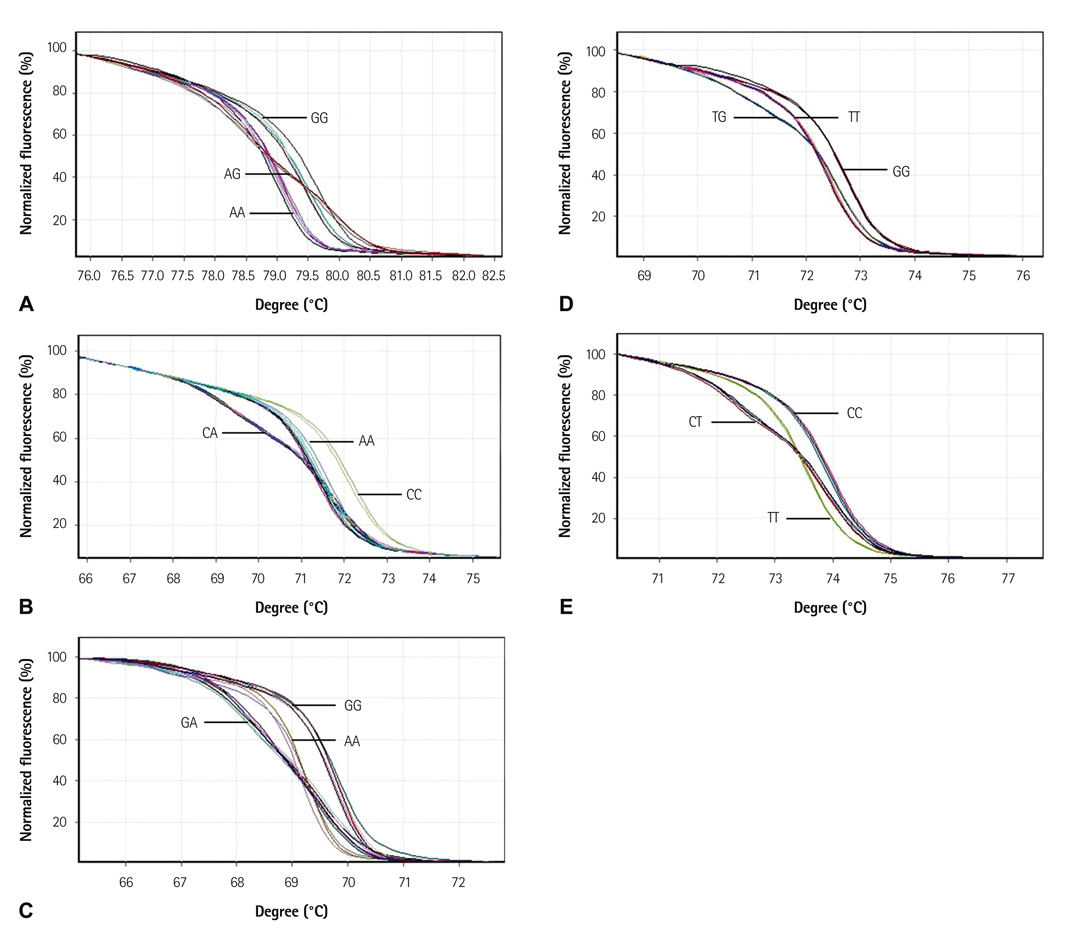
We studied 106 patients with VA who exhibited spontaneous or provoked coronary spasm during coronary angiography and compared the prevalence of ROCK2 polymorphisms between this group of patients with VA and controls whose angiograms were normal, and in whom the ergonovine test did not cause spasm (n=107). Five single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the ROCK2 gene were selected. SNPs were genotyped by high-resolution melting. Linkage disequilibrium and haplotype analyses were performed using the SHEsis program.
RESULTS
The prevalence of genotypes of the 5 interesting SNPs in patients with VA was not different from that in the control group. In haplotype analysis, the haplotype G-T-C-T-G (in order of rs978906, rs2271621, rs2230774, rs1515210, and rs3771106) was significantly associated with a decreased risk of VA (p=0.007).
CONCLUSION
The haplotype G-T-C-T-G in the ROCK2 gene had a protective effect against VA, suggesting the involvement of ROCK2 in VA pathogenesis.
