J Vet Sci.
2008 Dec;9(4):345-349. 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.4.345.
The expression and localization of inhibin isotypes in mouse testis during postnatal development
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine and Veterinary Medical Research Center, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea. moonc@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Veterinary Toxicology, College of Veterinary Medicine and Veterinary Medical Research Center, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea.
- 3Department of Veterinary Surgery, College of Veterinary Medicine and Veterinary Medical Research Center, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea.
- 4Department of Veterinary Obstetrics, College of Veterinary Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 702-701, Korea.
- 5Department of Veterinary Anatomy, College of Veterinary Medicine and Applied Radiological Science Research Institute, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- KMID: 1104908
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2008.9.4.345
Abstract
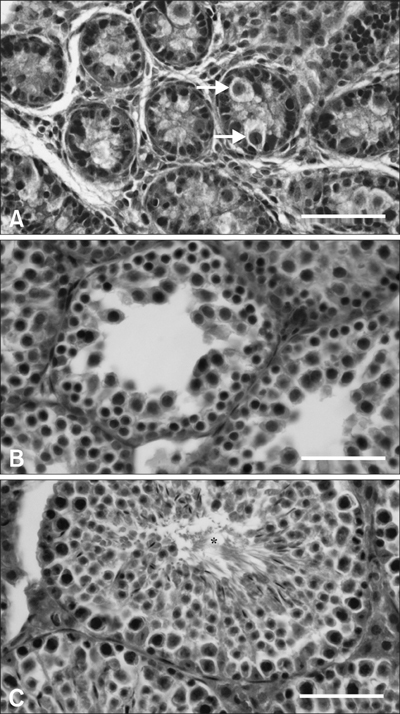
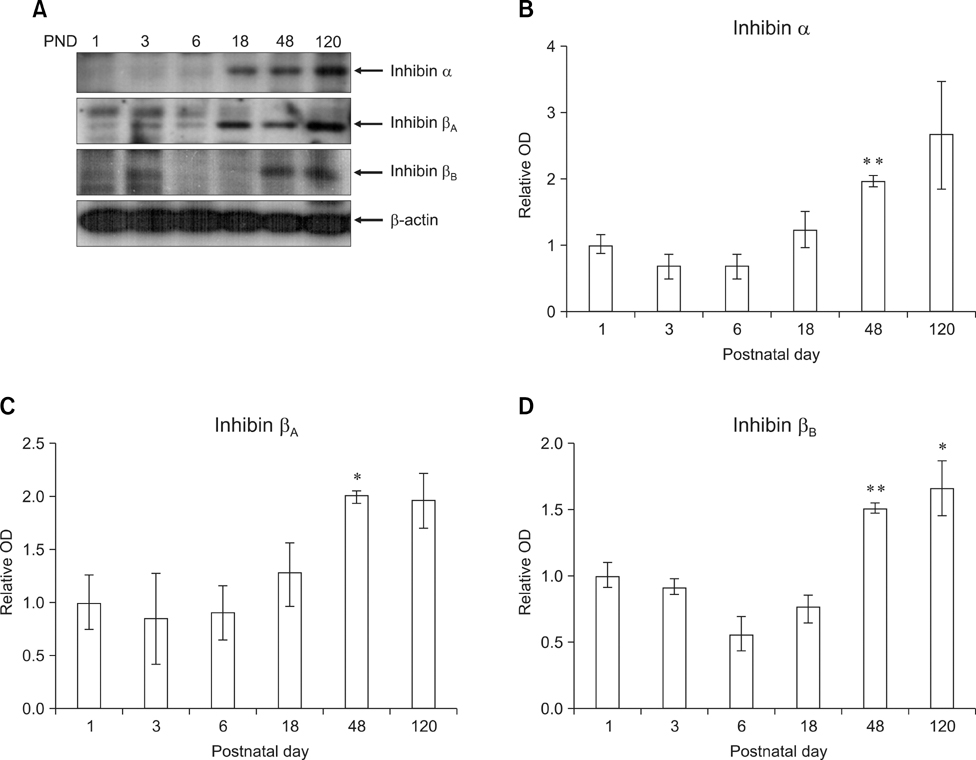
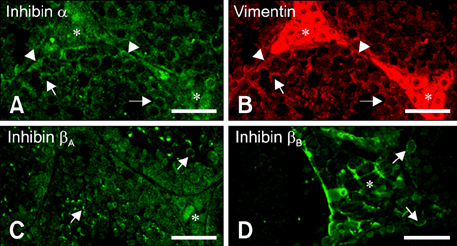
- Inhibin, which is important for normal gonadal function, acts on the pituitary gonadotropins to suppress folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) secretion. The level and cellular localization of the inhibin isotypes, alpha, beta(A) and beta(B), in the testis of mice were examined during postnatal development in order to determine if inhibin expression is related to testicular maturation. Mouse testes were sampled on postnatal days (PNDs) 1, 3, 6, 18, 48 and 120, and analyzed by Western blotting and immunofluorescence. Western blot analysis showed very low levels of inhibin alpha, beta(A) and beta(B) expression in the testes at days 1 to 6 after birth. The levels then increased gradually from PND 18 to 48-120, and there were significant peaks at PND 48. Inhibin alpha, beta(A) and beta(B) were detected in testicular cells during postnatal development using immunohistochemistry. The immunoreactivity of inhibin alpha was rarely observed in testicular cells during PND 1 to 6, or in the cytoplasmic process of Sertoli cells surrounding the germ cells and interstitial cells during PND 18 to 120. Inhibin beta(A) and beta(B) immunoreactivity was rarely observed in the testis from PND 1 to 6. On the other hand, it was observed in some spermatogonial cells, as well as