Prog Med Phys.
2023 Sep;34(3):33-39. 10.14316/pmp.2023.34.3.33.
Initial Dosimetry of a Prototype Ultra-High Dose Rate Electron-Beam Irradiator for FLASH RT Preclinical Studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2546689
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2023.34.3.33
Abstract
- Purpose
FLASH radiotherapy (RT) using ultra-high dose rate (>40 Gy/s) radiation is being studied worldwide. However, experimental studies such as preclinical studies using small animals are difficult to perform due to the limited availability of irradiation devices and methods for generating a FLASH beam. In this paper, we report the initial dosimetry results of a prototype electron linear accelerator (LINAC)-based irradiation system to perform ultra-high dose rate (UHDR) preclinical experiments.
Methods
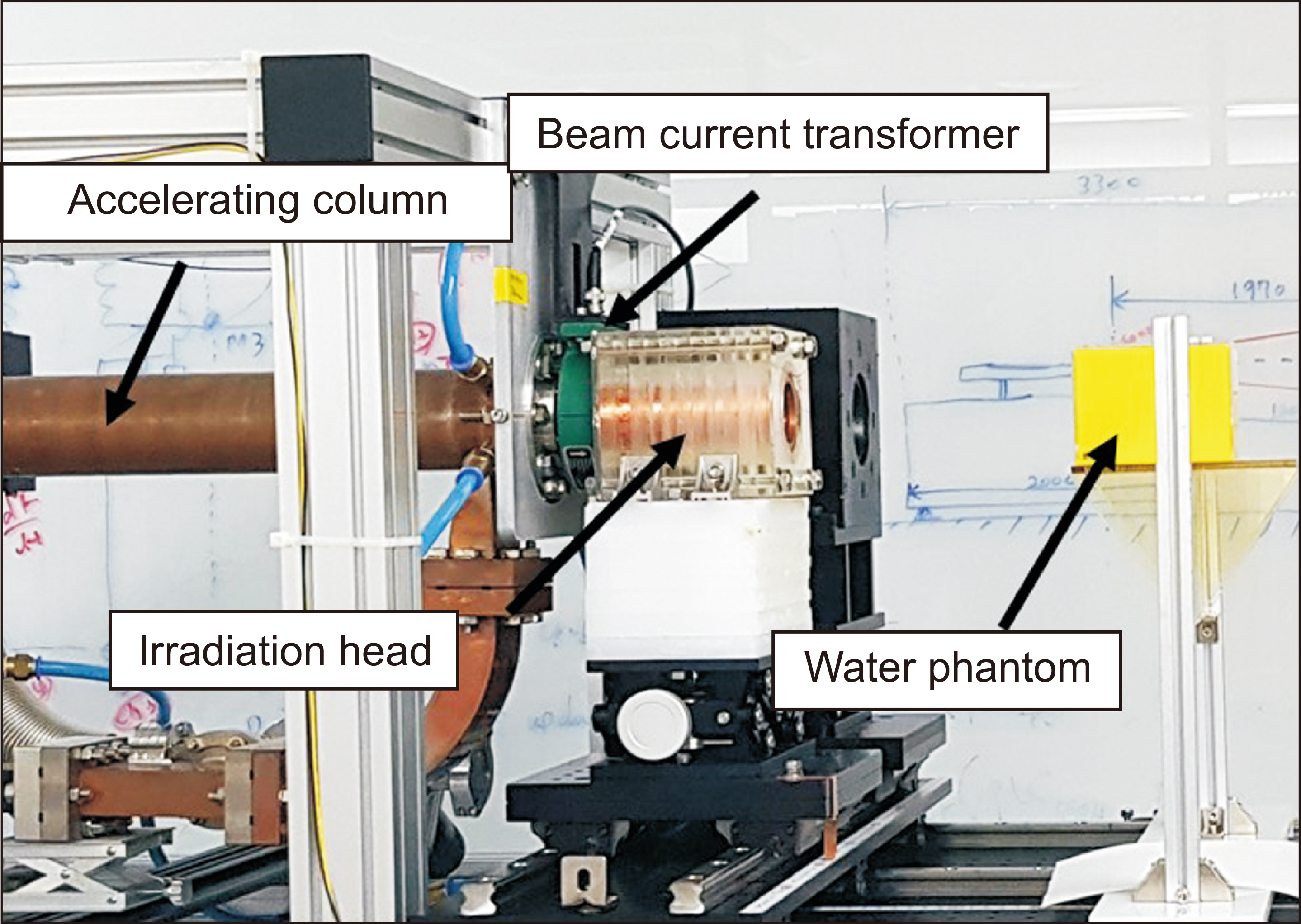
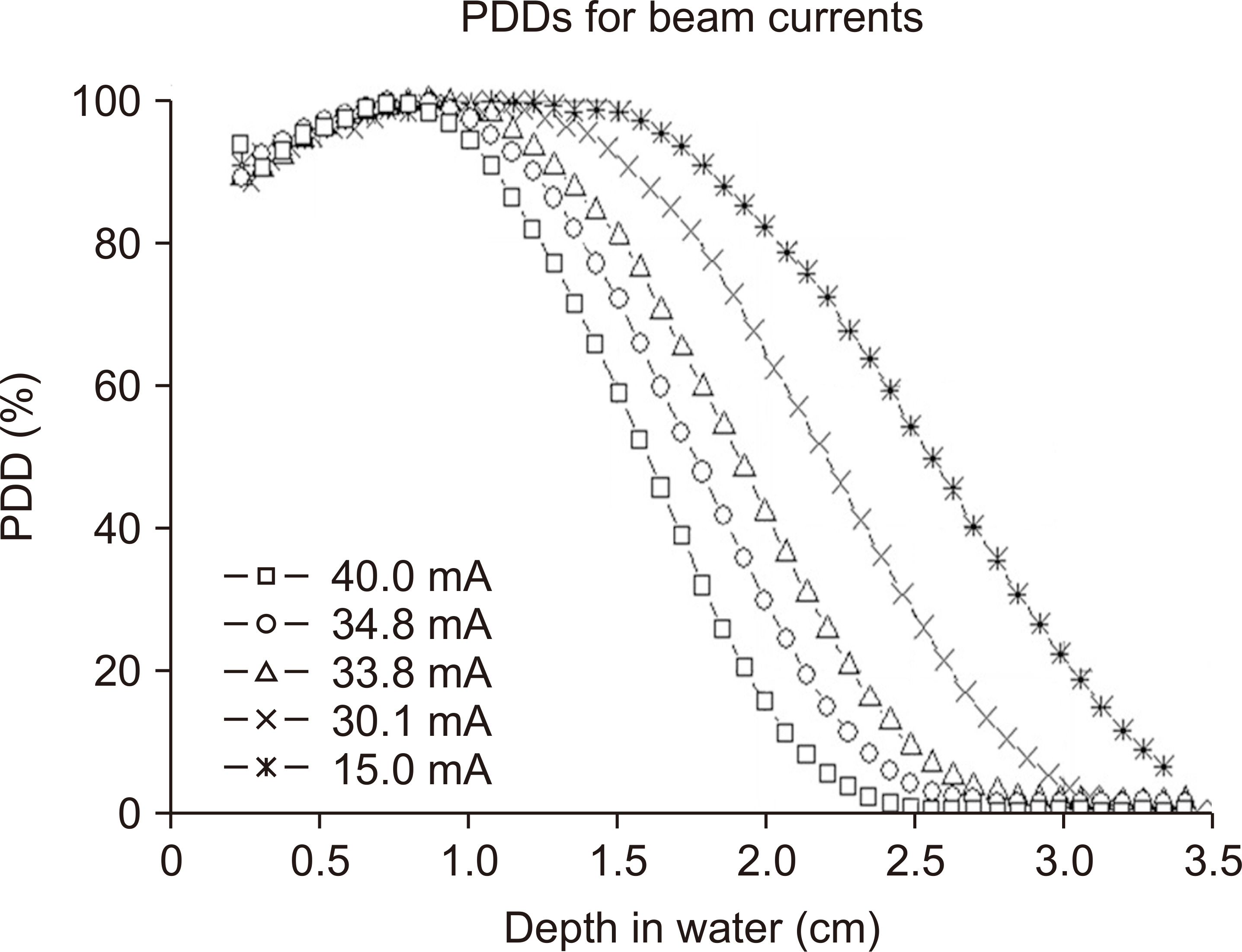
The present study used the prototype electron LINAC developed by the Research Center of Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences (DIRAMS) in Korea. We investigated the beam current dependence of the depth dose to determine the optimal beam current for preclinical experiments. The dose rate in the UHDR region was measured by film dosimetry.
