Korean J Radiol.
2013 Feb;14(1):30-37. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.30.
In Vitro and In Vivo Imaging of Prostate Cancer Angiogenesis Using Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 Antibody-Conjugated Quantum Dot
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medicinal Chemistry Laboratory, Institute Pasteur Korea (IP-K), Seongnam 463-400, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Clinical Research Institute, Seongnam 463-707, Korea. h
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine and Biomedical Sciences Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Therapy, Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- KMID: 1430041
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.30
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Authors aimed to determine the targeting ability of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2)-conjugated quantum dots (QDs) in vitro, and apply it for a xenograft prostate cancer mouse model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
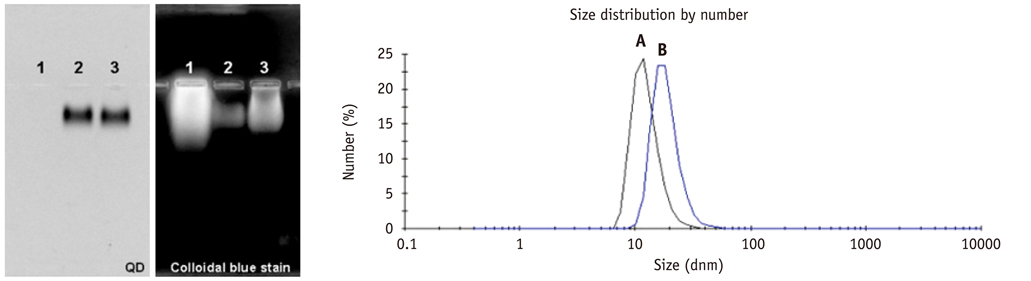
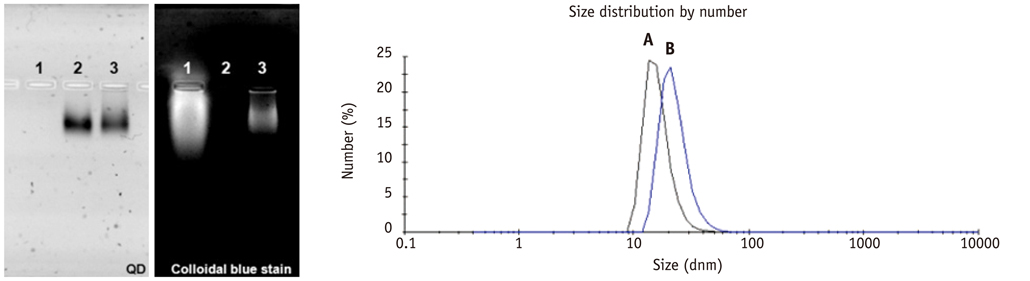
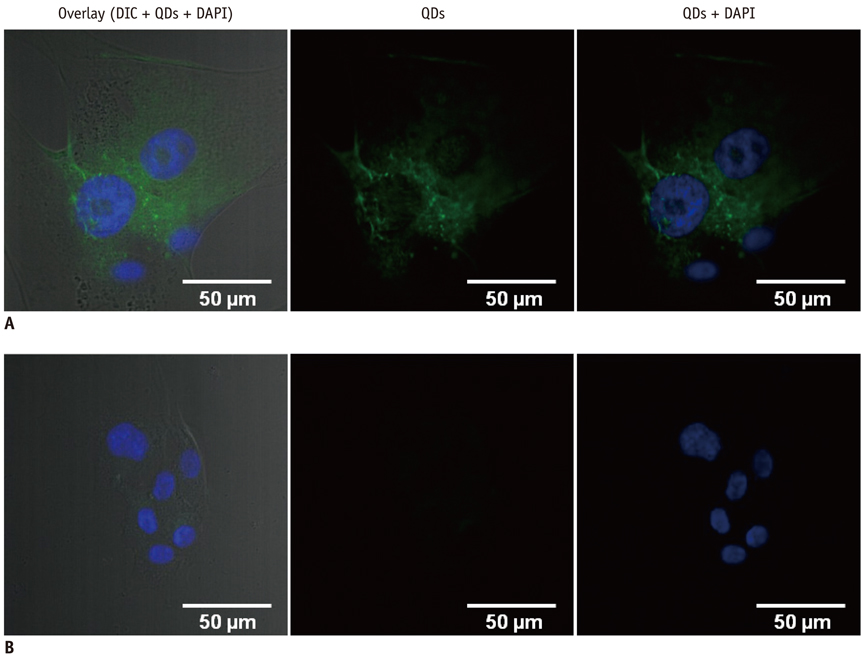
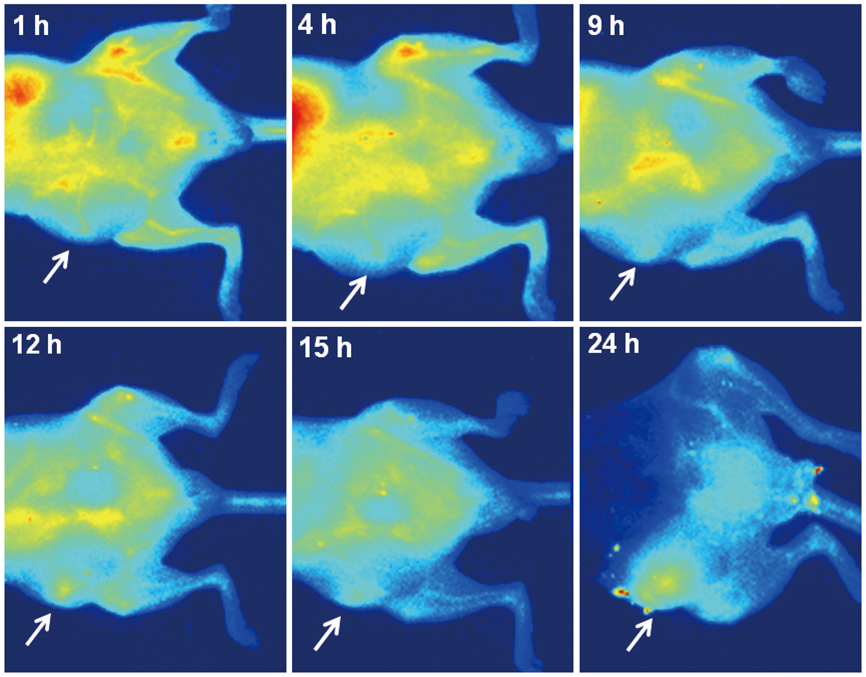
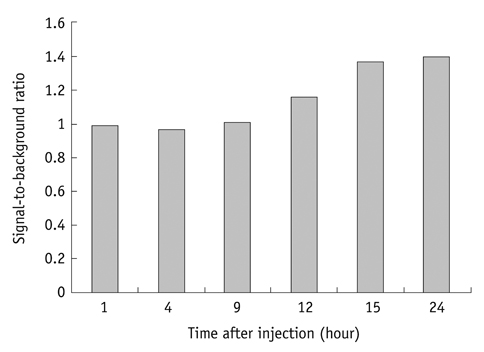
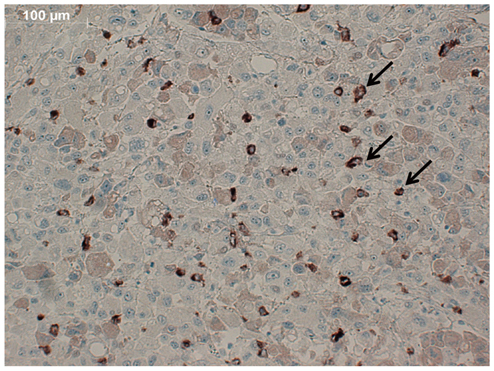
Conjugation reaction of QDs was performed by using the N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethylcarbodiimide (EDC) and sulfo-(N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) (Sulfo-NHS). The human umbilical vein cord endothelial cells (HUVECs) were incubated with QDs, conjugated with antiVGFR2, to see a specific binding in vitro. Fluorescent cell images were taken by a confocal microscope. The human prostate cancer cells (PC3) were injected to five nude mice on hind limbs to make the xenograft tumor model. QD-antiVEGFR2 antibody complex was injected into the tumor model and fluorescence measurements were performed at 1, 4, 9, 12, 15, and 24 hours after the injection.
RESULTS
The specific interaction between HUVECs and QD-antiVEGFR2 antibody was clearly shown in vitro. The in vivo fluorescence image disclosed that there was an increased signal of tumor, 12 hours after the injection of QDs.
CONCLUSION
By showing endothelial cells binding with QDs-antiVEGFR2 antibodyand an experimental application of the antibody for VEGFR2 imaging in the prostate cancer xenograft mouse model, we suggests that the antibody-conjugated QDs can be a potential imaging tool for angiogenesis of the cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Carbodiimides/pharmacology
Cell Line, Tumor
Disease Models, Animal
Electrophoresis, Agar Gel
Fluorescence
Male
Mice
Mice, Nude
Microscopy, Confocal
Neovascularization, Pathologic/*pathology
Prostatic Neoplasms/*pathology
*Quantum Dots
Succinimides/pharmacology
Transplantation, Heterologous