MeSH Terms
-
Coronary Angiography
Coronary Vasospasm
Coronary Vessels
Ergonovine
Freezing
Genotype
GTP Phosphohydrolases
Haplotypes
Humans
Linkage Disequilibrium
Muscle Spasticity
Muscle, Smooth, Vascular
Myosin Light Chains
Phosphorylation
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Prevalence
rho-Associated Kinases
RNA, Messenger
Spasm
Ergonovine
GTP Phosphohydrolases
Myosin Light Chains
RNA, Messenger
rho-Associated Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sueda S, Kohno H, Fukuda H, Uraoka T. Did the widespread use of long-acting calcium antagonists decrease the occurrence of variant angina? Chest. 2003. 124:2074–2078.2. Yoo SY, Shin DH, Jeong JI, et al. Long-term prognosis and clinical characteristics of patients with variant angina. Korean Circ J. 2008. 38:651–658.3. Yasue H, Nakagawa H, Itoh T, Harada E, Mizuno Y. Coronary artery spasm: clinical features, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Cardiol. 2008. 51:2–17.4. Chahine RA, Raizner AE, Ishimori T, Luchi RJ, McIntosh HD. The incidence and clinical implications of coronary artery spasm. Circulation. 1975. 52:972–978.5. Liew M, Pryor R, Palais R, et al. Genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms by high-resolution melting of small amplicons. Clin Chem. 2004. 50:1156–1164.6. Reed GH, Wittwer CT. Sensitivity and specificity of single-nucleotide polymorphism scanning by high-resolution melting analysis. Clin Chem. 2004. 50:1748–1754.7. Wittwer CT, Reed GH, Gundry CN, Vandersteen JG, Pryor RJ. High-resolution genotyping by amplicon melting analysis using LCGreen. Clin Chem. 2003. 49(6 Pt 1):853–860.8. Rozen S, Skaletsky H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol. 2000. 132:365–386.9. Shi YY, He L. SHEsis, a powerful software platform for analyses of linkage disequilibrium, haplotype construction, and genetic association at polymorphism loci. Cell Res. 2005. 15:97–98.10. Li Z, Zhang Z, He Z, et al. A partition-ligation-combination-subdivision EM algorithm for haplotype inference with multiallelic markers: update of the SHEsis (http://analysis.bio-x.cn). Cell Res. 2009. 19:519–523.11. Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science. 2002. 296:2225–2229.12. Fukata Y, Amano M, Kaibuchi K. Rho-Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001. 22:32–39.13. Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T. Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 2001. 81:153–208.14. Noma K, Oyama N, Liao JK. Physiological role of ROCKs in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. 290:C661–C668.15. Riento K, Ridley AJ. Rocks: multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. 4:446–456.16. Nakagawa O, Fujisawa K, Ishizaki T, Saito Y, Nakao K, Narumiya S. ROCK-I and ROCK-II, two isoforms of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein serine/threonine kinase in mice. FEBS Lett. 1996. 392:189–193.17. Shimokawa H. Rho-kinase as a novel therapeutic target in treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2002. 39:319–327.18. Shimokawa H. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of coronary artery spasm: lessons from animal models. Jpn Circ J. 2000. 64:1–12.19. Kandabashi T, Shimokawa H, Miyata K, et al. Inhibition of myosin ph-osphatase by upregulated rho-kinase plays a key role for coronary artery spasm in a porcine model with interleukin-1beta. Circulation. 2000. 101:1319–1323.20. Masumoto A, Mohri M, Shimokawa H, Urakami L, Usui M, Takeshita A. Suppression of coronary artery spasm by the Rho-kinase inhibitor fasudil in patients with vasospastic angina. Circulation. 2002. 105:1545–1547.21. Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV. Signal transduction and regulation in smooth muscle. Nature. 1994. 372:231–236.22. Laufs U, Liao JK. Post-transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA stability by Rho GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:24266–24271.23. Wolfrum S, Dendorfer A, Rikitake Y, et al. Inhibition of Rho-kinase leads to rapid activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase Akt and cardiovascular protection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. 24:1842–1847.24. Kamiunten H, Koike J, Mashiba J, Shimokawa H, Takeshita A. A comprehensive analysis of a novel missense mutation in Rho-kinase that causes coronary vasospasm in the Japanese. Circ J. 2004. 68:suppl I. 211. Abstract.25. Yoo SY, Kim JY. Recent insights into the mechanisms of vasospastic angina. Korean Circ J. 2009. 39:505–511.26. Sugiishi M, Takatsu F. Cigarette smoking is a major risk factor for coronary spasm. Circulation. 1993. 87:76–79.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rho-Associated Kinase 2 Polymorphism of Vasospastic Angina in Korean Population
- Exercise-Induced Vasospastic Angina With Prominent Regional Wall Motion Abnormality
- The Vasomotor Tone In Vasospastic Angina
- Recent Insights Into the Mechanisms of Vasospastic Angina
- Diagnostic Significance of ECG Ergonovine Provocation Test in Patients with Vasospastic Angina