Ann Surg Treat Res.
2021 Jun;100(6):338-346. 10.4174/astr.2021.100.6.338.
Clinical significance and prognostic value of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in gastric cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmaceutics, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin, China
- 2Department of Research, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, China
- 3Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University, Guilin, China
- KMID: 2516227
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2021.100.6.338
Abstract
- Purpose
This study was aimed to evaluate the clinical significance and prognostic value of CRP/albumin ratio (CAR) in patients with gastric cancer.
Methods
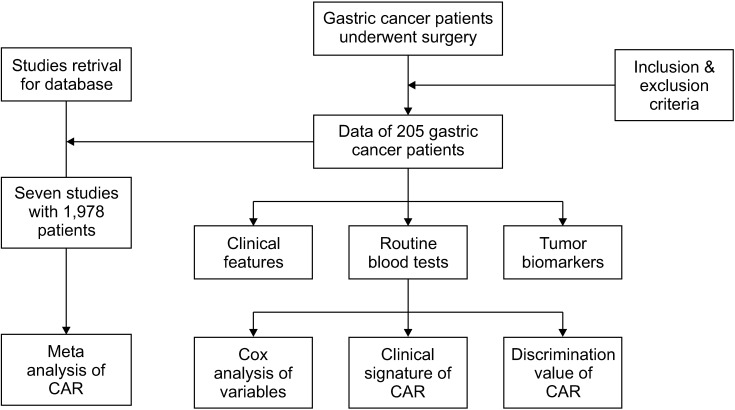
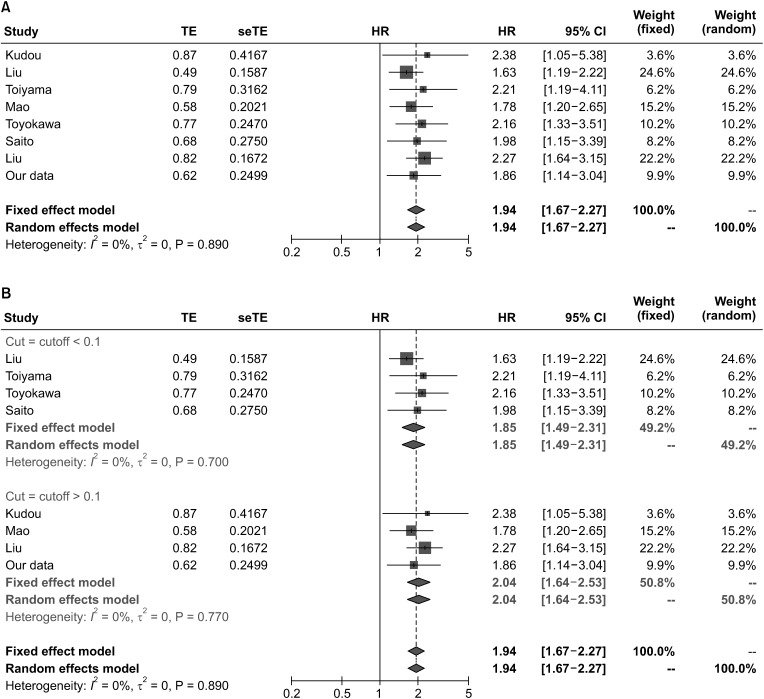
The data of 205 gastric cancer patients who underwent surgery was analyzed retrospectively. The association of CAR with the clinical features and prognostic value in gastric cancer was analyzed. The data of this study was combined with previous studies to further determine the prognostic value of CAR in patients with gastric cancer using a metaanalysis method.
