J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Dec;23(6):1068-1089. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.6.1068.
Chromosomal Losses are Associated with Hypomethylation of the Gene-Control Regions in the Stomach with a Low Number of Active Genes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. rhyumung@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Clinical Pathology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1107535
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.6.1068
Abstract
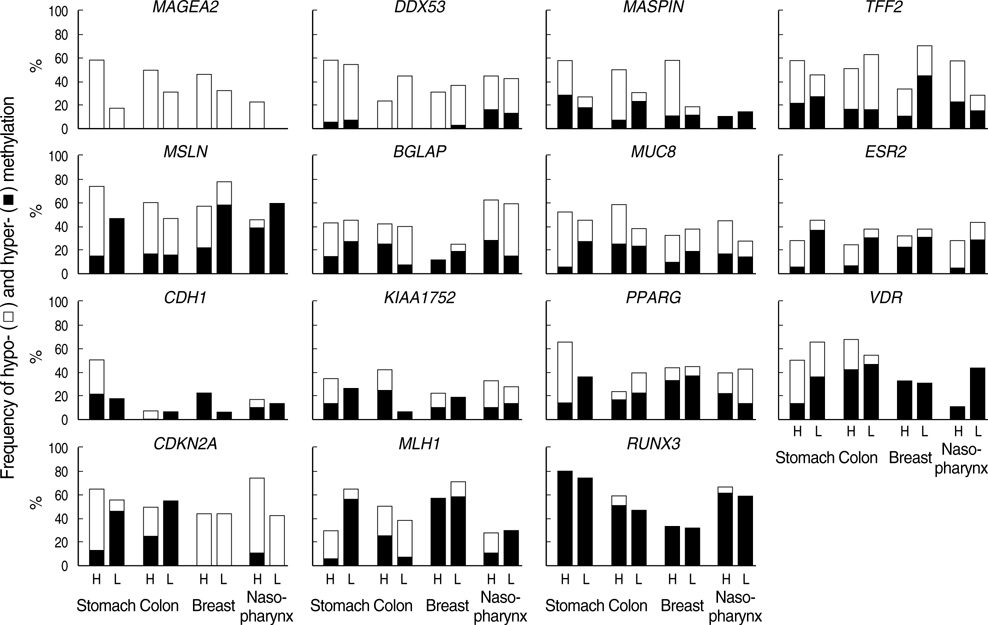
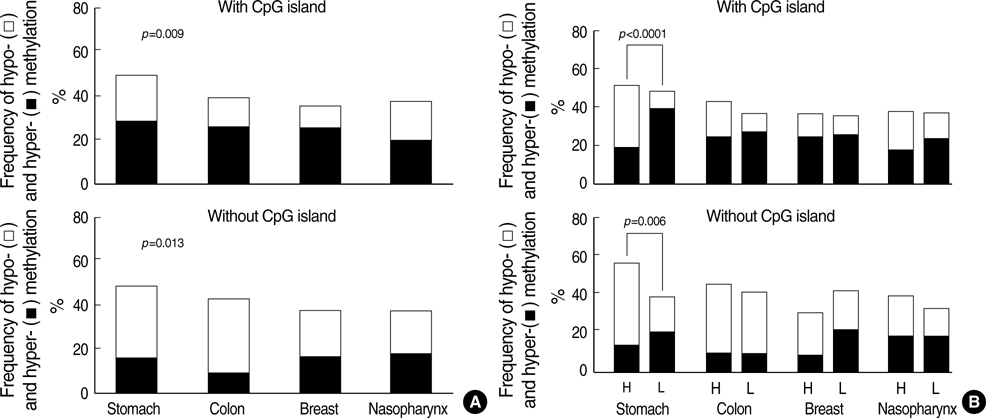
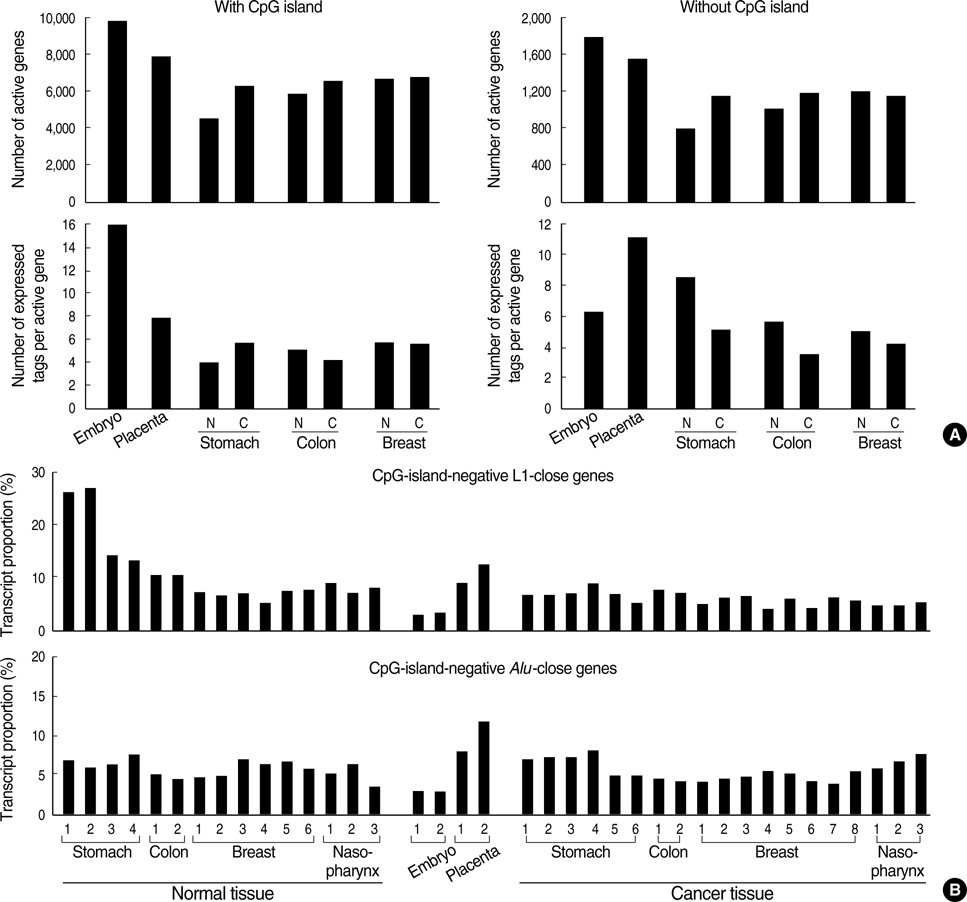
- Transitional-CpG methylation between unmethylated promoters and nearby methylated retroelements plays a role in the establishment of tissue-specific transcription. This study examined whether chromosomal losses reducing the active genes in cancers can change transitional-CpG methylation and the transcription activity in a cancer-type-dependent manner. The transitional-CpG sites at the CpG-island margins of nine genes and the non-island-CpG sites round the transcription start sites of six genes lacking CpG islands were examined by methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis. The number of active genes in normal and cancerous tissues of the stomach, colon, breast, and nasopharynx were analyzed using the public data in silico. The CpG-island margins and non-island CpG sites tended to be hypermethylated and hypomethylated in all cancer types, respectively. The CpG-island margins were hypermethylated and a low number of genes were active in the normal stomach compared with other normal tissues. In gastric cancers, the CpG-island margins and non-island-CpG sites were hypomethylated in association with high-level chromosomal losses, and the number of active genes increased. Colon, breast, and nasopharyngeal cancers showed no significant association between the chromosomal losses and methylation changes. These findings suggest that chromosomal losses in gastric cancers are associated with the hypomethylation of the gene-control regions and the increased number of active genes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
