J Korean Acad Nurs.
2010 Aug;40(4):580-588. 10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.580.
Effect of Decreased Locomotor Activity on Hindlimb Muscles in a Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Bredin Institute, Edmonton, AB, Canada.
- 2College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. machoe@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1073080
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.580
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to examine effects of decreased locomotor activity on mass, Type I and II fiber cross-sectional areas of ipsilateral and contralateral hindlimb muscles 21 days after establishing the Parkinson's disease rat model.
METHODS
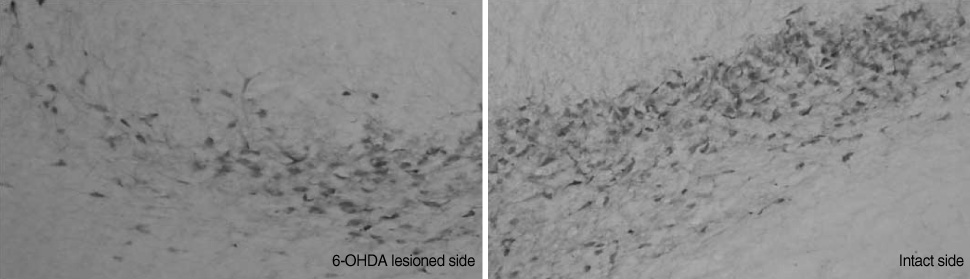
The rat model was established by direct injection of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA, 50 microgram) into the left substantia nigra after stereotaxic surgery. Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were assigned to one of two groups; the Parkinson's disease group (PD; n=17) and a sham group (S; n=8). Locomotor activity was assessed before and 21 days after the experiment. At 22 days after establishing the rat model, all rats were anesthetized and soleus and plantaris muscles were dissected from both ipsilateral and contralateral sides. The brain was dissected to identify dopaminergic neuronal death of substantia nigra in the PD group.
RESULTS
The PD group at 21 days after establishing the Parkinson's disease rat model showed significant decrease in locomotor activity compared with the S group. Weights and Type I and II fiber cross-sectional areas of the contralateral soleus muscle of the PD group were significantly lower than those of the S group.
CONCLUSION
Contralateral soleus muscle atrophy occurs 21 days after establishing the Parkinson's disease rat model.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bloem BR, Grimbergen YA, van Dijk JG, Munneke M. The "posture second" strategy: A review of wrong priorities in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology Science. 2006. 248(1-2):196–204.2. Brooke MH, Kaiser KK. Muscle fiber types: How many and what kind? Archives Neurology. 1970. 23:369–379.3. Chaturvedi RK, Agrawal AK, Seth K, Shukla S, Chauhan S, Shukla Y, et al. Effect of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) co-transplantation with fetal ventral mesencephalic cells (VMC) on functional restoration in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) lesioned rat model of Parkinson's disease: Nneurobehavioral, neurochemical and immunohistochemical studies. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience. 2003. 21:391–400.4. Cho H, Baik JS, Park JH, Kim JY, Kang SY. A Case of Subcortical Heterotopia in Hemiparkinson-Hemiatrophy Syndrome. Journal of the Korean Neurological Association. 2005. 23:274–277.5. Choe MA. Human structure & function. 2003. Seoul: Seoul National University Press.6. Choe MA, An GJ, Lee YK, Im JH, Choi-Kwon S, Heitkemper M. Effect of inactivity and undernutrition after acute ischemic stroke in a rat hindlimb muscle model. Nursing Research. 2004. 53:283–292.7. Choe MA, Ji JK, Kim EH. Effect of intermittent low-intensity, short duration exercise on type II muscle of suspended rats. The Journal of Nurses Academic Society. 1995. 25:193–209.8. Choe MA, Park SC, Koh CS. Effect of periodic low intensity exercise on the Type I and II muscle in suspended rats. Korean Journal of Sports Medicine. 1994. 12:182–196.9. Dunnewold RJ, Hoff JI, van Pelt HC, Fredrikze PQ, Wagemans EA, van Hilten BJ. Ambulatory quantitative assessment of body position, bradykinesia, and hypokinesia in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Clinical Neurophysiology. 1998. 15:235–242.10. Frimel TN, Kapadia F, Gaidosh GS, Li Y, Walter GA, Vandenborne K. A model of muscle atrophy using cast immobilization in mice. Muscle & Nerve. 2005. 32:672–674.11. Hong SK, Park KW, Cha JK, Kim SH, Chun DR, Yang CK, et al. Quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease. Journal of the Korean Neurological Association. 2002. 20:227–233.12. Hudson JL, van Horne CG, Stromberg I, Brock S, Clayton J, Masserano J, et al. Correlation of apomorphine- and amphetamine-induced turning with nigrostriatal dopamine content in unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Brain Research. 