Results
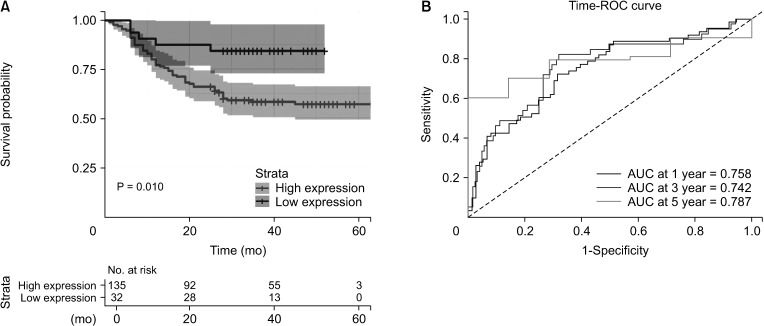
Cox analysis revealed that preoperative CAR was an independent prognosis indicator in patients with gastric cancer. High expression of CAR indicated a shorter survival time than in those with lower expression. CAR has a higher prognostic value in the 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival in patients with gastric cancer. CAR showed significant difference regarding the gastric cancer patients’ age, M stage, and clinical stage. The discriminate value of CAR in M stage of gastric cancer was high (area under the curve, 0.809). A meta-analysis combining previous data and our data showed that preoperative CAR demonstrated a significant association with the overall survival of patients with gastric cancer.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that preoperative CAR could serve as an important prognostic indicator in patients with gastric cancer.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424. PMID: 30207593.
Article2. Hundahl SA, Phillips JL, Menck HR. The National Cancer Data Base Report on poor survival of U.S. gastric carcinoma patients treated with gastrectomy: Fifth Edition American Joint Committee on Cancer staging, proximal disease, and the “different disease” hypothesis. Cancer. 2000; 88:921–932. PMID: 10679663.3. Feng F, Tian Y, Xu G, Liu Z, Liu S, Zheng G, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19-9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2017; 17:737. PMID: 29121872.
Article4. Tian SB, Yu JC, Kang WM, Ma ZQ, Ye X, Cao ZJ, et al. Combined detection of CEA, CA 19-9, CA 242 and CA 50 in the diagnosis and prognosis of resectable gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014; 15:6295–6300. PMID: 25124614.
Article5. Mellor KL, Powell AG, Lewis WG. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prognostic significance of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Rat io (NLR) af ter R0 gastrectomy for cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2018; 49:237–244. PMID: 29949048.6. Kim JH, Han DS, Bang HY, Kim PS, Lee KY. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic factor for overall survival in patients with gastric cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015; 89:81–86. PMID: 26236697.
Article7. Xu Z, Xu W, Cheng H, Shen W, Ying J, Cheng F, et al. The prognostic role of the platelet-lymphocytes ratio in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0163719. PMID: 27684077.
Article8. Tanaka H, Tamura T, Toyokawa T, Muguruma K, Kubo N, Sakurai K, et al. C-reactive protein elevation ratio as an early predictor of postoperative severe complications after laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2019; 19:114. PMID: 31429742.
Article9. Xu BB, Lu J, Zheng ZF, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, et al. The predictive value of the preoperative C-reactive proteinalbumin ratio for early recurrence and chemotherapy benefit in patients with gastric cancer after radical gastrectomy: using randomized phase III trial data. Gastric Cancer. 2019; 22:1016–1028. PMID: 30739259.
Article10. Ranzani OT, Zampieri FG, Forte DN, Azevedo LC, Park M. C-reactive protein/ albumin ratio predicts 90-day mortality of septic patients. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e59321. PMID: 23555017.11. YXMLLink_XYZlmaz EM, Kandemir A. Significance of red blood cell distribution width and C-reactive protein/albumin levels in predicting prognosis of acute pancreatitis. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2018; 24:528–531. PMID: 30516251.12. Wu J, Tan W, Chen L, Huang Z, Mai S. Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in patients with solid tumors: an updated systemic review and metaanalysis. Oncotarget. 2018; 9:13934–13947. PMID: 29568406.
Article13. Mao M, Wei X, Sheng H, Chi P, Liu Y, Huang X, et al. C-reactive protein/albumin and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratios and their combination predict overall survival in patients with gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017; 14:7417–7424. PMID: 29344182.
Article14. Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Prognostic significance of the preoperative ratio of C-Reactive protein to albumin and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in gastric cancer patients. World J Surg. 2018; 42:1819–1825. PMID: 29270656.
