J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Oct;42(5):243-250. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.5.243.
C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as prognostic score in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea. kimchoms@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2356249
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.5.243
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Many studies have examined histopathological factors and various prognostic scores related to inflammation to predict outcomes. Here, we examined the prognostic value of the C-reactive protein/albumin (CRP/alb) ratio in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
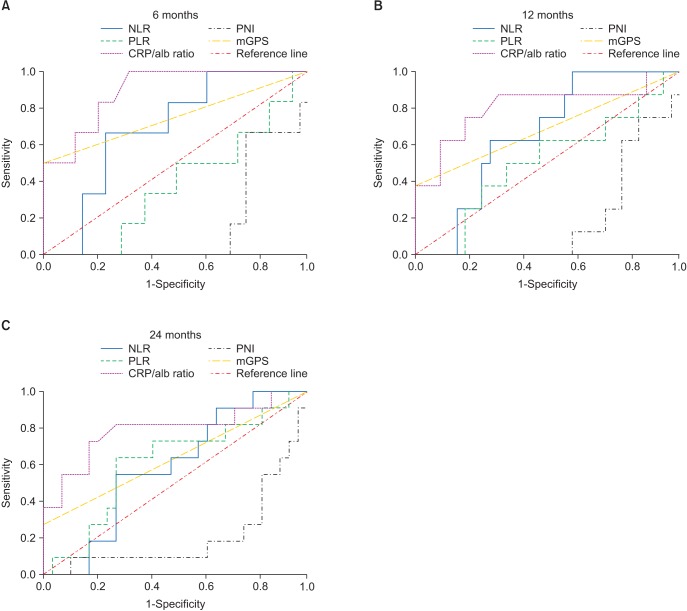
This retrospective study included 40 patients with OSCC. Using univariate and multivariate analyses, we focused on the correlation of the CRP/alb ratio with clinicopathological characteristics and with overall survival. We then compared five inflammation-based prognostic scores, CRP/alb ratio, modified Glasgow Prognostic Score (mGPS), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and prognostic nutritional index (PNI), based on receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
RESULTS
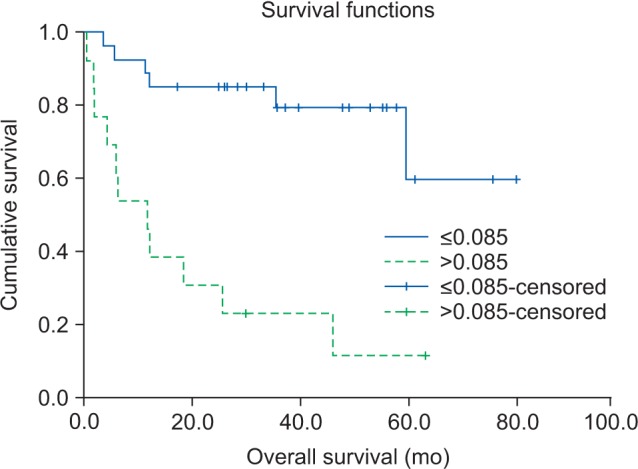
The optimal cut-off value for the CRP/alb ratio was 0.085. The group with a high CRP/alb ratio had a high TNM clinical stage (P=0.002) and larger primary tumors (P=0.029), with statistically significant differences in lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis. In addition, when the CRP/alb ratio was high, multivariate analysis showed a lower survival rate (P=0.002; hazard ratio=6.078), and the ROC curve showed more outstanding discriminatory ability regarding overall survival compared to other inflammation-based prognostic scores.
CONCLUSION
The CRP/alb ratio can be an independent prognostic factor when predicting prognosis in OSCC and has good prognostic ability.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Count of platelet and mean platelet volume score: serologic prognostic factor in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
Jae Woo Park, Chul-Hwan Kim, Yong Chan Ha, Moon Young Kim, Sung Min Park
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;43(5):305-311. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.5.305.
Reference
-
1. Sun JR, Kim SM, Seo MH, Kim MJ, Lee JH, Myoung H. Oral cancer incidence based on annual cancer statistics in Korea. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 38:20–28.