DNA Methylation and Expression Patterns of Key Tissue-specific Genes in Adult Stem Cells and Stomach Tissues
Seung-Jin Hong, Moo-Il Kang, Jung-Hwan Oh, Yu-Chae Jung, Young-Ho Kim, Sung-Ja Kim, Seung-Hye Choi, Eun-Joo Seo, Sang-Wook Choi, Mun-Gan Rhyu
J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24(5):918-929. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.918.DNA Methylation Patterns of Ulcer-Healing Genes Associated with the Normal Gastric Mucosa of Gastric Cancers
Seung-Jin Hong, Jung-Hwan Oh, Yu-Chae Jung, Young-Ho Kim, Sung-Ja Kim, Seok-Jin Kang, Eun-Joo Seo, Sang-Wook Choi, Moo-Il Kang, Mun-Gan Rhyu
J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25(3):405-417. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.405.
Reference
-
1. Walsh CP, Bestor TH. Cytosine methylation and mammalian development. Genes Dev. 1999. 13:26–34.
Article2. Gardiner-Garden M, Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987. 196:261–282.
Article3. Larsen F, Gundersen G, Lopez R, Prydz H. CpG islands as gene markers in the human genome. Genomics. 1992. 13:1095–1107.
Article4. Eckhardt F, Lewin J, Cortese R, Rakyan VK, Attwood J, Burger M, Burton J, Cox TV, Davies R, Down TA, Haefliger C, Horton R, Howe K, Jackson DK, Kunde J, Koenig C, Liddle J, Niblett D, Otto T, Pettett R, Seemann S, Thompson C, West T, Rogers J, Olek A, Berlin K, Beck S. DNA methylation profiling of human chromosomes 6, 20 and 22. Nat Genet. 2006. 38:1378–1385.
Article5. Jones PA. The DNA methylation paradox. Trends Genet. 1999. 15:34–37.
Article6. Feinberg AP, Ohlsson R, Henikoff S. The epigenetic progenitor origin of human cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2006. 7:21–33.