in the interstitial space between PND 48 and PND 120. We conclude that the expression of inhibin isotypes increases progressively in the testis of mice with increasing postnatal age, suggesting that inhibin is associated with a negative feedback signal for FSH in testicular maturation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Allenby G, Foster PM, Sharpe RM. Evidence that secretion of immunoactive inhibin by seminiferous tubules from the adult rat testis is regulated by specific germ cell types: correlation between in vivo and in vitro studies. Endocrinology. 1991. 128:467–476.
Article2. Au CL, Robertson DM, de Kretser DM. Measurement of inhibin and an index of inhibin production by rat testes during postnatal development. Biol Reprod. 1986. 35:37–43.
Article3. Buzzard JJ, Loveland KL, O'Bryan MK, O'Connor AE, Bakker M, Hayashi T, Wreford NG, Morrison JR, de Kretser DM. Changes in circulating and testicular levels of inhibin A and B and activin A during postnatal development in the rat. Endocrinology. 2004. 145:3532–3541.
Article4. Clifton RJ, O'Donnell L, Robertson DM. Pachytene spermatocytes in co-culture inhibit rat Sertoli cell synthesis of inhibin βB-subunit and inhibin B but not the inhibin α-subunit. J Endocrinol. 2002. 172:565–574.
Article5. de Kretser DM, Robertson DM. The isolation and physiology of inhibin and related proteins. Biol Reprod. 1989. 40:33–47.
Article6. Guitton N, Touzalin AM, Sharpe RM, Cheng CY, Pinon-Lataillade G, Méritte H, Chenal C, Jégou B. Regulatory influence of germ cells on Sertoli cell function in the pre-pubertal rat after acute irradiation of the testis. Int J Androl. 2000. 23:332–339.
Article7. Illingworth PJ, Groome NP, Byrd W, Rainey WE, McNeilly AS, Mather JP, Bremner WJ. Inhibin-B: a likely candidate for the physiologically important form of inhibin in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996. 81:1321–1325.
Article8. Jin W, Arai KY, Herath CB, Kondo M, Ishi H, Tanioka Y, Watanabe G, Groome NP, Taya K. Inhibins in the male Göttingen miniature pig: Leydig cells are the predominant source of inhibin B. J Androl. 2001. 22:953–960.
Article9. Jin W, Wada S, Arai KY, Kishi H, Herath CB, Watanabe G, Suzuki AK, Groome NP, Taya K. Testicular secretion of inhibin in the male golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). J Androl. 2001. 22:207–211.10. Lee VW, de Kretser DM, Hudson B, Wang C. Variations in serum FSH, LH and testosterone levels in male rats from birth to sexual maturity. J Reprod Fertil. 1975. 42:121–126.
