Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Aug;28(4):274-281. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.4.274.
Standardized Sweat Chloride Analysis for the Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jeongho@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 854889
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.4.274
Abstract
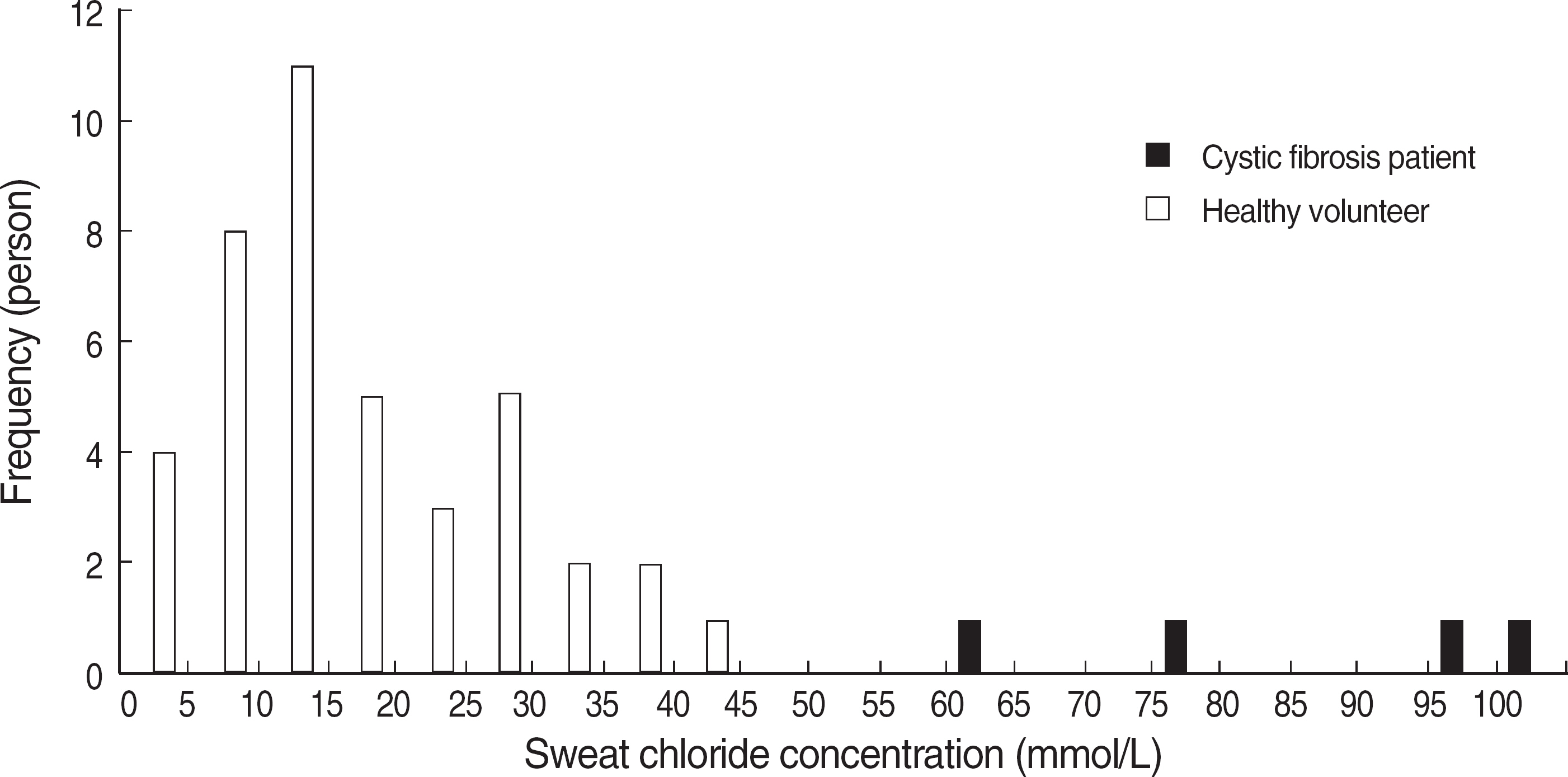
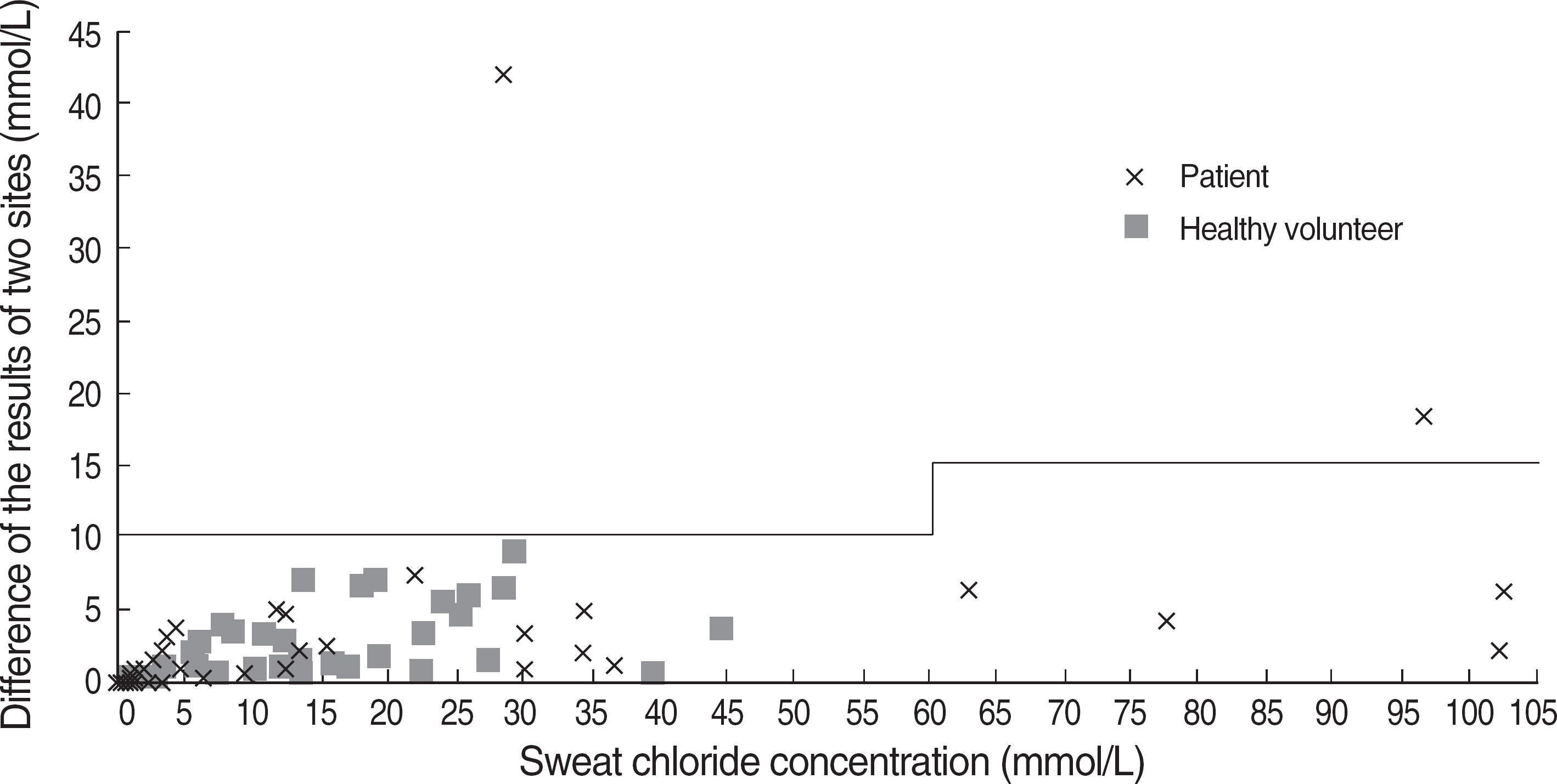
- BACKGROUND: Cystic fibrosis is a chronic progressive autosomal recessive disorder caused by the CFTR gene mutations. It is quite common in Caucasians, but very rare in Asians. Sweat chloride test is known to be a screening test for the cystic fibrosis due to the fact that electrolyte levels in sweat are elevated in patients. In this study, sweat chloride levels in Korean population were measured and analyzed by using standardized pilocarpine iontophoresis sweat chloride test. METHODS: The sweat chloride test was performed in 47 patients referred to Yondong Severance Hospital from August, 2001 to April, 2007 and 41 healthy volunteers. The sweat chloride tests were conducted according to the CLSI C34-A2 guideline using pilocarpine iontophoresis method, and the chloride concentrations in sweat were measured by mercurimetric titration. RESULTS: Four patients showed sweat chloride concentrations higher than 60 