J Gastric Cancer.
2019 Jun;19(2):183-192. 10.5230/jgc.2019.19.e15.
Albumin-Bilirubin Score Predicts Tolerability to Adjuvant S-1 Monotherapy after Curative Gastrectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterological Surgery (Surgery II), Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan. m-kanda@med.nagoya-u.ac.jp
- KMID: 2449939
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2019.19.e15
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Due to adverse events, dose reduction or withdrawal of adjuvant chemotherapy is required for some patients. To identify the predictive factors for tolerability to postoperative adjuvant S-1 monotherapy in gastric cancer (GC) patients, we evaluated the predictive values of blood indicators.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed 98 patients with pStage II/III GC who underwent postoperative adjuvant S-1 monotherapy. We retrospectively analyzed correlations between 14 parameters obtained from perioperative routine blood tests to assess their influence on the withdrawal of postoperative adjuvant S-1 monotherapy, within 6 months after discontinuation.
RESULTS
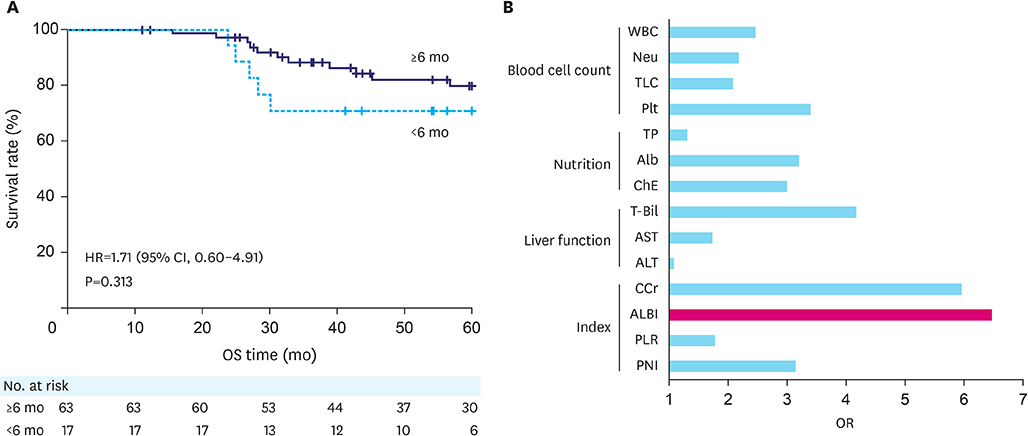
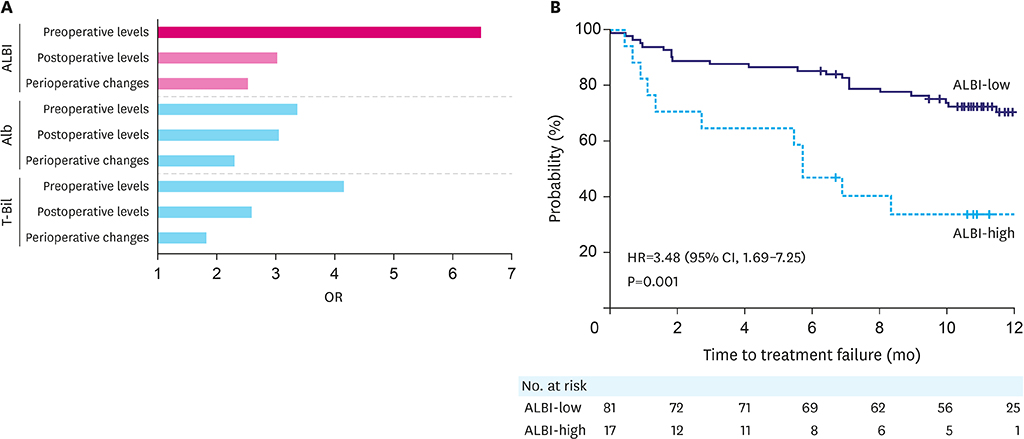
Postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy was discontinued in 21 patients (21.4%) within 6 months. Univariable analysis revealed that high preoperative albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) scores had the highest odds ratio (OR) for predicting the failure of adjuvant S-1 chemotherapy (OR, 6.47; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.08-20.1; cutoff value, -2.696). The high ALBI group had a significantly shorter time to failure of postoperative adjuvant S-1monotherapy (hazard ratio, 3.48; 95% CI, 1.69-7.25; P=0.001). Multivariable analysis identified high preoperative ALBI score as an independent prognostic factor for tolerability (OR, 10.3; 95% CI, 2.33-45.8; P=0.002).
CONCLUSIONS
Preoperative ALBI shows promise as an indicator associated with the tolerability of adjuvant S-1 monotherapy in patients with pStage II/III GC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article2. Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaguchi T, Kinoshita T, Fujii M, Nashimoto A, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral fluoropyrimidine. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:1810–1820.