Results
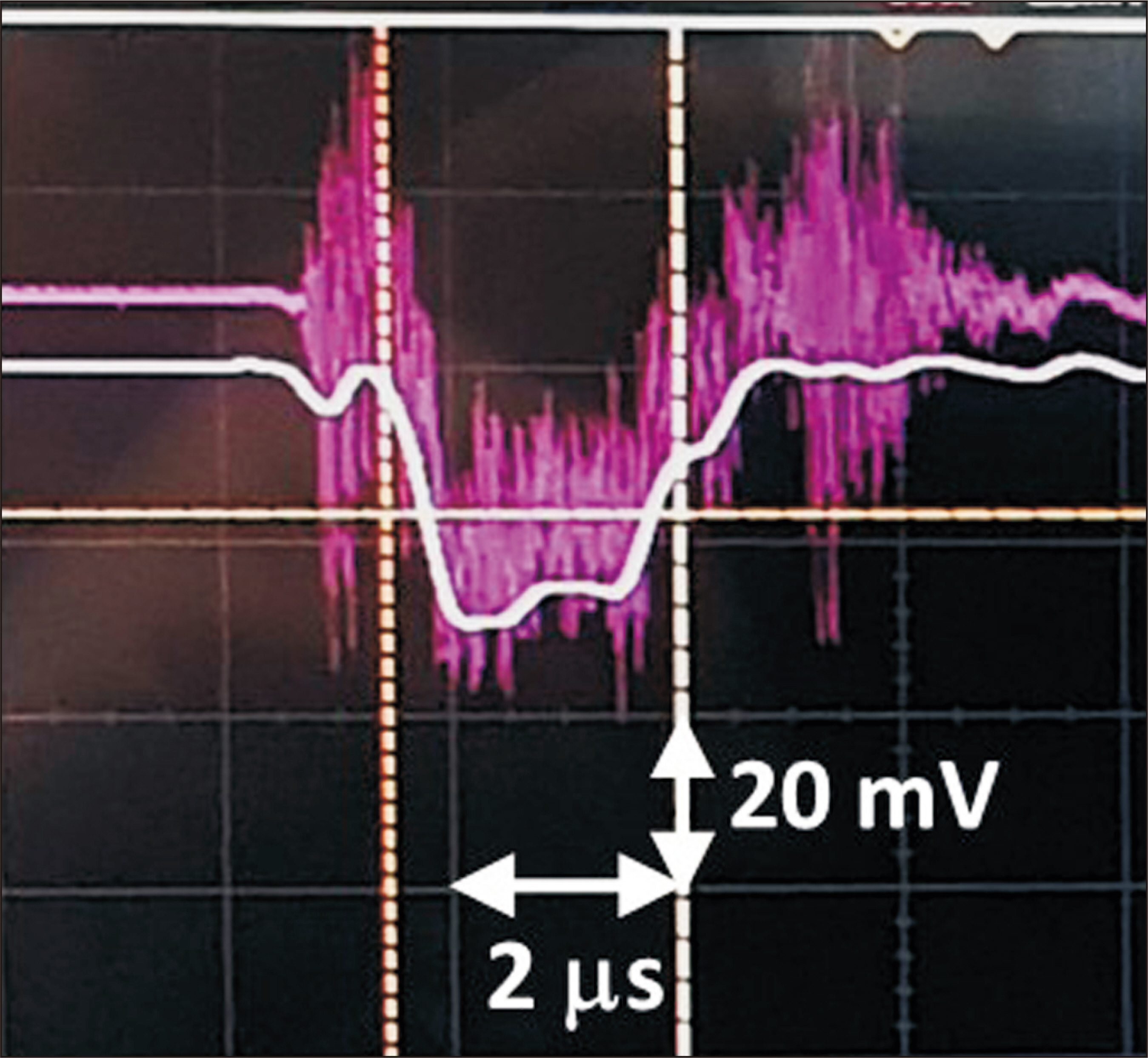
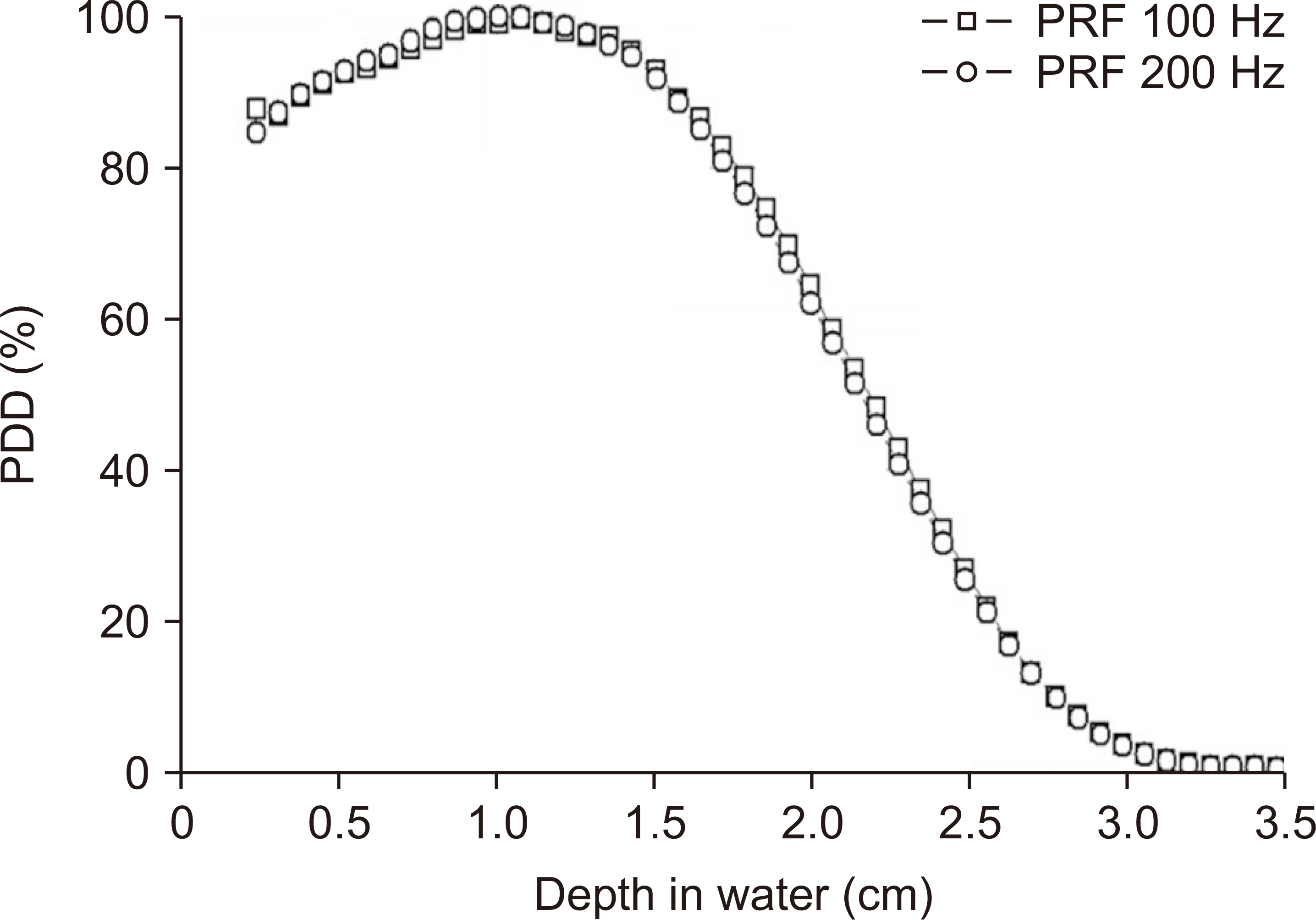
Depth dose measurements showed that the optimal beam current for preclinical experiments was approximately 33 mA, corresponding to a mean energy of 4.4 MeV. Additionally, the average dose rates of 80.4 Gy/s and 162.0 Gy/s at a source-to-phantom surface distance of 30 cm were obtained at pulse repetition frequencies of 100 Hz and 200 Hz, respectively. The dose per pulse and instantaneous dose rate were estimated to be approximately 0.80 Gy and 3.8×10 5 Gy/s, respectively.
