Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2013 Jun;17(3):223-228. 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.3.223.
Activation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor Is Coupled to Enhancement of Ca(2+)-Activated Potassium Channel Currents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, College of Veterinary Medicine and Bio/Molecular Informatics Center, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea. synah@konkuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1429302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.3.223
Abstract
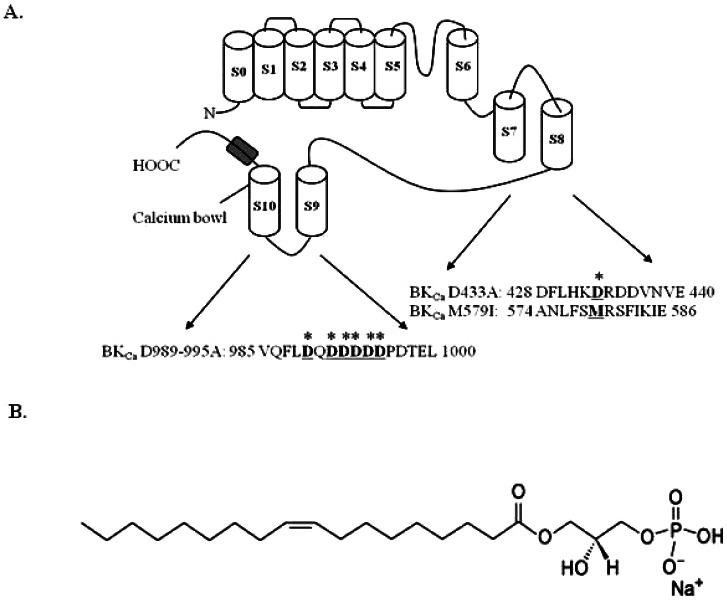
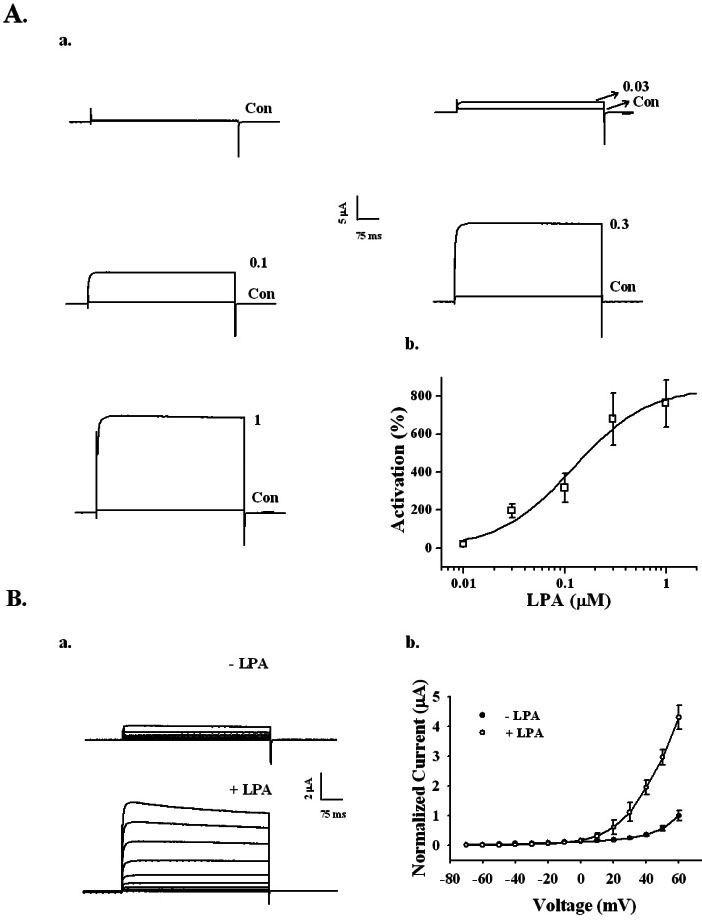
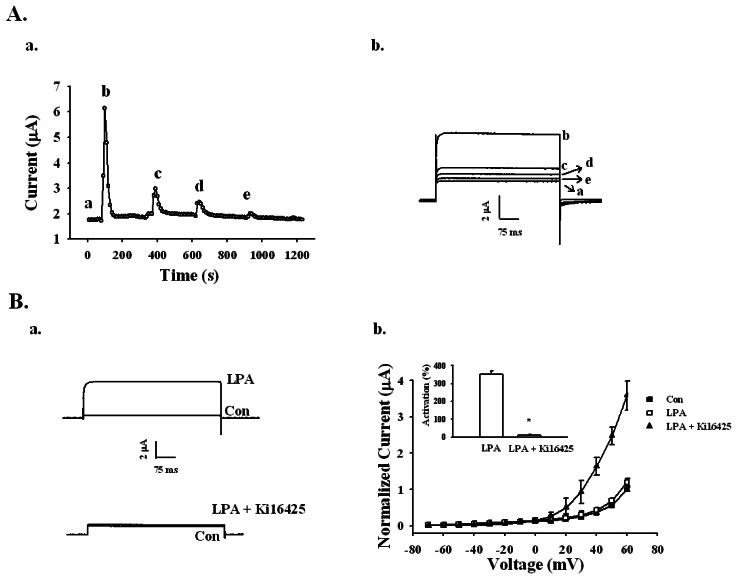
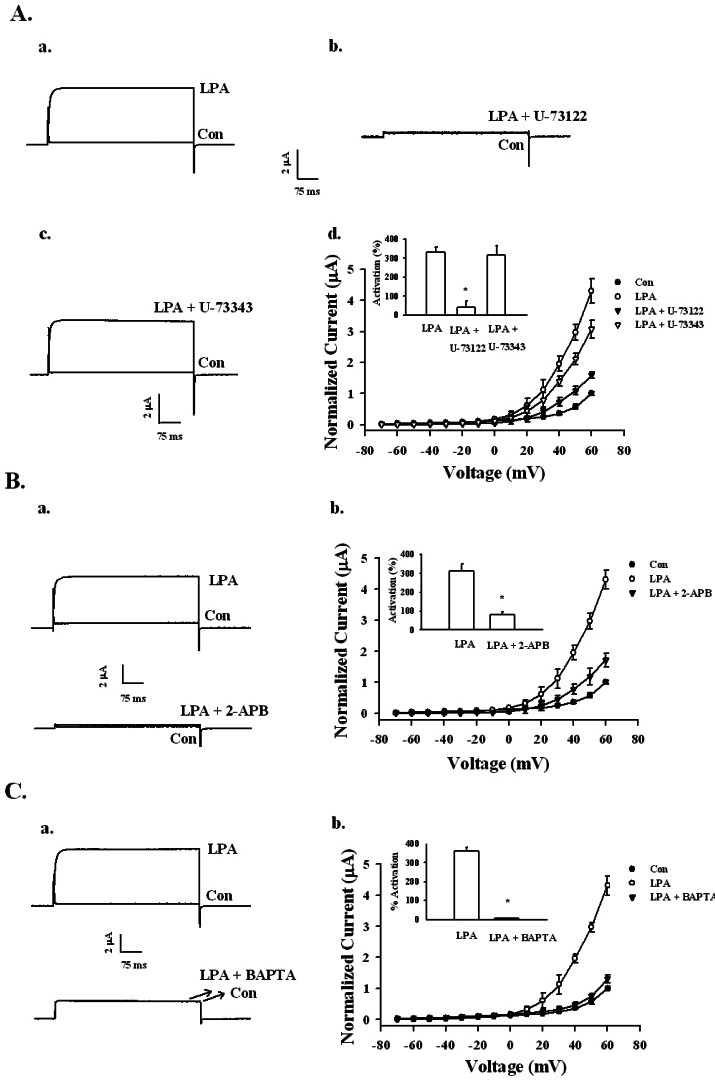
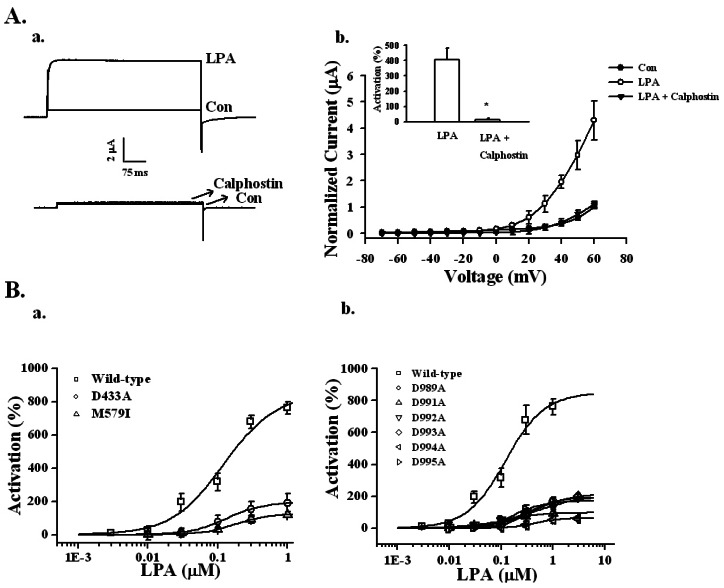
- The calcium-activated K+ (BKCa) channel is one of the potassium-selective ion channels that are present in the nervous and vascular systems. Ca2+ is the main regulator of BKCa channel activation. The BKCa channel contains two high affinity Ca2+ binding sites, namely, regulators of K+ conductance, RCK1 and the Ca2+ bowl. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA, 1-radyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphate) is one of the neurolipids. LPA affects diverse cellular functions on many cell types through G protein-coupled LPA receptor subtypes. The activation of LPA receptors induces transient elevation of intracellular Ca2+ levels through diverse G proteins such as Galphaq/11, Galphai, Galpha12/13, and Galphas and the related signal transduction pathway. In the present study, we examined LPA effects on