Article2. Lo Muzio L, Santarelli A, Panzarella V, Campisi G, Carella M, Ciavarella D, et al. Oral squamous cell carcinoma and biological markers: an update on the molecules mainly involved in oral carcinogenesis. Minerva Stomatol. 2007; 56:341–347. PMID: 17625491.3. Spencer KR, Ferguson JW, Wiesenfeld D. Current concepts in the management of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Aust Dent J. 2002; 47:284–289. quiz 351. PMID: 12587762.
Article4. Klug C, Berzaczy D, Voracek M, Millesi W. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy in the management of oral cancer: a review. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2008; 36:75–88. PMID: 18222699.
Article5. Genden EM, Ferlito A, Silver CE, Takes RP, Suárez C, Owen RP, et al. Contemporary management of cancer of the oral cavity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 267:1001–1017. PMID: 20155361.
Article6. Geum DH, Roh YC, Yoon SY, Kim HG, Lee JH, Song JM, et al. The impact factors on 5-year survival rate in patients operated with oral cancer. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 39:207–216. PMID: 24471047.
Article7. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008; 454:436–444. PMID: 18650914.
Article8. Sun K, Chen S, Xu J, Li G, He Y. The prognostic significance of the prognostic nutritional index in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014; 140:1537–1549. PMID: 24878931.
Article9. Paramanathan A, Saxena A, Morris DL. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the impact of pre-operative neutrophil lymphocyte ratio on long term outcomes after curative intent resection of solid tumours. Surg Oncol. 2014; 23:31–39. PMID: 24378193.
Article10. Gomez D, Farid S, Malik HZ, Young AL, Toogood GJ, Lodge JP, et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2008; 32:1757–1762. PMID: 18340479.
Article11. Pinato DJ, North BV, Sharma R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: the prognostic nutritional index (PNI). Br J Cancer. 2012; 106:1439–1445. PMID: 22433965.
Article12. Liu H, Wu Y, Wang Z, Yao Y, Chen F, Zhang H, et al. Pretreatment platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as a predictor of response to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy and prognosis for patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2013; 5:783–789. PMID: 24409356.13. Khandavilli SD, Ceallaigh PO, Lloyd CJ, Whitaker R. Serum C-reactive protein as a prognostic indicator in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2009; 45:912–914. PMID: 19502100.
Article14. Jin Y, Zhao L, Peng F. Prognostic impact of serum albumin levels on the recurrence of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2013; 68:686–693. PMID: 23778417.
Article15. Liu X, Sun X, Liu J, Kong P, Chen S, Zhan Y, et al. Preoperative C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for gastric cancer. Transl Oncol. 2015; 8:339–345. PMID: 26310380.
Article16. Zhou T, Zhan J, Hong S, Hu Z, Fang W, Qin T, et al. Ratio of C-reactive protein/albumin is an inflammatory prognostic score for predicting overall survival of patients with small-cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:10481. PMID: 26084991.
Article17. Wei XL, Wang FH, Zhang DS, Qiu MZ, Ren C, Jin Y, et al. A novel inflammation-based prognostic score in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio. BMC Cancer. 2015; 15:350. PMID: 25934640.
Article18. Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N, Iwaku A, Oishi M, Tanaka K, et al. The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, a novel inflammation-based prognostic score, predicts outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015; 22:803–810. PMID: 25190127.
Article19. Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010; 17:1471–1474. PMID: 20180029.
Article20. Budczies J, Klauschen F, Sinn BV, Győrffy B, Schmitt WD, Darb-Esfahani S, et al. Cutoff Finder: a comprehensive and straightforward Web application enabling rapid biomarker cutoff optimization. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e51862. PMID: 23251644.
Article21. Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:e493–e503. PMID: 25281468.
Article22. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011; 144:646–674. PMID: 21376230.
Article23. Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001; 357:539–545. PMID: 11229684.
Article24. Allavena P, Germano G, Marchesi F, Mantovani A. Chemokines in cancer related inflammation. Exp Cell Res. 2011; 317:664–673. PMID: 21134366.
