Korean J Leg Med.
2013 May;37(2):84-89. 10.7580/kjlm.2013.37.2.84.
A Forensic Autopsy Case of Lissencephaly for Evaluating the Possibility of Child Abuse
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Legal Medicine, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Forensic Medicine, National Institute of Scientific Investigation, Seoul, Korea. sjsme@korea.kr
- KMID: 1433184
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2013.37.2.84
Abstract
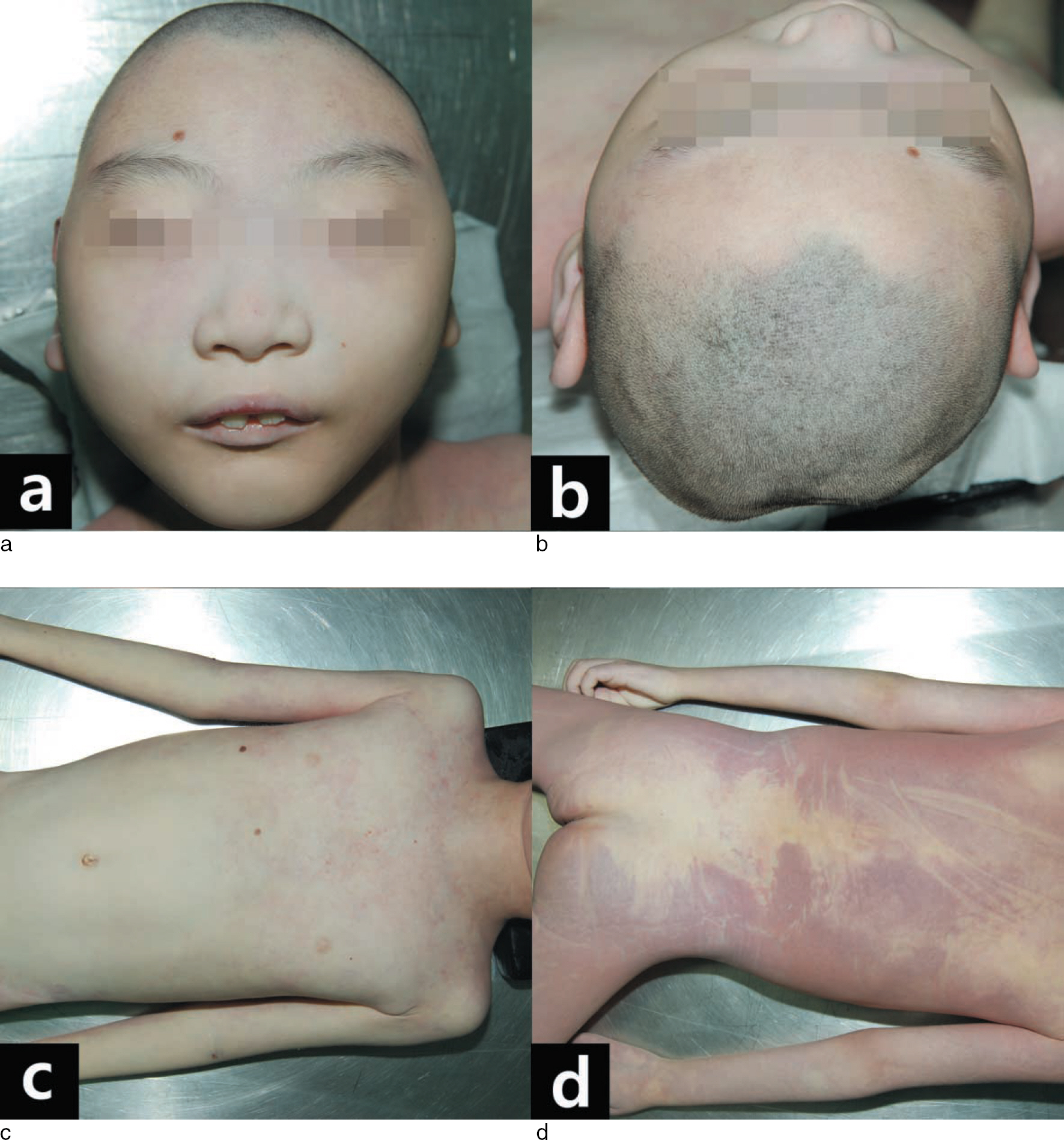
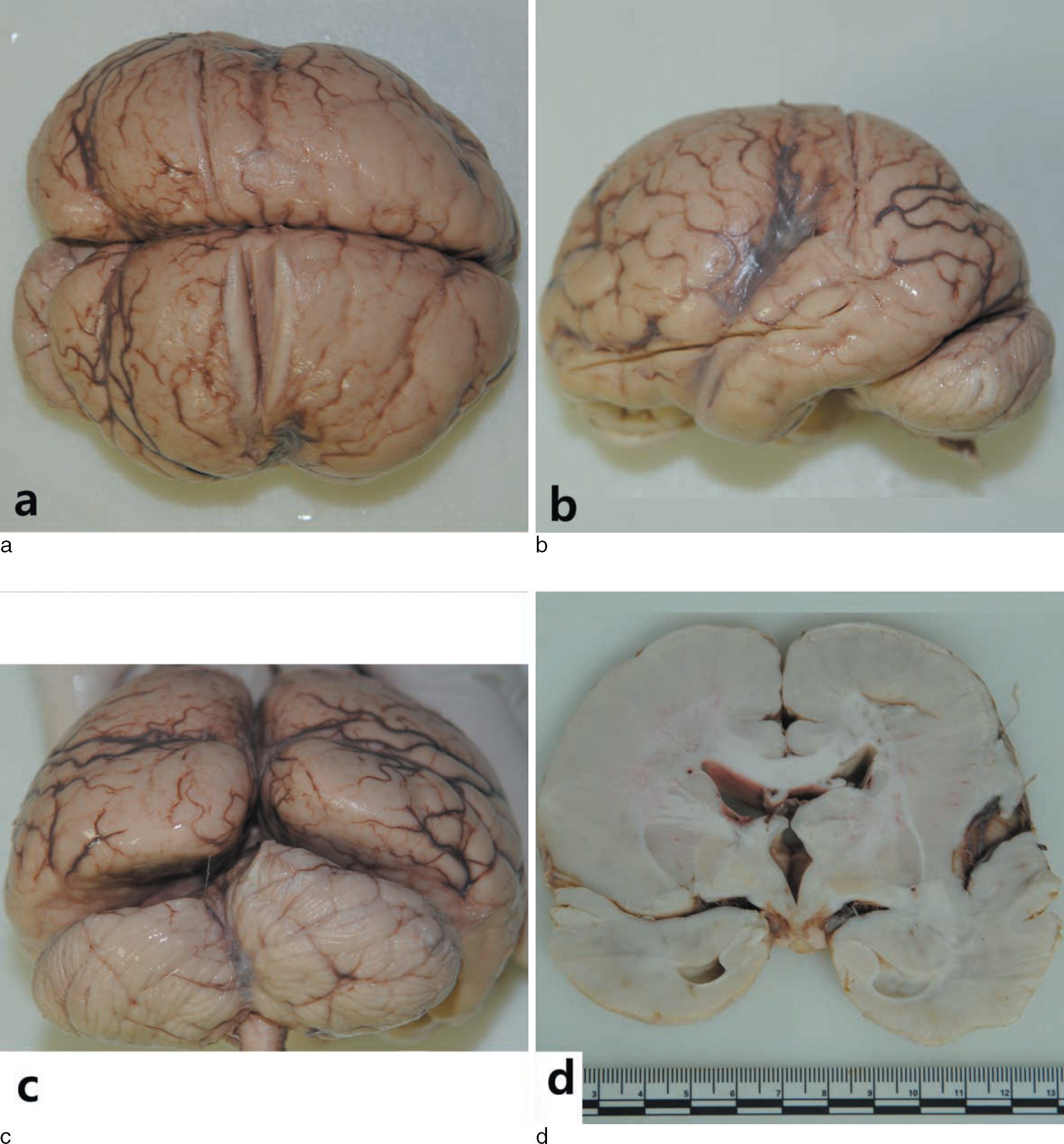
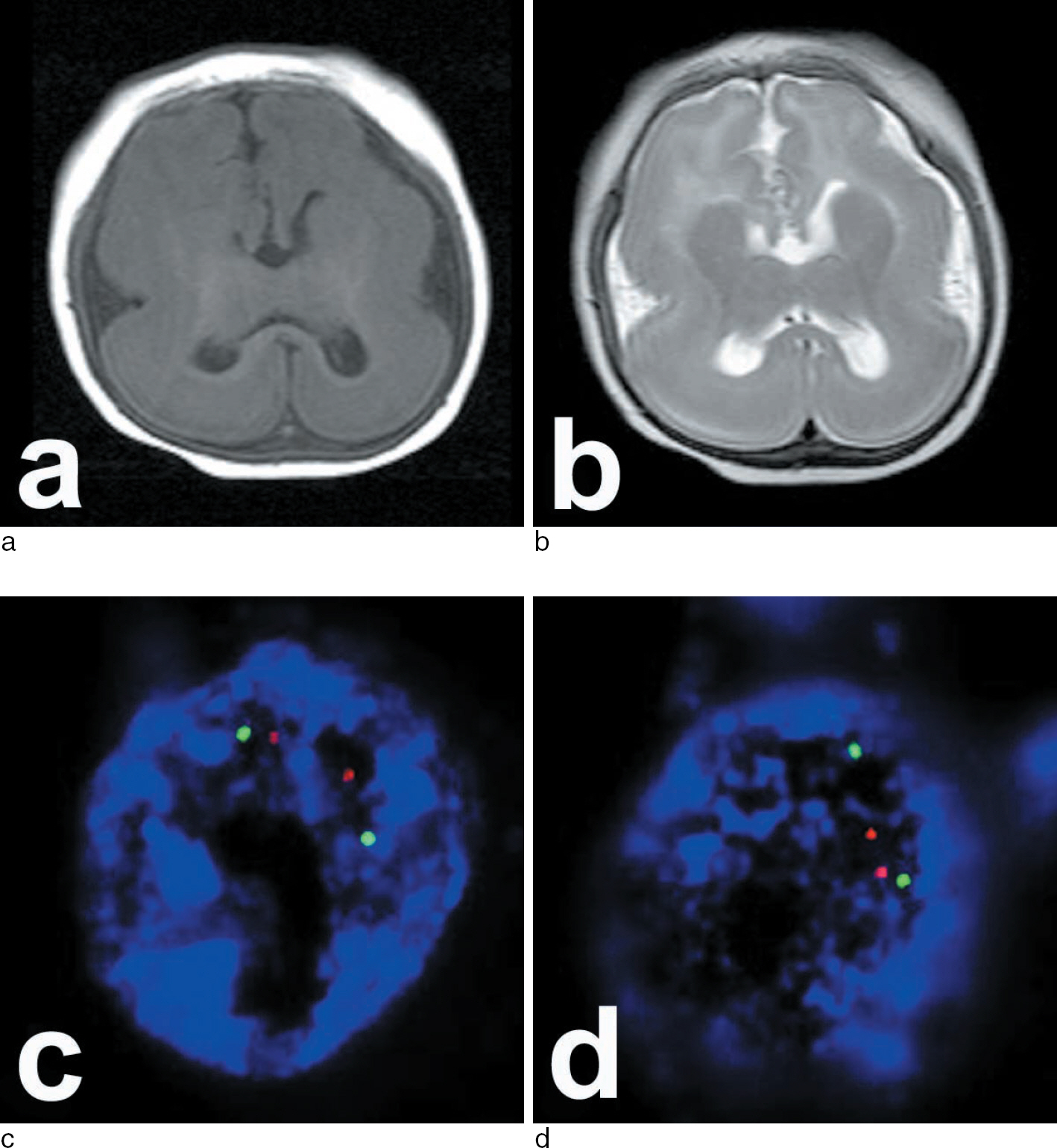
- A 9-year-old Korean boy with lissencephaly was found dead at home. He had previously been diagnosed with lissencephaly that presented with infantile spasm on the basis of magnetic resonance imaging and electroencephalogram results. Antemortem chromosomal banding revealed a normal karyotype. A legal autopsy was requested to eliminate the possibility of neglect or abuse by his parents. The autopsy findings revealed type I lissencephaly with the associated microcephaly. No external wounds or decubitus ulcers were noted. Postmortem fluorescence in situ hybridization