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2/*antagonists & inhibitors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971. 285:1182–1186.2. Oostendorp M, Douma K, Hackeng TM, Dirksen A, Post MJ, van Zandvoort MA, et al. Quantitative molecular magnetic resonance imaging of tumor angiogenesis using cNGR-labeled paramagnetic quantum dots. Cancer Res. 2008. 68:7676–7683.3. Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003. 9:653–660.4. Meitar D, Crawford SE, Rademaker AW, Cohn SL. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastatic disease, N-myc amplification, and poor outcome in human neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 1996. 14:405–414.5. Daldrup H, Shames DM, Wendland M, Okuhata Y, Link TM, Rosenau W, et al. Correlation of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging with histologic tumor grade: comparison of macromolecular and small-molecular contrast media. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 171:941–949.6. Massoud TF, Gambhir SS. Molecular imaging in living subjects: seeing fundamental biological processes in a new light. Genes Dev. 2003. 17:545–580.7. Mulder WJ, Castermans K, van Beijnum JR, Oude Egbrink MG, Chin PT, Fayad ZA, et al. Molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis using alphavbeta3-integrin targeted multimodal quantum dots. Angiogenesis. 2009. 12:17–24.8. Zhang H, Yee D, Wang C. Quantum dots for cancer diagnosis and therapy: biological and clinical perspectives. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2008. 3:83–91.9. Willmann JK, Paulmurugan R, Chen K, Gheysens O, Rodriguez-Porcel M, Lutz AM, et al. US imaging of tumor angiogenesis with microbubbles targeted to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 in mice. Radiology. 2008. 246:508–518.10. Yang YA, Wu H, Williams KR, Cao YC. Synthesis of CdSe and CdTe nanocrystals without precursor injection. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005. 44:6712–6715.11. Lee J, Choi Y, Kim K, Hong S, Park HY, Lee T, et al. Characterization and cancer cell specific binding properties of anti-EGFR antibody conjugated quantum dots. Bioconjug Chem. 2010. 21:940–946.12. Schellenberger EA, Bogdanov A Jr, Petrovsky A, Ntziachristos V, Weissleder R, Josephson L. Optical imaging of apoptosis as a biomarker of tumor response to chemotherapy. Neoplasia. 2003. 5:187–192.13. Deshpande N, Pysz MA, Willmann JK. Molecular ultrasound assessment of tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2010. 13:175–188.14. Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:1011–1027.15. Smith AM, Duan H, Mohs AM, Nie S. Bioconjugated quantum dots for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008. 60:1226–1240.16. Kim S, Lim YT, Soltesz EG, De Grand AM, Lee J, Nakayama A, et al. Near-infrared fluorescent type II quantum dots for sentinel lymph node mapping. Nat Biotechnol. 2004. 22:93–97.17. Bentolila LA, Ebenstein Y, Weiss S. Quantum dots for in vivo small-animal imaging. J Nucl Med. 2009. 50:493–496.18. Chen K, Li ZB, Wang H, Cai W, Chen X. Dual-modality optical and positron emission tomography imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor on tumor vasculature using quantum dots. