Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Oct;55(4):1261-1269. 10.4143/crt.2022.1444.
Clinical Significance of Combining Preoperative and Postoperative Albumin-Bilirubin Score in Colorectal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Pathology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Biostatistic Collaboration Unit, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2547800
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2022.1444
Abstract
- Purpose
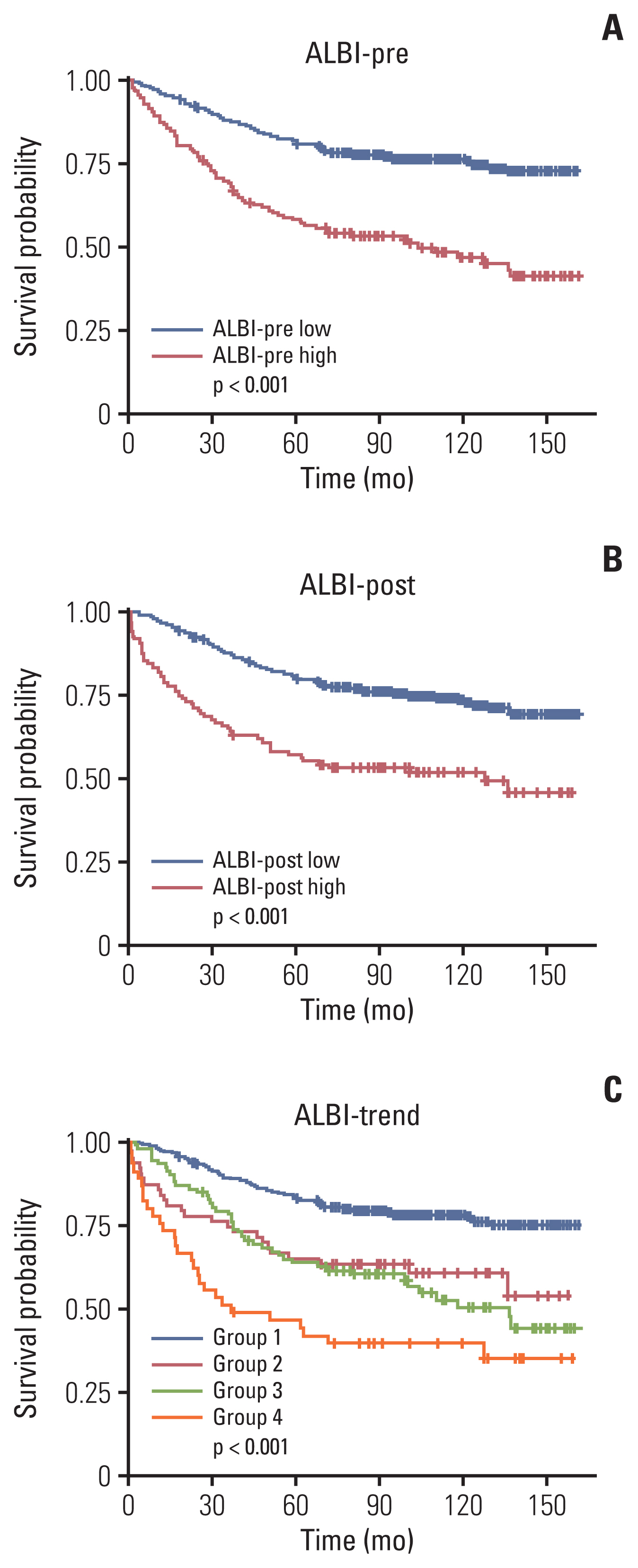
Albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score is a well-known prognostic factor for various diseases, including colorectal cancer (CRC). However, little is known about the significance of postoperative ALBI score changes in patients with CRC.
Materials and Methods
A total of 723 patients who underwent surgery were enrolled. Preoperative ALBI (ALBI-pre) and postoperative ALBI (ALBI-post) scores were divided into low and high score groups. ALBI-trend was defined as a combination of four groups comprising the low and high ALBI-pre and ALBI-post score groups. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to compare the overall survival (OS) between the different ALBI groups. The Cox proportional hazards model was used to examine the independent relevant factors of OS. Stratification performance was compared between the different ALBI groupings using Harrell’s concordance index (C-index).
Results
ALBI-pre, ALBI-post, and ALBI-trend score groups were significant prognostic factors of OS in the univariable analysis. However, multivariable analysis showed that ALBI-trend was an independent prognostic factor while ALBI-pre and ALBI-post were not. The C-index of ALBI-trend (0.622; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.587 to 0.655) was higher than that of ALBI-pre (0.589; 95% CI, 0.557 to 0.621; bootstrap mean difference, 0.033; 95% CI, 0.013 to 0.057) and ALBI-post (0.575; 95% CI, 0.545 to 0.605; bootstrap mean difference, 0.047; 95% CI, 0.024 to 0.074).
Conclusion
Combining ALBI-pre and ALBI-post scores is an independent prognostic factor of OS and shows superior predictive power compared to ALBI-pre or ALBI-post alone in patients with CRC.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Brody H. Colorectal cancer. Nature. 2015; 521:S1.