for the LIS1 locus and nucleotide sequence analysis of the whole coding regions of the LIS1 gene did not reveal any deletions. The antemortem and postmortem findings revealed that lissencephaly syndrome was associated with isolated lissencephaly sequence. External causes of death were excluded by the full autopsy and toxicology test results. Because patients with mental retardation are frequently victimized and suffer neglect or abuse, thorough external and internal examinations should be conducted at the time of autopsy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Autopsy
Base Sequence
Cause of Death
Child
Child Abuse
Classical Lissencephalies and Subcortical Band Heterotopias
Clinical Coding
Electroencephalography
Fluorescence
Forensic Pathology
Humans
In Situ Hybridization
Infant
Infant, Newborn
Intellectual Disability
Karyotype
Lissencephaly
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Microcephaly
Parents
Pressure Ulcer
Spasms, Infantile
Toxicology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Garg A, Sridhar MR, Gulati S. Autosomal recessive type I lissencephaly. Indian J Pediatr. 2007; 74:199–201.
Article2. Dobyns WB, Reiner O, Carrozzo R, et al. Lissencephaly. A human brain malformation associated with deletion of the LIS1 gene located at chromosome 17p13. JAMA. 1993; 270:2838–42.
Article3. Orphanet, the European portal for rare diseases and orphan drugs. [online]. Available at:. http://www.orpha.net//consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Lng=GB&Expert=48471.4. Ledbetter SA, Kuwano A, Dobyns WB, et al. Microdeletions of chromosome 17p13 as a cause of isolated lissencephaly. Am J Hum Genet. 1992; 50:182–9.5. Chong SS, Pack SD, Roschke AV, et al. A revision of the lissencephaly and Miller-Dieker syndrome critical regions in chromosome 17p13.3. Hum Mol Genet. 1997; 6:147–55.
Article6. Dobyns WB, Stratton RF, Greenberg F. Syndromes with lissencephaly. I: Miller-Dieker and Norman-Roberts syndromes and isolated lissencephaly. Am J Med Genet. 1984; 18:509–26.
Article7. Iannetti P, Schwartz CE, Dietz-Band J, et al. Norman-Roberts syndrome: clinical and molecular studies. Am J Med Genet. 1993; 47:95–9.
Article8. Sergi C, Zoubaa S, Schiesser M. Norman-Roberts syndrome: prenatal diagnosis and autopsy findings. Prenat Diagn. 2000; 20:505–9.
Article9. Elias RC, Galera MF, Schnabel B, et al. Deletion of 17p13 and LIS1 gene mutation in isolated lissencephaly sequence. Pediatr Neurol. 2006; 35:42–6.
Article10. Dobyns WB, Garg BP. Vascular abnormalities in epidermal nevus syndrome. Neurology. 1991; 41:276–8.
Article11. Reiter S, Bryen DN, Shachar I. Adolescents with intellectual disabilities as victims of abuse. J Intellect Disabil. 2007; 11:371–87.
Article12. De Paul J, Guibert M. Empathy and child neglect: a theoretical model. Child Abuse Negl. 2008; 32:1063–71.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Myositis Ossificans of the Thighs Due to Repeated Assault: A Case Report
- Forensic Anthropological Implication of Undetected Rib Fractures in Child Abuse Case
- Education and Training of Clinical Forensic Examination in the Management of Child Abuse in Korea: Comparison with Germany, the United Kingdom, Australia, and the United States of America
- Review of child abuse through 20-year autopsies in Jeju
- Exploring the Relationship between Psychosocial Risk Factors and Sudden Unexplained Infant Death: A Study of Autopsy Cases from a Perspective of Child Welfare