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008. 35:2235–2244.19. Zhang H, Zeng X, Li Q, Gaillard-Kelly M, Wagner CR, Yee D. Fluorescent tumour imaging of type I IGF receptor in vivo: comparison of antibody-conjugated quantum dots and small-molecule fluorophore. Br J Cancer. 2009. 101:71–79.20. Chen LD, Liu J, Yu XF, He M, Pei XF, Tang ZY, et al. The biocompatibility of quantum dot probes used for the targeted imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Biomaterials. 2008. 29:4170–4176.21. Weidner N, Carroll PR, Flax J, Blumenfeld W, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993. 143:401–409.22. Schlemmer HP, Merkle J, Grobholz R, Jaeger T, Michel MS, Werner A, et al. Can pre-operative contrast-enhanced dynamic MR imaging for prostate cancer predict microvessel density in prostatectomy specimens? Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:309–317.23. Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RM, Chung LW, Nie S. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2004. 22:969–976.24. Cai W, Chen K, Li ZB, Gambhir SS, Chen X. Dual-function probe for PET and near-infrared fluorescence imaging of tumor vasculature. J Nucl Med. 2007. 48:1862–1870.25. Cai W, Shin DW, Chen K, Gheysens O, Cao Q, Wang SX, et al. Peptide-labeled near-infrared quantum dots for imaging tumor vasculature in living subjects. Nano Lett. 2006. 6:669–676.26. Hardman R. A toxicologic review of quantum dots: toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental factors. Environ Health Perspect. 2006. 114:165–172.27. Ipe BI, Lehnig M, Niemeyer CM. On the generation of free radical species from quantum dots. Small. 2005. 1:706–709.28. Lovrić J, Cho SJ, Winnik FM, Maysinger D. Unmodified cadmium telluride quantum dots induce reactive oxygen species formation leading to multiple organelle damage and cell death. Chem Biol. 2005. 12:1227–1234.29. Jun HY, Yin HH, Kim SH, Park SH, Kim HS, Yoon KH. Visualization of tumor angiogenesis using MR imaging contrast agent Gd-DTPA-anti-VEGF receptor 2 antibody conjugate in a mouse tumor model. Korean J Radiol. 2010. 11:449–456.30. Ko EY, Lee SH, Kim HH, Kim SM, Shin MJ, Kim N, et al. Evaluation of tumor angiogenesis with a second-generation US contrast medium in a rat breast tumor model. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:243–249.31. Kim JW, Jeong YY, Chang NK, Heo SH, Shin SS, Lee JH, et al. Perfusion CT in colorectal cancer: comparison of perfusion parameters with tumor grade and microvessel density. Korean J Radiol. 2012. 13:Suppl 1. S89–S97.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Zerumbone, Sesquiterpene Photochemical from Ginger, Inhibits Angiogenesis
- Endocrine Therapy Inhibits Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiogenesis in Prostate Cancer
- Pivotal role of vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor angiogenesis
- KR-31831, a new synthetic anti-ischemic agent, inhibits in vivo and in vitro angiogenesis
- VEGF-VEGFR Signals in Health and Disease