BKCa channel activity expressed in Xenopus oocytes, which are known to endogenously express the LPA receptor. Treatment with LPA induced a large outward current in a reversible and concentration-dependent manner. However, repeated treatment with LPA induced a rapid desensitization, and the LPA receptor antagonist Ki16425 blocked LPA action. LPA-mediated BKCa channel activation was also attenuated by the PLC inhibitor U-73122, IP3 inhibitor 2-APB, Ca2+ chelator BAPTA, or PKC inhibitor calphostin. In addition, mutations in RCK1 and RCK2 also attenuated LPA-mediated BKCa channel activation. The present study indicates that LPA-mediated activation of the BKCa channel is achieved through the PLC, IP3, Ca2+, and PKC pathway and that LPA-mediated activation of the BKCa channel could be one of the biological effects of LPA in the nervous and vascular systems.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Binding Sites
Egtazic Acid
Estrenes
GTP-Binding Proteins
Ion Channels
Isoxazoles
Lysophospholipids
Naphthalenes
Oocytes
Potassium
Potassium Channels
Propionates
Pyrrolidinones
Receptors, Lysophosphatidic Acid
Signal Transduction
Xenopus
Egtazic Acid
Estrenes
GTP-Binding Proteins
Ion Channels
Isoxazoles
Lysophospholipids
Naphthalenes
Potassium
Potassium Channels
Propionates
Pyrrolidinones
Receptors, Lysophosphatidic Acid
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ghatta S, Nimmagadda D, Xu X, O'Rourke ST. Large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels: structural and functional implications. Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 110:103–116. PMID: 16356551.