mmol/L. Reference interval was calculated as 1.4-44.5 mmol/L by analysis of the results of healthy volunteers (n=41). Four patients who exhibited high sweat chloride levels, had characteristic clinical features of cystic fibrosis and their diagnoses were confirmed either by repeated sweat chloride test or genetic analysis. CONCLUSIONS: Standardized sweat chloride test can be utilized as a useful diagnostic tool for cystic fibrosis in Koreans. In cases of sweat chloride levels higher than 40 mmol/L, the test should be repeated for the possible diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. All the confirmed Korean cases of cystic fibrosis showed sweat chloride level above 60 mmol/L.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Heterogeneous Spectrum of
CFTR Gene Mutations in Korean Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
Haiyoung Jung, Chang-Seok Ki, Won-Jung Koh, Kang-Mo Ahn, Sang-Il Lee, Jeong-Ho Kim, Jae Sung Ko, Jeong Kee Seo, Seung-Ick Cha, Eun-Sil Lee, Jong-Won Kim
Korean J Lab Med. 2011;31(3):219-224. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.3.219.
Reference
-
1.Andersen D., Hodges R. Celiac syndrome v. genetics of cystic fibrosis of the pancreas with a consideration of etiology. Am J Dis Child. 1946. 72:62–80.2.Tsui LC., Buchwald M., Barker D., Braman JC., Knowlton R., Schumm JW, et al. Cystic fibrosis locus defined by a genetically linked polymorphic DNA marker. Science. 1985. 230:1054–7.
