Korean J Ophthalmol.
2004 Dec;18(2):132-140. 10.3341/kjo.2004.18.2.132.
The Effects of Glucose on the Expression of MMP and TIMP in Cultured Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 121c Eye Hospital, Inje University, College of Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Inje University, College of Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Chung-Ang University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 754378
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2004.18.2.132
Abstract
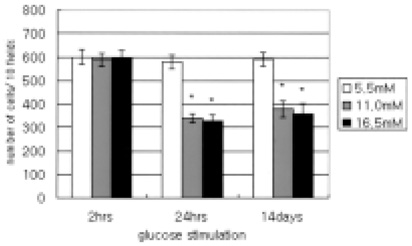
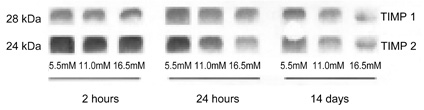
- This study evaluated the effects of glucose in human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells to investigate the cause of diabetic retinal complications. Human RPE cells were cultured in media containing 5.5 mM, 11.0 mM, and 16.5 mM D-glucose. The present study performed proliferation and migration assays, and conducted western blotting for the protein expression, as well as RT-PCR for the mRNA expression, of MMP-2 and -9, and TIMP-1 and -2. The results of the western blotting analysis showed that increasing glucose concentration significantly increased the expression of MMP-2 and -9, but significantly decreased the expression of TIMP-1 and -2. Moreover, the RT-PCR results indicated significant increases in the mRNA expression of MMP-2 and -9, as well as of TIMP-1 and -2, by raising glucose concentration. This study provides fundamental data for future research on the mechanism of retinal complication in diabetic patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Blotting, Western
Cell Movement
Cell Proliferation
Cells, Cultured
Comparative Study
Dose-Response Relationship, Drug
Glucose/*pharmacology
Humans
In Vitro
Matrix Metalloproteinases/genetics/*metabolism
Pigment Epithelium of Eye/*drug effects/enzymology
RNA, Messenger/metabolism
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Time Factors
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases/genetics/*metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Miller JW. Intraocular neovascularization. Retina. 2001. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;2427–2435.2. Battegay EJ. Angiogenesis: mechanistic insights, neovascular diseases, and therapeutic prospects. J Mol Med. 1995. 73:333–346.3. Michel JB, Maurice BL III. Pathogenic mechanisms of retinal detachment. Retina. 2001. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;1987–1993.4. Padgett LC, Lui GM, Werb Z, LaVail MM. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in the retinal pigment epithelium and interphotoreceptor matrix: vectorial secretion and regulation. Exp Eye Res. 1997. 64:927–938.5. Ahir A, Guo L, Hussain AA, Marshall J. Expression of metalloproteinases from human retinal pigment epithelial cells and their effects on the hydraulic conductivity of Bruch's membrane. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. 43:458–465.6. Sone H, Kawakami Y, Okuda Y, Kondo S, Hanatani M, Suzuki H, Yamashita K. Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced by long-term high glucose concentration and up-regulated by acute glucose deprivation in cultured bovine retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996. 221:193–198.7. Sang QX. Complex role of matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis. Cell Res. 1998. 8:1171–1177.8. Hoffmann S, Friedrichs U, Eichler W, Rosenthal A, Wiedemann P. Advanced glycation end products induce choroidal endothelial cell proliferation, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and VEGF upregulation in vitro. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2002. 240:996–1002.9. Uemura S, Matsushita H, Li W, Glassford AJ, Asagami T, Lee KH, Harrison DG, Tsao PS. Diabetes mellitus enhances vascular matrix metalloproteinase activity. Role of oxidative stress. Circ Res. 2001. 88:1291–1298.10. Grant MB, Caballero S, Tarnuzzer RW, Bass KE, Ljubimov AV, Spoerri PE, Galardy RE. Matrix metalloproteinase expression in human retinal microvascular cells. Diabetes. 1998. 47:1311–1317.11. Ravanti L, Kahari VM. Matrix metalloproteinases in wound repair. Int J Mol Med. 2000. 6:391–407.12. McCawley LJ, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases: multifunctional contributors to tumor progression. Mol Med Today. 2000. 6:149–156.13. Plantner JJ, Jiang C, Smine A. Increase in interphotoreceptor matrix gelatinase A (MMP-2) associated with age-related macular degeneration. Exp Eye Res. 1998. 67:637–645.14. Steen B, Sejersen S, Berglin L, Seregard S, Kvanta A. Matrix metalloproteinases and metalloproteinases inhibitors in choroidal neovascular membranes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998. 39:2194–2200.15. Eichler W, Friedrichs U, Thies A, Tratz C, Wiedemann P. Modulation of matrix metalloproteinase and TIMP-1 expression by cytokines in human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. 43:2767–2773.16. Jin M, Kashiwagi K, Iizuka Y, Tanaka Y, Imai M, Tsukahara S. Matrix metalloproteinases in human diabetic and nondiabetic vitreous. Retina. 2001. 21:28–33.17. Noda K, Ishida S, Inoue M, Obata K, Oguchi Y, Okada Y, Ikeda E. Production and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. 44:2163–2170.18. Salzmann J, Limb GA, Khaw PK, Gregor ZJ, Webster L, Chignell AH, Charteris DG. Matrix metalloproteinases and their natural inhibitors in fibrovascular membranes of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000. 84:1091–1096.19. Brown D, Hamdi H, Bahri S, Kenney MC. Characterization of an endogenous metalloproteinase in human vitreous. Curr Eye Res. 1994. 13:639–647.20. Nathan D. Kahn CR, Weir G, editors. Relationship between metabolic control and long-term complications of diabetes. Joslins' Diabetes. 1994. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;620–631.21. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Progression of retinopathy with intensive versus conventional treatment in the diabetes control and complication trial. Ophthalmology. 1995. 102:647–661.22. Brownlee M. Glycation products and the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Diabetes Care. 1992. 15:1835–1843.23. Beisswenger PJ, Makita Z, Curphey TJ, Moore LL, Jean S, Brinck-Johnsen T, Bucala R, Vlassara H. Formation of immunochemical advanced glycosylation end products precedes and correlates with early manifestations of renal and retinal disease in diabetes. Diabetes. 1995. 44:824–829.24. Sensi M, Pricci F, Pugliese G, De Rossi MG, Petrucci AF, Cristina A, Morano S, Pozzessere G, Valle E, Andreani D. Role of advanced glycation end-products (AGE) in late diabetic complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995. 28:9–17.25. Lu M, Kuroki M, Amano S, Tolentino M, Keough K, Kim I, Bucala R, Adamis AP. Advanced glycation end products increase retinal vascular endothelial growth factor expression. J Clin Invest. 1998. 101:1219–1224.26. Rellier N, Ruggiero D, Lecomte M, Lagarde M, Wiernsperger N. Advanced glycation end products induce specific glycoprotein alterations in retinal microvascular cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997. 235:281–285.27. Natarazan R, Bai W, Lanting L, Gonzales N, Nadler J. Effects of high glucose on vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1997. 273:2224–2231.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of 5-Fluorouraci1 on the Activity of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Vitro
- Culture of Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells on Collagen Membrane
- The Effects of Glucose Concentrations on Reactive Oxygen production and Cellular Activity in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Growth Patterns of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium in Vitro
- The Effect of Cigarette Smoking on the Expression of MMP-9, TIMP-1 and VEGF in Nasal Polyp Epithelial Cells and Fibroblasts