Article2. Salkoff L, Butler A, Ferreira G, Santi C, Wei A. High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006; 7:921–931. PMID: 17115074.
Article3. Yuan P, Leonetti MD, Pico AR, Hsiung Y, MacKinnon R. Structure of the human BK channel Ca2+-activation apparatus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 2010; 329:182–186. PMID: 20508092.4. Weiger TM, Hermann A, Levitan IB. Modulation of calciumactivated potassium channels. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2002; 188:79–87. PMID: 11919690.
Article5. Fahanik-Babaei J, Eliassi A, Saghiri R. How many types of large conductance Ca2+-activated potassium channels exist in brain mitochondrial inner membrane: evidence for a new mitochondrial large conductance Ca2+-activated potassium channel in brain mitochondria. Neuroscience. 2011; 199:125–132. PMID: 21996476.6. Jiang Y, Pico A, Cadene M, Chait BT, MacKinnon R. Structure of the RCK domain from the E. coli K+ channel and demonstration of its presence in the human BK channel. Neuron. 2001; 29:593–601. PMID: 11301020.7. Lee US, Cui J. BK channel activation: structural and functional insights. Trends Neurosci. 2010; 33:415–423. PMID: 20663573.
Article8. Niu X, Qian X, Magleby KL. Linker-gating ring complex as passive spring and Ca2+-dependent machine for a voltage- and Ca2+-activated potassium channel. Neuron. 2004; 42:745–756. PMID: 15182715.9. Tigyi G. Aiming drug discovery at lysophosphatidic acid targets. Br J Pharmacol. 2010; 161:241–270. PMID: 20735414.
Article10. Contos JJ, Ishii I, Chun J. Lysophosphatidic acid receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2000; 58:1188–1196. PMID: 11093753.