Article3.Accurso FJ. Update in cystic fibrosis 2006. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007. 175:754–7.
Article4.World Health Organization. The molecular genetic epidemiology of cystic fibrosis: report of a joint meeting of WHO/ECFTN/ICF(M)A/ECFS Genoa, Italy, 19 June 2002: World Health Organization. 2004.5.Kosorok MR., Wei WH., Farrell PM. The incidence of cystic fibrosis. Stat Med. 1996. 15:449–62.
Article6.Yamashiro Y., Shimizu T., Oguchi S., Shioya T., Nagata S., Ohtsuka Y. The estimated incidence of cystic fibrosis in Japan. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1997. 24:544–7.
Article7.Moon HR., Ko TS., Ko YY., Choi JH., Kim YC. Cystic fibrosis–a case presented with recurrent bronchiolitis in infancy in a Korean male infant. J Korean Med Sci. 1988. 3:157–62.8.Strausbaugh SD., Davis PB. Cystic fibrosis: a review of epidemiology and pathobiology. Clin Chest Med. 2007. 28:279–88.
Article9.Di Sant'Agnese PA., Darling RC., Perera GA., Shea E. Abnormal electrolyte composition of sweat in cystic fibrosis of the pancreas; clinical significance and relationship to the disease. Pediatrics. 1953. 12:549–63.10.LeGrys VA. Sweat testing for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: practical considerations. J Pediatr. 1996. 129:892–7.
