Immune Netw.
2013 Apr;13(2):70-74. 10.4110/in.2013.13.2.70.
Vitamin C Is an Essential Factor on the Anti-viral Immune Responses through the Production of Interferon-alpha/beta at the Initial Stage of Influenza A Virus (H3N2) Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Anti-oxidant Immunology and Vitamin C, Department of Anatomy, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea. genius29@snu.ac.kr, kinglee@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1431928
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2013.13.2.70
Abstract
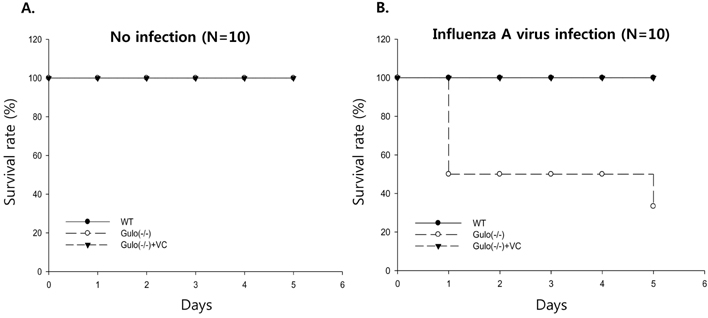
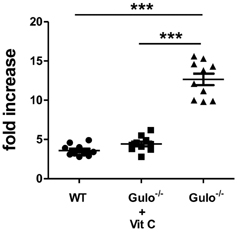
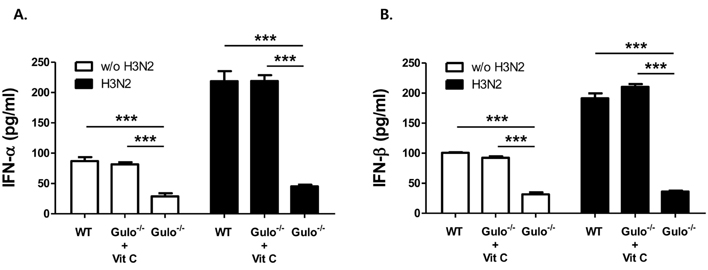
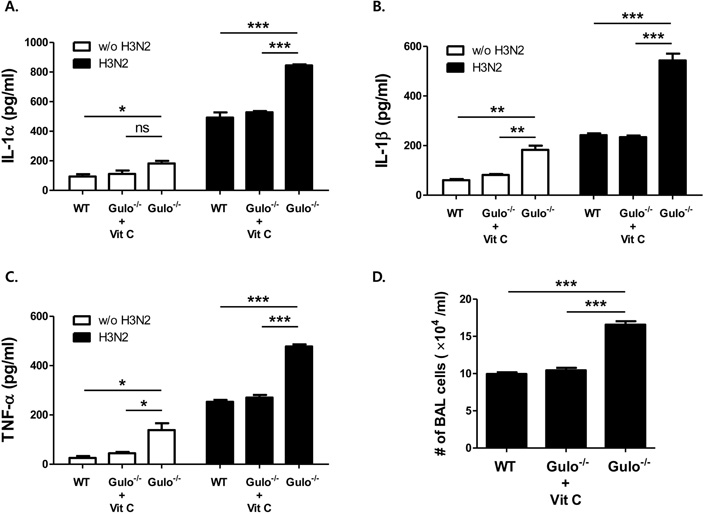
- L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is one of the well-known anti-viral agents, especially to influenza virus. Since the in vivo anti-viral effect is still controversial, we investigated whether vitamin C could regulate influenza virus infection in vivo by using Gulo (-/-) mice, which cannot synthesize vitamin C like humans. First, we found that vitamin C-insufficient Gulo (-/-) mice expired within 1 week after intranasal inoculation of influenza virus (H3N2/Hongkong). Viral titers in the lung of vitamin C-insufficient Gulo (-/-) mice were definitely increased but production of anti-viral cytokine, interferon (IFN)-alpha/beta, was decreased. On the contrary, the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the lung and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-alpha/beta, were increased in the lung. Taken together, vitamin C shows in vivo anti-viral immune responses at the early time of infection, especially against influenza virus, through increased production of IFN-alpha/beta.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Nutrient modulation of viral infection-implications for COVID-19
Hye-Keong Kim, Chan Yoon Park, Sung Nim Han
Nutr Res Pract. 2021;15(Suppl 1):S1-S21. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2021.15.S1.S1.