Article11. Moolenaar WH, Kranenburg O, Postma FR, Zondag GC. Lysophosphatidic acid: G-protein signalling and cellular responses. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997; 9:168–173. PMID: 9069262.
Article12. Dyer D, Tigyi G, Miledi R. The effect of active serum albumin on PC12 cells: I Neurite retraction and activation of the phosphoinositide second messenger system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992; 14:293–301. PMID: 1326692.
Article13. Chettibi S, Lawrence AJ, Stevenson RD, Young JD. Effect of lysophosphatidic acid on motility, polarisation and metabolic burst of human neutrophils. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1994; 8:271–281. PMID: 8004064.
Article14. Ha TS, Lim HH, Lee GE, Kim YC, Park CS. Electrophysiological characterization of benzofuroindole-induced potentiation of large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels. Mol Pharmacol. 2006; 69:1007–1014. PMID: 16332986.15. Choi S, Rho SH, Jung SY, Kim SC, Park CS, Nah SY. A novel activation of Ca2+-activated Cl- channel in Xenopus oocytes by Ginseng saponins: evidence for the involvement of phospholipase C and intracellular Ca2+ mobilization. Br J Pharmacol. 2001; 132:641–648. PMID: 11159716.16. Lee JH, Lee BH, Choi SH, Yoon IS, Pyo MK, Shin TJ, Choi WS, Lim Y, Rhim H, Won KH, Lim YW, Choe H, Kim DH, Kim YI, Nah SY. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits human Kv14 channel currents by interacting with the Lys531 residue. Mol Pharmacol. 2008; 73:619–626. PMID: 17959711.
Article17. Lu L, Montrose-Rafizadeh M, Guggino WB. Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit kidney medullary thick ascending limb cells expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265:16190–16194. PMID: 1697853.18. Candia S, Garcia ML, Latorre R. Mode of action of iberiotoxin, a potent blocker of the large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel. Biophys J. 1992; 63:583–590. PMID: 1384740.19. Langer P, Gründer S, Rüsch A. Expression of Ca2+-activated BK channel mRNA and its splice variants in the rat cochlea. J Comp Neurol. 2003; 455:198–209. PMID: 12454985.20. Kaczorowski GJ, Knaus HG, Leonard RJ, McManus OB, Garcia ML. High-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels; structure, pharmacology, and function. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1996; 28:255–267. PMID: 8807400.
Article21. Kimura Y, Schmitt A, Fukushima N, Ishii I, Kimura H, Nebreda AR, Chun J. Two novel Xenopus homologs of mammalian LP(A1)/EDG-2 function as lysophosphatidic acid receptors in Xenopus oocytes and mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:15208–15215. PMID: 11278944.22. Yusifov T, Savalli N, Gandhi CS, Ottolia M, Olcese R. The RCK2 domain of the human BKCa channel is a calcium sensor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:376–381. PMID: 18162557.
Article23. Schreiber M, Salkoff L. A novel calcium-sensing domain in the BK channel. Biophys J. 1997; 73:1355–1363. PMID: 9284303.
Article24. Ma L, Uchida H, Nagai J, Inoue M, Aoki J, Ueda H. Evidence for de novo synthesis of lysophosphatidic acid in the spinal cord through phospholipase A2 and autotaxin in nerve injuryinduced neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010; 333:540–546. PMID: 20123931.
Article25. Hayashi Y, Kawaji K, Sun L, Zhang X, Koyano K, Yokoyama T, Kohsaka S, Inoue K, Nakanishi H. Microglial Ca2+-activated K+ channels are possible molecular targets for the analgesic effects of S-ketamine on neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 2011; 31:17370–17382. PMID: 22131399.26. Gao Y, Yang Y, Guan Q, Pang X, Zhang H, Zeng D. IL-1beta modulate the Ca2+-activated big-conductance K channels (BK) via reactive oxygen species in cultured rat aorta smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010; 338:59–68. PMID: 19949838.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Phytoestrogen on Potassium Channel Activities of Smooth Muscle Cells of Rabbit Seminal Vesicle
- Nimodipine as a potential pharmacological tool for characterizing R-type calcium currents
- Effects of Fluoxetine on Potassium Channels in Cat Gastric Smooth Muscle Cells
- Membrane stretch increases the activity of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in rabbit coronary vascular smooth muscles
- Presynaptic Mechanism Underlying Regulation of Transmitter Release by G Protein Coupled Receptors