Article7. Sieber OM, Heinimann K, Tomlinson IP. Genomic instability--the engine of tumorigenesis? Nat Rev Cancer. 2003. 3:701–708.8. Turker MS. Gene silencing in mammalian cells and the spread of DNA methylation. Oncogene. 2002. 21:5388–5393.
Article9. Kang MI, Rhyu MG, Kim YH, Jung YC, Hong SJ, Cho CS, Kim HS. The length of CpG islands is associated with the distribution of Alu and L1 retroelements. Genomics. 2006. 87:580–590.
Article10. Kang MI, Kim HS, Jung YC, Kim YH, Hong SJ, Kim MK, Baek KH, Kim CC, Rhyu MG. Transitional CpG methylation between promoters and retroelements of tissue-specific genes during human mesenchymal cell differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2007. 102:224–239.
Article11. Hong SJ, Choi SW, Lee KH, Lee S, Min KO, Rhyu MG. Preoperative genetic diagnosis of gastric carcinoma based on chromosomal loss and microsatellite instability. Int J Cancer. 2005. 113:249–258.
Article12. Hong SJ, Kim YH, Choi YD, Min KO, Choi SW, Rhyu MG. Relationship between the extent of chromosomal losses and the pattern of CpG methylation in gastric carcinomas. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:790–805.
Article13. Kim YH, Hong SJ, Jung YC, Kim SJ, Seo EJ, Choi SW, Rhyu MG. The 5'-end transitional CpGs between the CpG islands and retroelements are hypomethylated in association with loss of heterozygosity in gastric cancers. BMC Cancer. 2006. 6:180.
Article14. Kim KM, Kwon MS, Hong SJ, Min KO, Seo EJ, Lee KY, Choi SW, Rhyu MG. Genetic classification of intestinal-type and diffuse-type gastric cancers based on chromosomal loss and microsatellite instability. Virchows Arch. 2003. 443:491–500.
Article15. Ishii M, Hashimoto S, Tsutsumi S, Wada Y, Matsushima K, Kodama T, Aburatani H. Direct comparison of GeneChip and SAGE on the quantitative accuracy in transcript profiling analysis. Genomics. 2000. 68:136–143.
Article16. van Ruissen F, Ruijter JM, Schaaf GJ, Asgharnegad L, Zwijnenburg DA, Kool M, Baas F. Evaluation of the similarity of gene expression data estimated with SAGE and Affymetrix GeneChips. BMC Genomics. 2005. 6:91.
Article17. Cross SH, Bird AP. CpG islands and genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995. 5:309–314.
Article18. Yoder JA, Walsh CP, Bestor TH. Cytosine methylation and the ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet. 1997. 13:335–340.
Article19. Baylin SB, Belinsky SA, Herman JG. Aberrant methylation of gene promoters in cancer---concepts, misconcepts, and promise. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000. 92:1460–1461.
Article20. Gold P, Freedman SO. Specific carcinoembryonic antigens of the human digestive system. J Exp Med. 1965. 122:467–481.
Article21. Edynak EM, Old LJ, Vrana M, Lardis MP. A fetal antigen associated with human neoplasia. N Engl J Med. 1972. 286:1178–1183.
Article22. Tanaka M, Sasaki H, Kino I, Sugimura T, Terada M. Genes preferentially expressed in embryo stomach are predominantly expressed in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1992. 52:3372–3377.23. Soundararajan R, Rao AJ. Trophoblast 'pseudo-tumorigenesis': significance and contributory factors. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2004. 2:15.24. Medstrand P, van de Lagemaat LN, Mager DL. Retroelement distributions in the human genome: variations associated with age and proximity to genes. Genome Res. 2002. 12:1483–1495.
Article25. Meunier J, Khelifi A, Navratil V, Duret L. Homology-dependent methylation in primate repetitive DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005. 102:5471–5476.
Article26. Sun M, Zhou G, Lee S, Chen J, Shi RZ, Wang SM. SAGE is far more sensitive than EST for detecting low-abundance transcripts. BMC Genomics. 2004. 5:1.
Article27. Fulka H, Mrazek M, Tepla O, Fulka J Jr. DNA methylation pattern in human zygotes and developing embryos. Reproduction. 2004. 128:703–708.
Article28. Razin A, Kafri T. DNA methylation from embryo to adult. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1994. 48:53–81.
Article29. Ehrlich M, Gama-Sosa MA, Huang LH, Midgett RM, Kuo KC, McCune RA, Gehrke C. Amount and distribution of 5-methylcytosine in human DNA from different types of tissues of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982. 10:2709–2721.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship Between the Extent of Chromosomal Losses and the Pattern of CpG Methylation in Gastric Carcinomas
- The Extent of Chromosomal Losses and the Status of CpG Methylation in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
- Methylation and Chromosomal Losses in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
- Clinical and Pathological Significance of the Genetic Analysis in Colorectal Carcinomas
- Genomic Alterations Detected in Colon Cancer Cell Lines by Using Array-Comparative Genomic Hybridization