1993. 626:167–174.13. Iancu R, Mohapel P, Brundin P, Paul G. Behavioral characterization of a unilateral 6-OHDA-lesion model of Parkinson's disease in mice. Behavioural Brain Research. 2005. 162:1–10.14. Jakobsson F, Borg K, Edström L, Grimby L. Use of motor units in relation to muscle fiber type and size in man. Muscle & Nerve. 1988. 11:1211–1218.15. Jankovic J. Parkinson's disease: Cclinical features and diagnosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 2008. 79:368–376.16. Johnell O, Melton LJ 3rd, Atkinson EJ, O'Fallon WM, Kurland LT. Fracture risk in patients with Parkinsonism: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Age and Ageing. 1992. 21:32–38.17. Kasper CE, Talbot LA, Gaines JM. Skeletal muscle damage and recovery. AACN Clinical Issues. 2002. 13:237–247.18. Koh SB. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease. Journal of the Korean Academy of Family Medicine. 2003. 24:1059–1068.19. Koh SB, Kwon DY, Lee JM, Han JK, Kim BJ, et al. Prevalence of Parkinsonism in Ansan-city. Journal of the Korean Neurological Association. 2003. 21:498–501.20. Lee DH. Parkinson's disease: Questions and Answers (F. W. Robert Hauser Trans.). 2005. Seoul: E-pulic;original work published in 2003.21. Lee DK, Son NW, Jung DS, Cho SK, Jin YS. Effect of endurance training on fiber composition of rat hindlimb muscles. Report of Korean Sports Science Institute. 1990. 12. Seoul, Korea:22. Lee PH, Joo US, Yong SW, Huh K. Asymmetric freezing of gait in hemiparkinsonism-hemiatrophy. Neurology. 2004. 63(2):E7.23. Lee SC, Moon MS, Lee SJ, Yoo M, Yoon CH, Yoo GH. The Characteristics of Circling Behavior Induced by Dopamine Agonists Following Treatment with 6-OHDA to Unilaterally into Left Stratum in Rats. Korean Journal of Ginseng Science. 1997. 21:61–67.24. Lee WT, Park KA. Medical Neuroanatomy. 2008. 2nd ed. Seoul: Korea Medical Book Publisher.25. Metz GA, Tse A, Ballermann M, Smith LK, Fouad K. The unilateral 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson's disease revisited: An electromyographic and behavioural analysis. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2005. 22:735–744.26. Miklyaeva EI, Martens DJ, Whishaw IQ. Impairments and compensatory adjustments in spontaneous movement after unilateral dopamine depletion in rats. Brain Research. 1995. 681:23–40.27. Park MJ, Cheon SM, Kim JW. Three Cases of Hemiparkinsonism-hemiatrophy Syndrome. Journal of the Korean Neurological Association. 2005. 23:823–826.28. Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 2007. 6th ed. Boston: Academic Press.29. Thomason DB, Booth FW. Atrophy of the soleus muscle by hindlimb unweighting. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1990. 68:1–12.30. Ungerstedt U. Postsynaptique supersensitivity after 6-hydroxydopamine induced degeneration of the nigrostriatal system in the rat brain. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 1971. 367:69–93.31. Ungerstedt U, Arbuthnott GW. Quantitative recording of rotational behavior in rats after 6-hydroxy-dopamine lesions of the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Research. 1970. 24:485–493.32. van Iersel MB, Hoefsloot W, Munneke M, Bloem BR, Olde Rikkert MG. Systematic review of quantitative clinical gait analysis in patients with dementia. Zeitschrift fur Gerontologie und Geriatrie: Organ der Deutschen Gesellschaft fur Gerontologie und Geriatrie. 2004. 37:27–32.33. Whishaw IQ, Li K, Whishaw PA, Gorny B, Metz GA. Distinct forelimb and hind limb stepping impairments in unilateral dopamine-depleted rats: Use of the rotorod as a method for the qualitative analysis of skilled walking. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 2003. 126:13–23.34. Wijemanne S, Jankovic J. Hemiparkinsonism-hemiatrophy syndrome. Neurology. 2007. 69:1585–1594.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Nicotine on MPTP-induced Parkinson's Disease Animal Model
- A Histochemical Changes of Calf Muscle Fibers after Rat Hindlimb Suspension
- Morphological Changes in Dopaminergic Neurons in Selective Parkinson's Rat Model
- Weightlessness-simulated Experimental Apparatus: Hindlimb Unloading Model in Rat-Technical Aspects
- Beneficial Effect of Vitamin E in Rotenone Induced Model of PD: Behavioural, Neurochemical and Biochemical Study