Article15. Toiyama Y, Shimura T, Yasuda H, Fujikawa H, Okita Y, Kobayashi M, et al. Clinical burden of C-reactive protein/albumin ratio before curative surgery for patients with gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016; 36:6491–6498. PMID: 27919972.
Article16. Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene F, Byrd DR, Brookland RK, Washington MK, et al. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. Cham, Switzerland: Springer;2017.17. Fu YJ, Li KZ, Bai JH, Liang ZQ. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio is a prognostic indicator in Asians with pancreatic cancers: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98:e18219. PMID: 31770284.18. Kudou K, Saeki H, Nakashima Y, Kamori T, Kawazoe T, Haruta Y, et al. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio is a poor prognostic factor of esophagogastric junction and upper gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 34:355–363. PMID: 30119141.
Article19. Liu X, Sun X, Liu J, Kong P, Chen S, Zhan Y, et al. Preoperative C-reactive protein/ albumin ratio predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for gastric cancer. Transl Oncol. 2015; 8:339–345. PMID: 26310380.20. Toyokawa T, Muguruma K, Tamura T, Sakurai K, Amano R, Kubo N, et al. Comparison of the prognostic impact and combination of preoperative inflammation-based and/or nutritional markers in patients with stage II gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2018; 9:29351–29364. PMID: 30034622.
Article21. Liu HC, Chen YJ, Xu YF, Xu ZH, Xu CY. Effect of preoperative ratio of C reactive protein to albumin on prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. Chin J Lab Diagn. 2018; 22:27–29.22. Abdi E, Latifi-Navid S, Zahri S, Yazdanbod A, Pourfarzi F. Risk factors predisposing to cardia gastric adenocarcinoma: insights and new perspectives. Cancer Med. 2019; 8:6114–6126. PMID: 31448582.
Article23. Liu Y, Chen S, Zheng C, Ding M, Zhang L, Wang L, et al. The prognostic value of the preoperative c-reactive protein/albumin ratio in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer. 2017; 17:285. PMID: 28431566.
Article24. Uchimoto T, Komura K, Fujiwara Y, Saito K, Tanda N, Matsunaga T, et al. Prognostic impact of C-reactive protein-albumin ratio for the lethality in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Med Oncol. 2019; 37:9. PMID: 31754918.
Article25. Khedher S, Fouthaili N, Maoui A, Lahiani S, Salem M, Bouzid K. The diagnostic and prognostic values of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin during bacterial infections in decompensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018; 2018:5915947. PMID: 31582968.
Article26. Chen IM, Johansen AZ, Dehlendorff C, Jensen BV, Bojesen SE, Pfeiffer P, et al. Prognostic value of combined detection of serum IL6, YKL-40, and C-reactive protein in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2020; 29:176–184. PMID: 31685562.
Article27. Lee SH, Kim KH, Choi CW, Kim SJ, Kim DH, Choi CI, et al. Reduction rate of C-reactive protein as an early predictor of postoperative complications and a reliable discharge indicator after gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2019; 97:65–73. PMID: 31384611.
Article28. Takeda K, Umezawa R, Takahashi N, Matsushita H, Kozumi M, Ishikawa Y, et al. Impact of change in serum albumin level during and after chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer. Esophagus. 2018; 15:190–197. PMID: 29951984.
Article29. Lim WS, Roh JL, Kim SB, Choi SH, Nam SY, Kim SY. Pretreatment albumin level predicts survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2017; 127:E437–E442. PMID: 28561532.
Article30. Dupré A, Malik HZ. Inf lammation and cancer: what a surgical oncologist should know. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018; 44:566–570. PMID: 29530345.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognostic prediction of colorectal cancer using the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio: the importance of inflammatory biomarkers and their association with long-term outcomes
- C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as prognostic score in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Evaluating prognostic significance of preoperative C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in older patients with pathological stage II or III colorectal cancer
- Clinical impact of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio of the 7th postoperative day on prognosis after laparoscopic colorectal cancer surgery
- Comparison of the Nutritional Status and the Acute Inflammatory Reaction between Laparoscopy-assisted Distal Gastrectomy and Conventional Open Distal Gastrectomy for Early Gastric Cancer