Reference
-
1. Padayatty SJ, Katz A, Wang Y, Eck P, Kwon O, Lee JH, Chen S, Corpe C, Dutta A, Dutta SK, Levine M. Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003. 22:18–35.
Article2. Kojo S. Vitamin C: basic metabolism and its function as an index of oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 2004. 11:1041–1064.
Article3. Boyera N, Galey I, Bernard BA. Effect of vitamin C and its derivatives on collagen synthesis and cross-linking by normal human fibroblasts. Int J Cosmet Sci. 1998. 20:151–158.
Article4. Englard S, Seifter S. The biochemical functions of ascorbic acid. Annu Rev Nutr. 1986. 6:365–406.
Article5. Noh K, Lim H, Moon SK, Kang JS, Lee WJ, Lee D, Hwang YI. Mega-dose Vitamin C modulates T cell functions in Balb/c mice only when administered during T cell activation. Immunol Lett. 2005. 98:63–72.
Article6. Wintergerst ES, Maggini S, Hornig DH. Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions. Ann Nutr Metab. 2006. 50:85–94.
Article7. Linster CL, Van Schaftingen E. Vitamin C. Biosynthesis, recycling and degradation in mammals. FEBS J. 2007. 274:1–22.8. Maeda N, Hagihara H, Nakata Y, Hiller S, Wilder J, Reddick R. Aortic wall damage in mice unable to synthesize ascorbic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. 97:841–846.
Article9. Kim H, Bae S, Yu Y, Kim Y, Kim HR, Hwang YI, Kang JS, Lee WJ. The analysis of vitamin C concentration in organs of gulo(-/-) mice upon vitamin C withdrawal. Immune Netw. 2012. 12:18–26.
Article10. Bae S, Cho CH, Kim H, Kim Y, Kim HR, Hwang YI, Yoon JH, Kang JS, Lee WJ. In Vivo Consequence of Vitamin C Insufficiency in Liver Injury: Vitamin C Ameliorates T-Cell-Mediated Acute Liver Injury in Gulo(-/-) Mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013. [Epub ahead of print].11. Pauling L. The significance of the evidence about ascorbic acid and the common cold. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971. 68:2678–2681.
Article12. Hemilä H, Chalker E. Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. 1:CD000980. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000980.pub4.
Article13. Hwang I, Scott JM, Kakarla T, Duriancik DM, Choi S, Cho C, Lee T, Park H, French AR, Beli E, Gardner E, Kim S. Activation mechanisms of natural killer cells during influenza virus infection. PLoS One. 2012. 7:e51858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051858.
Article14. Zhou NN, Senne DA, Landgraf JS, Swenson SL, Erickson G, Rossow K, Liu L, Yoon KJ, Krauss S, Webster RG. Genetic reassortment of avian, swine, and human influenza A viruses in American pigs. J Virol. 1999. 73:8851–8856.
Article15. Müller U, Steinhoff U, Reis LF, Hemmi S, Pavlovic J, Zinkernagel RM, Aguet M. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in anti-viral defense. Science. 1994. 264:1918–1921.
Article16. Trinchieri G. Type I interferon: friend or foe? J Exp Med. 2010. 207:2053–2063.
Article17. Horvath CM. The Jak-STAT pathway stimulated by interferon gamma. Sci STKE. 2004. 2004:tr8.18. Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994. 264:1415–1421.
Article19. Gongora C, Mechti N. Interferon signaling pathways. Bull Cancer. 1999. 86:911–919.20. Aymard-Henry M, Coleman MT, Dowdle WR, Laver WG, Schild GC, Webster RG. Influenzavirus neuraminidase and neuraminidase-inhibition test procedures. Bull World Health Organ. 1973. 48:199–202.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Host Immune Responses Against Type A Influenza Viruses
- The Protective Role of TLR3 and TLR9 Ligands in Human Pharyngeal Epithelial Cells Infected with Influenza A Virus
- Genetic characterization of bovine viral diarrhea virus strains in Beijing, China and innate immune responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in persistently infected dairy cattle
- Anti-influenza properties of herbal extract of Althaea rosea in mice
- IL-5 and IFN-gamma Levels in Nasopharyngeal Secretions from Non-Asthmatic Wheezing Children with Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Influenza A Virus Infection and Asthmatic Children