Article3. André T, Tournigand C, Achille E, Tubiana-Mathieu N, Lledo G, Raoul Y, et al. Adjuvant treatment of colon cancer MOSAIC study's main results. Bull Cancer. 2006; 93:Suppl 1. S5–S9.4. Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Peto R, Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Pan HC, et al. Comparisons between different polychemotherapy regimens for early breast cancer: meta-analyses of long-term outcome among 100,000 women in 123 randomised trials. Lancet. 2012; 379:432–444.5. Sandra-Petrescu F, Herrle F, Burkholder I, Kienle P, Hofheinz RD. Influence of complete administration of adjuvant chemotherapy cycles on overall and disease-free survival in locally advanced rectal cancer: post hoc analysis of a randomized, multicenter, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18:369.
Article6. Yoshikawa T, Terashima M, Mizusawa J, Nunobe S, Nishida Y, Yamada T, et al. Four courses versus eight courses of adjuvant S-1 for patients with stage II gastric cancer (JCOG1104 [OPAS-1]): an open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 4:208–216.
Article7. Aoyama T, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi T, Kuwabara H, Mikayama Y, Ogata T, et al. Risk factors for 6-month continuation of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2013; 16:133–139.
Article8. Aoyama T, Yoshikawa T, Shirai J, Hayashi T, Yamada T, Tsuchida K, et al. Body weight loss after surgery is an independent risk factor for continuation of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:2000–2006.
Article9. Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C, Satomura S, Teng M, Reeves HL, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:550–558.
Article10. Bennett AV, Dueck AC, Mitchell SA, Mendoza TR, Reeve BB, Atkinson TM, et al. Mode equivalence and acceptability of tablet computer-, interactive voice response system-, and paper-based administration of the U.S. National Cancer Institute's Patient-Reported Outcomes version of the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (PRO-CTCAE). Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2016; 14:24.
Article11. Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2014 (ver. 4). Gastric Cancer. 2017; 20:1–19.12. Kanda M, Mizuno A, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Fujiwara M, Iwata N, et al. Nutritional predictors for postoperative short-term and long-term outcomes of patients with gastric cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3781.
Article13. Kanda M, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Uda H, Inaoka K, Tanaka Y, et al. Preoperative albumin-bilirubin grade predicts recurrences after radical gastrectomy in patients with pT2-4 gastric cancer. World J Surg. 2018; 42:773–781.
Article14. Andreatos N, Amini N, Gani F, Margonis GA, Sasaki K, Thompson VM, et al. Albumin-bilirubin score: predicting short-term outcomes including bile leak and post-hepatectomy liver failure following hepatic resection. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017; 21:238–248.
Article15. Ho SY, Liu PH, Hsu CY, Hsia CY, Su CW, Lee YH, et al. Comparison of twelve liver functional reserve models for outcome prediction in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing surgical resection. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:4773.
Article16. Ichikawa W. Prediction of clinical outcome of fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy for gastric cancer patients, in terms of the 5-fluorouracil metabolic pathway. Gastric Cancer. 2006; 9:145–155.
Article17. Maring JG, Groen HJ, Wachters FM, Uges DR, de Vries EG. Genetic factors influencing pyrimidine-antagonist chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics J. 2005; 5:226–243.
Article18. Joel SP, Shah R, Clark PI, Slevin ML. Predicting etoposide toxicity: relationship to organ function and protein binding. J Clin Oncol. 1996; 14:257–267.
Article19. Miura K, Konishi J, Miyake T, Makita M, Hojo A, Masaki Y, et al. A host-dependent prognostic model for elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncologist. 2017; 22:554–560.
Article20. Gong J, Cho M, Fakih M. Chemotherapy in patients with hepatobiliary cancers and abnormal hepatic function. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2017; 8:314–323.
Article21. Kanda M, Kodera Y, Sakamoto J. Updated evidence on adjuvant treatments for gastric cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 9:1549–1560.
Article22. Kanda M, Murotani K, Kobayashi D, Tanaka C, Yamada S, Fujii T, et al. Postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 alters recurrence patterns and prognostic factors among patients with stage II/III gastric cancer: a propensity score matching analysis. Surgery. 2015; 158:1573–1580.
Article23. Imamura H, Nishikawa K, Kishi K, Inoue K, Matsuyama J, Akamaru Y, et al. Effects of an oral elemental nutritional supplement on post-gastrectomy body weight loss in gastric cancer patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016; 23:2928–2935.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Actual 5-Year Nutritional Outcomes of Patients with Gastric Cancer
- Risk Factors for Gallbladder Stone Formation after Gastric Cancer Surgery
- Bilirubin Metabolism and Bilirubin Encephalopathy
- Nutritional Status Indicators Affecting the Tolerability of Postoperative Chemotherapy After Total Gastrectomy in Patients With Gastric Cancer
- The role of bilirubin to albumin ratio as a predictor for mortality in critically ill patients without existing liver or biliary tract disease