J Vet Sci.
2007 Sep;8(3):209-212. 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.3.209.
The expression and cellular localization of phospholipase D isozymes in the developing mouse testis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Medicine, College of Applied Life Sciences, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea. shint@cheju.ac.k
- 2Applied Radiological Science Research Institute, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- 3Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Cheju National University, Jeju 690-756, Korea.
- 4Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 301-131, Korea.
- 5Department of Molecular Biology, College of Natural Science, Pusan National University, Busan 609-735, Korea. minds@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 1090792
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2007.8.3.209
Abstract
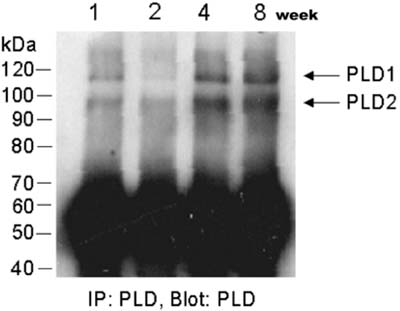
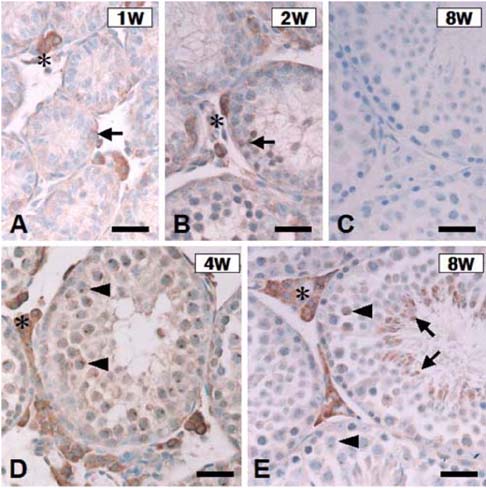
- To examine the involvement of phospholipase D (PLD)isozymes in postnatal testis development, the expression ofPLD1 and PLD2 was examined in the mouse testis atpostnatal weeks 1, 2, 4, and 8 using Western blot analysisand immunohistochemistry. The expression of both PLD1and PLD2 increased gradually with development frompostnatal week 1 to 8. Immunohistochemically, PLDimmunoreactivity was detected in some germ cells in thetestis and interstitial Leydig cells at postnatal week 1.PLD was mainly detected in the spermatocytes andresidual bodies of spermatids in the testis after 8 weeksafter birth. The intense immunostaining of PLD in Leydigcells remained unchanged by postnatal week 8. Thesefindings suggest that PLD isozymes are involved in thespermatogenesis of the mouse testis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn M, Min DS, Kang J, Jung K, Shin T. Increased expression of phospholipase D1 in the spinal cords of rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurosci Lett. 2001. 316:95–98.
Article2. Andresen BT, Rizzo MA, Shome K, Romero G. The role of phosphatidic acid in the regulation of the Ras/MEK/Erk signaling cascade. FEBS Lett. 2002. 531:65–68.
Article3. Baldassare JJ, Jarpe MB, Alferes L, Raben DM. Nuclear translocation of Rho A mediates the mitogen-induced activation of phospholipase D involved in nuclear envelope signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:4911–4914.
Article4. Boarder MR. A role for phospholipase D in control of mitogenesis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994. 15:57–62.5. Exton JH. Phospholipase D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. 1436:105–115.
Article6. Exton JH. Regulation of phospholipase D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. 1439:121–133.
Article7. Freyberg Z, Sweeney D, Siddhanta A, Bourgoin S, Frohman M, Shields D. Intracellular localization of phospholipase D1 in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. 12:943–955.
Article8. Frohman MA, Morris AJ. Phospholipase D structure and regulation. Chem Phys Lipids. 1999. 98:127–140.
Article9. Jung K, Min DS, Sim KB, Ahn M, Kim H, Cheong J, Shin T. Upregulation of phospholipase D1 in the spinal cords of rats with clip compression injury. Neurosci Lett. 2003. 336:126–130.
Article10. Kim H, Lee J, Kim S, Shin MK, Min DS, Shin T. Differential expression of phospholipase D1 and D2 in mouse tissues. Cell Biol Int. 2006. 31:148–155.11. Lauritzen L, Hansen HS. Differential phospholipid-labeling suggests two subtypes of phospholipase D in rat Leydig cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995. 217:747–754.
Article12. Lee EJ, Min DS, Kang WS, Lee MY, Oh SJ, Chun MH. The expression and cellular localization of phospholipase D1 in the rodent retina. Brain Res. 2001. 905:240–244.
Article13. Lee EJ, Min DS, Lee MY, Chung JW, Chun MH, Oh SJ. Differential expression of phospholipase D1 in the developing retina. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. 15:1006–1012.
Article14. Lee MY, Kim SY, Min DS, Choi YS, Shin SL, Chun MH, Lee SB, Kim MS, Jo YH. Upregulation of phospholipase D in astrocytes in response to transient forebrain ischemia. Glia. 2000. 30:311–317.
Article15. Meier KE, Gibbs TC, Knoepp SM, Ella KM. Expression of phospholipase D isoforms in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. 1439:199–213.
Article16. Min DS, Ahn BH, Rhie DJ, Yoon SH, Hahn SJ, Kim MS, Jo YH. Expression and regulation of phospholipase D during neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. Neuropharmacology. 2001. 41:384–391.
Article17. Min DS, Choi JS, Chun MH, Chung JW, Lee MY. Transient expression of phospholipase D1 in developing rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 2001. 310:125–128.
Article18. Min DS, Kim EG, Exton JH. Involvement of tyrosine phosphorylation and protein kinase C in the activation of phospholipase D by H2O2 in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1998. 273:29986–29994.
Article19. Sharpe RM, Maddocks S, Kerr JB. Cell-cell interactions in the control of spermatogenesis as studied using Leydig cell destruction and testosterone replacement. Am J Anat. 1990. 188:3–20.
Article20. Strand AM, Lauritzen L, Vinggaard AM, Hansen HS. The subcellular localization of phospholipase D activities in rat Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1999. 152:99–110.
Article21. Vinggaard AM, Hansen HS. Phorbol ester and vasopressin activate phospholipase D in Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991. 79:157–165.
Article22. Zhao Y, Ehara H, Akao Y, Shamoto M, Nakagawa Y, Banno Y, Deguchi T, Ohishi N, Yagi K, Nozawa Y. Increased activity and intranuclear expression of phospholipase D2 in human renal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. 278:140–143.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunohistochemical localization of eight phospholipase C isozymes in pancreatic islets of the mouse
- Distribution of phospholipase C isozymes in normal human lung tissue and their immunohistochemical localization
- Expression of Fas-associated Factor 1 in the Developing Testis
- Expression of phospholiapse C isozymes in human lung cancer tissues
- Cytoplasmatic Localization of Six1 in Male Testis and Spermatogonial Stem Cells