Article2. Kuipers EJ, Grady WM, Lieberman D, Seufferlein T, Sung JJ, Boelens PG, et al. Colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015; 1:15065.3. Varela C, Kim NK. Surgical treatment of low-lying rectal cancer: updates. Ann Coloproctol. 2021; 37:395–424.4. Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2014; 383:1490–502.5. Luo XJ, Zhao Q, Liu J, Zheng JB, Qiu MZ, Ju HQ, et al. Novel genetic and epigenetic biomarkers of prognostic and predictives in stage II/III colorectal cancer. Mol Ther. 2021; 29:587–96.6. An S, Shim H, Kim K, Kim B, Bang HJ, Do H, et al. Pretreatment inflammatory markers predicting treatment outcomes in colorectal cancer. Ann Coloproctol. 2022; 38:97–108.7. Feng Y, Luo J, Liu P, Liu L, Zhu Y, Cheng G, et al. Glasgow prognostic score and combined positive score for locally advanced rectal cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2022; 102:153–8.8. Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C, Satomura S, Teng M, Reeves HL, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:550–8.9. Koh HH, Cho ES, Lee JH, Shin SJ, Lee HS, Park EJ, et al. Association of albumin-bilirubin hrade and myosteatosis with its prognostic significance for patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022; 29:3868–76.10. Zhu C, Wang X, Yang X, Sun J, Pan B, Zhang W, et al. Preoperative albumin-bilirubin grade as a prognostic predictor in colorectal cancer patients who undergo radical resection. Cancer Manag Res. 2020; 12:12363–74.11. Kuo YH, Wang JH, Hung CH, Rau KM, Wu IP, Chen CH, et al. Albumin-bilirubin grade predicts prognosis of HCC patients with sorafenib use. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 32:1975–81.12. Ye L, Liang R, Zhang J, Chen C, Chen X, Zhang Y, et al. Postoperative albumin-bilirubin grade and albumin-bilirubin change predict the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Ann Transl Med. 2019; 7:367.13. Lin PT, Teng W, Jeng WJ, Chen WT, Hsieh YC, Huang CH, et al. Dynamic change of albumin-bilirubin score is good predictive parameter for prognosis in chronic hepatitis C-hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving transarterial chemoembolization. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12:665.14. Fragaki M, Sifaki-Pistolla D, Orfanoudaki E, Kouroumalis E. Comparative evaluation of ALBI, MELD, and Child-Pugh scores in prognosis of cirrhosis: is ALBI the new alternative? Ann Gastroenterol. 2019; 32:626–32.15. Wang J, Zhang Z, Yan X, Li M, Xia J, Liu Y, et al. Albumin-Bilirubin (ALBI) as an accurate and simple prognostic score for chronic hepatitis B-related liver cirrhosis. Dig Liver Dis. 2019; 51:1172–8.16. Matsukane R, Watanabe H, Hata K, Suetsugu K, Tsuji T, Egashira N, et al. Prognostic significance of pre-treatment ALBI grade in advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving immune checkpoint therapy. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:15057.17. Zhang TN, Yin RH, Wang LW. The prognostic and predictive value of the albumin-bilirubin score in advanced pancreatic cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99:e20654.18. Zhu C, Wang X, Chen S, Yang X, Sun J, Pan B, et al. Efficacy of the preoperative albumin-bilirubin grade for predicting survival and outcomes of postoperative chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2020; 12:11921–32.19. Tamas K, Walenkamp AM, de Vries EG, van Vugt MA, Beets-Tan RG, van Etten B, et al. Rectal and colon cancer: not just a different anatomic site. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015; 41:671–9.20. Pallan A, Dedelaite M, Mirajkar N, Newman PA, Plowright J, Ashraf S. Postoperative complications of colorectal cancer. Clin Radiol. 2021; 76:896–907.21. Menon V, Wang X, Greene T, Beck GJ, Kusek JW, Marcovina SM, et al. Relationship between C-reactive protein, albumin, and cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 42:44–52.22. Sheinenzon A, Shehadeh M, Michelis R, Shaoul E, Ronen O. Serum albumin levels and inflammation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021; 184:857–62.23. Miler I, Sima P, Vetvicka V, Indrova M, Slavikova M. The potential immunosuppressive effect of bilirubin. Allerg Immunol (Leipz). 1988; 34:177–84.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Albumin-Bilirubin Score Predicts Tolerability to Adjuvant S-1 Monotherapy after Curative Gastrectomy
- Clinical impact of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio of the 7th postoperative day on prognosis after laparoscopic colorectal cancer surgery
- Correlations between the Rate of Decrease in Preoperative Bilirubin and Postoperative Complications after Biliary Drainage for Distal Common Bile Duct Cancer
- Clinical significance and prognostic value of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in gastric cancer
- Low Serum Albumin Level, Male Sex, and Total Gastrectomy Are Risk Factors of Severe Postoperative Complications in Elderly Gastric Cancer Patients