Article25. Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ, David M, Fabra R, Trullenque R, Heinrich PC. Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6. Hepatology. 1990; 12:1179–1186. PMID: 1699862.
Article26. Gallo O, Gori AM, Attanasio M, Martini F, Giusti B, Brunelli T, et al. Interleukin-6 and acute-phase proteins in head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1995; 252:159–162. PMID: 7544987.
Article27. Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM. C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest. 2003; 111:1805–1812. PMID: 12813013.
Article28. Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002; 420:860–867. PMID: 12490959.
Article29. Nozoe T, Saeki H, Sugimachi K. Significance of preoperative elevation of serum C-reactive protein as an indicator of prognosis in esophageal carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2001; 182:197–201. PMID: 11574097.
Article30. Gockel I, Dirksen K, Messow CM, Junginger T. Significance of preoperative C-reactive protein as a parameter of the perioperative course and long-term prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:3746–3750. PMID: 16773693.
Article31. von Meyenfeldt M. Cancer-associated malnutrition: an introduction. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2005; 9(Suppl 2):S35–S38. PMID: 16437756.
Article32. Gupta D, Lis CG. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: a systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr J. 2010; 9:69. PMID: 21176210.
Article33. Alberici Pastore C, Paiva Orlandi S, González MC. Association between an inflammatory-nutritional index and nutritional status in cancer patients. Nutr Hosp. 2013; 28:188–193. PMID: 23808449.34. Roxburgh CS, McMillan DC. Cancer and systemic inflammation: treat the tumour and treat the host. Br J Cancer. 2014; 110:1409–1412. PMID: 24548867.
Article35. Metgud R, Patel S. Serum and salivary levels of albumin as diagnostic tools for oral pre-malignancy and oral malignancy. Biotech Histochem. 2014; 89:8–13. PMID: 23738795.
Article36. Rachidi S, Wallace K, Wrangle JM, Day TA, Alberg AJ, Li Z. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and overall survival in all sites of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2016; 38(Suppl 1):E1068–E1074. PMID: 26040762.
Article37. Farhan-Alanie OM, McMahon J, McMillan DC. Systemic inflammatory response and survival in patients undergoing curative resection of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 53:126–131. PMID: 25440150.
Article38. Fang HY, Huang XY, Chien HT, Chang JT, Liao CT, Huang JJ, et al. Refining the role of preoperative C-reactive protein by neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:2690–2699. PMID: 23619955.
Article39. Fairclough E, Cairns E, Hamilton J, Kelly C. Evaluation of a modified early warning system for acute medical admissions and comparison with C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a predictor of patient outcome. Clin Med (Lond). 2009; 9:30–33. PMID: 19271597.
Article40. Ranzani OT, Zampieri FG, Forte DN, Azevedo LC, Park M. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts 90-day mortality of septic patients. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e59321. PMID: 23555017.
Article41. Xu XL, Yu HQ, Hu W, Song Q, Mao WM. A novel inflammation-based prognostic score, the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts the prognosis of patients with operable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0138657. PMID: 26390126.
Article42. Proctor MJ, Horgan PG, Talwar D, Fletcher CD, Morrison DS, McMillan DC. Optimization of the systemic inflammation-based Glasgow prognostic score: a Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Cancer. 2013; 119:2325–2332. PMID: 23575969.43. Proctor MJ, Morrison DS, Talwar D, Balmer SM, O'Reilly DS, Foulis AK, et al. An inflammation-based prognostic score (mGPS) predicts cancer survival independent of tumour site: a Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Br J Cancer. 2011; 104:726–734. PMID: 21266974.
Article44. Shafique K, Proctor MJ, McMillan DC, Leung H, Smith K, Sloan B, et al. The modified Glasgow prognostic score in prostate cancer: results from a retrospective clinical series of 744 patients. BMC Cancer. 2013; 13:292. PMID: 23768149.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Count of platelet and mean platelet volume score: serologic prognostic factor in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Diagnostic problem of squamous papilloma and oral mucosa malignancy
- A clinical study on squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity ofKorean
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mimicking Herpes Simplex on the Lip
- Synchronous thyroid carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma: A case report