Article11. Mason AJ. Burger HG, de Kretser D, Findlay J, Igarashi M, editors. Human inhibin and activin: Structure and recombinant expression in mammalian cells. Inhibin-Non-Steroidal Regulation of Follicle Stimulating Hormone Secretion. 1987. New York: Raven Press;42–77.12. Matzuk MM, Finegold MJ, Su JG, Hsueh AJ, Bradley A. α-inhibin is a tumour-suppressor gene with gonadal specificity in mice. Nature. 1992. 360:313–319.
Article13. McMullen ML, Cho BN, Yates CJ, Mayo KE. Gonadal pathologies in transgenic mice expressing the rat inhibin α-subunit. Endocrinology. 2001. 142:5005–5014.
Article14. Mellor SL, Richards MG, Pedersen JS, Robertson DM, Risbridger GP. Loss of the expression and localization of inhibin α-subunit in high grade prostate cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998. 83:969–975.
Article15. Nagata S, Tsunoda N, Nagamine N, Tanaka Y, Taniyama H, Nambo Y, Watanabe G, Taya K. Testicular inhibin in the stallion: cellular source and seasonal changes in its secretion. Biol Reprod. 1998. 59:62–68.
Article16. Noguchi J, Hikono H, Sato S, Watanabe G, Taya K, Sasamoto S, Hasegawa Y. Ontogeny of inhibin secretion in the rat testis: secretion of inhibin-related proteins from fetal Leydig cells and of bioactive inhibin from Sertoli cells. J Endocrinol. 1997. 155:27–34.
Article17. O'Connor AE, de Kretser DM. Inhibins in normal male physiology. Semin Reprod Med. 2004. 22:177–185.18. Pierson TM, Wang Y, DeMayo FJ, Matzuk MM, Tsai SY, O'Malley BW. Regulable expression of inhibin A in wild-type and inhibin α null mice. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. 14:1075–1085.
Article19. Pineau C, Sharpe RM, Saunders PT, Gérard N, Jégou B. Regulation of Sertoli cell inhibin production and of inhibin α-subunit mRNA levels by specific germ cell types. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990. 72:13–22.
Article20. Plant TM, Marshall GR. The functional significance of FSH in spermatogenesis and the control of its secretion in male primates. Endocr Rev. 2001. 22:764–786.
Article21. Robertson DM, Cahir N, Findlay JK, Burger HG, Groome N. The biological and immunological characterization of inhibin A and B forms in human follicular fluid and plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997. 82:889–896.
Article22. Schmitt JF, Millar DS, Pedersen JS, Clark SL, Venter DJ, Frydenberg M, Molloy PL, Risbridger GP. Hypermethylation of the inhibin α-subunit gene in prostate carcinoma. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. 16:213–220.
Article23. Seok OS, Ahn JM, Mayo KE, Cho BN. Developmental changes in inhibin-α gene expression in the mouse testis. Mol Cells. 2004. 17:67–72.24. Sharpe RM, Turner KJ, McKinnell C, Groome NP, Atanassova N, Millar MR, Buchanan DL, Cooke PS. Inhibin B levels in plasma of the male rat from birth to adulthood: effect of experimental manipulation of Sertoli cell number. J Androl. 1999. 20:94–101.25. van Dissel-Emiliani FM, Grootenhuis AJ, de Jong FH, de Rooij DG. Inhibin reduces spermatogonial numbers in testes of adult mice and Chinese hamsters. Endocrinology. 1989. 125:1899–1903.
Article26. Woodruff TK, Besecke LM, Groome N, Draper LB, Schwartz NB, Weiss J. Inhibin A and inhibin B are inversely correlated to follicle-stimulating hormone, yet are discordant during the follicular phase of the rat estrous cycle, and inhibin A is expressed in a sexually dimorphic manner. Endocrinology. 1996. 137:5463–5467.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The expression and cellular localization of phospholipase D isozymes in the developing mouse testis
- Expression of c-Kit/SCF and Inhibin-alpha in Ovarian Follicles During Mouse Development
- Expression of Inhibin in the Whole-body gamma-irradiated Mouse Ovary
- Cytoplasmatic Localization of Six1 in Male Testis and Spermatogonial Stem Cells
- Distribution of the Mouse Striatal Cholinergic Neurons in Their Early Postnatal Period