Article11.National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Sweat testing: sample collection and quantitative analysis; approved guideline-second edition, C34-A2. Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2000.12.Gibson LE., Cooke RE. A test for concentration of electrolytes in sweat in cystic fibrosis of the pancreas utilizing pilocarpine by iontophoresis. Pediatrics. 1959. 23:545–9.
Article13.Park SH., Lee HJ., Kim JH., Park CH. Cystic fibrosis: case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2002. 47:693–6. (박시현, 이현주, 김지혜, 박철희. 낭성섬유증: 증례보고. 대한방사선의학회지 2002;47: 693-6.).
Article14.Jang IS., Park CK., Jeon SC., Choi YW., Park DW., Kim YS, et al. Radiologic findings of cystic fibrosis in a Korean child at follow up study: case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2003. 49:503–6. (장일수, 박충기, 전석철, 최요원, 박동우, 김용수등. 한국의소아에서발생한낭성섬유증의방사선학적추적관찰소견: 증례보고. 대한방사선의학회지2003;49: 503-6.).
Article15.Ahn KM., Park HY., Lee JH., Lee MG., Kim JH., Kang IJ, et al. Cystic fibrosis in Korean children: a case report identified by a quantitative pilocarpine iontophoresis sweat test and genetic analysis. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:153–7.
Article16.Koh WJ., Ki CS., Kim JW., Kim JH., Lim SY. Report of a Korean patient with cystic fibrosis, carrying Q98R and Q220X mutations in the CFTR gene. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:563–6.
Article17.Schales O., Schales SS. A Simple and accurate method for the determination of chloride in biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1941. 140:879–84.
Article18.Korean Center for Disease Control. http://helpline.cdc.go.kr/web/main.html. (Updated on Jan. 2008.19.Rosenstein BJ., Cutting GR. The diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: a consensus statement. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Panel. J Pediatr. 1998. 132:589–95.20.Farrell PM., Koscik RE. Sweat chloride concentrations in infants homozygous or heterozygous for F508 cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics. 1996. 97:524–8.21.Shwachman H., Mohmoodian A. Quality of sweat test performance in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. Clin Chem. 1979. 25:158–61.
Article22.LeGrys VA., Wood RE. Incidence and implications of false-negative sweat test reports in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1988. 4:169–72.
Article23.Hardy JD., Davison SH., Higgins MU., Polycarpou PN. Sweat tests in the newborn period. Arch Dis Child. 1973. 48:316–8.
Article24.Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Patient Registry Annual Data Report 2005. Maryland: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation;2006.25.Cystic fibrosis foundation. http://www.cff.org/aboutCFFoundation/Locations/FindACareCenter/. (Updated on Jan. 2008.26.Mackay R., George P., Kirk J. Sweat testing for cystic fibrosis: A review of New Zealand laboratories. J Paediatr Child Health. 2006. 42:160–4.
Article27.LeGrys VA., Burnett RW. Current status of sweat testing in North America. Results of the College of American Pathologists needs assessment survey. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994. 118:865–7.28.Davis PB., Hubbard VS., Di Sant'Agnese PA. Low sweat electrolytes in a patient with cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1980. 69:643–6.
Article29.Zielenski J., O'Brien A., Tsui LC. (Eds.).Cystic Fibrosis Mutation Database. http://www.genet.sickkids.on.ca/cftr/StatisticsPage.html. (Updated on Mar. 2007.30.Groman JD., Meyer ME., Wilmott RW., Zeitlin PL., Cutting GR. Variant cystic fibrosis phenotypes in the absence of CFTR mutations. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:401–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cystic fibrosis: a case presented with recurrent bronchiolitis in infancy in a Korean male infant
- Cystic Fibrosis in Korean Children: A Case Report Identified by a Quantitative Pilocarpine Iontophoresis Sweat Test and Genetic Analysis
- Cystic fibrosis lung disease: Current perspectives
- Radiologic Findings of Cystic Fibrosis in a Korean Child at Follow Up Study: Case Report
- Novel CFTR Mutations in a Korean Infant with Cystic Fibrosis and Pancreatic Insufficiency