Conclusions
Film dosimetry verified the appropriate dose rates to perform FLASH RT preclinical studies using the developed electron-beam irradiator. However, further research on the development of innovative beam monitoring systems and stabilization of the accelerator beam is required.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Friedl AA, Prise KM, Butterworth KT, Montay-Gruel P, Favaudon V. 2022; Radiobiology of the FLASH effect. Med Phys. 49:1993–2013. DOI: 10.1002/mp.15184. PMID: 34426981.
Article2. Schüler E, Acharya M, Montay-Gruel P, Loo BW Jr, Vozenin MC, Maxim PG. 2022; Ultra-high dose rate electron beams and the FLASH effect: from preclinical evidence to a new radiotherapy paradigm. Med Phys. 49:2082–2095. DOI: 10.1002/mp.15442. PMID: 34997969. PMCID: PMC9032195.
Article3. Romano F, Bailat C, Jorge PG, Lerch MLF, Darafsheh A. 2022; Ultra-high dose rate dosimetry: challenges and opportunities for FLASH radiation therapy. Med Phys. 49:4912–4932. DOI: 10.1002/mp.15649. PMID: 35404484. PMCID: PMC9544810.
Article4. Lempart M, Blad B, Adrian G, Bäck S, Knöös T, Ceberg C, et al. 2019; Modifying a clinical linear accelerator for delivery of ultra-high dose rate irradiation. Radiother Oncol. 139:40–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.01.031. PMID: 30755324.
Article5. Petersson K, Jaccard M, Germond JF, Buchillier T, Bochud F, Bourhis J, et al. 2017; High dose-per-pulse electron beam dosimetry - a model to correct for the ion recombination in the Advanced Markus ionization chamber. Med Phys. 44:1157–1167. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12111. PMID: 28094853.
Article6. Jeong DH, Lee M, Lim H, Kang SK, Jang KW. 2020; High-dose-rate electron-beam dosimetry using an Advanced Markus chamber with improved ionrecombination corrections. Prog Med Phys. 31:145–152. DOI: 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.145.
Article7. Kim SH, Park B, Yang HR, Jang SD, Son YG, Park SJ, et al. 2007. Design of C-band standing-wave accelerating structure. Paper presented at: APAC 2007, Raja Ramanna Centre for Advanced Technology (RRCAT); 2007 Jan 29-Feb 2. Indore;India: 440–442.8. Kim SH, Kang SK, Lee DE, Lee SJ, Kim HC, Yi J, et al. 2020; Fabrication and cold test of a 9-MeV C-band accelerating column. J Korean Phys Soc. 76:617–621. DOI: 10.3938/jkps.76.617.
Article9. Lim H, Kang SK, Kim HC, Kim SH, Lee DE, Lee SJ, et al. 2020; Compact integration and RF commissioning of the C-band 9-MeV electron linear accelerator at the Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences. J Korean Phys Soc. 76:622–627. DOI: 10.3938/jkps.76.622.
Article10. Lim H, Jeong DH, Jang KW, Lee K, Kang SK, Lee SJ, et al. 2021. Development of flash control system for implementation of ultra-high dose rate electron beams using a C-band linear accelerator. Paper presented at: Abstracts of the FRPT 2021 Conference; 2021 Dec 1-3. Virtual conference;S107. DOI: 10.1016/S1120-1797(22)01685-4.
Article11. Jeong DH, Lee M, Lim H, Kang SK, Lee SJ, Kim HC, et al. 2021; Electron beam scattering device for FLASH preclinical studies with 6-MeV LINAC. Nucl Eng Technol. 53:1289–1296. DOI: 10.1016/j.net.2020.09.019.
Article12. Andreo P, Burns DT, Hohlfeld K, Huq MS, Kanai T, Laitano F, et al. 2006. IAEA TRS-398. Absorbed dose determination in external beam radiotherapy: an international code of practice for dosimetry based on standards of absorbed dose to water. 12th ed. International Atomic Energy Agency;Vienna: p. 75–90. DOI: 10.1016/s0167-8140(01)80920-8.13. Lim H, Lee M, Kim MY, Yi J, Lee M, Kang SK, et al. 2016; Measurement of energy parameters for electron gun heater currents and output dose rate for electron beams from a prototype linac. Prog Med Phys. 27:25–30. DOI: 10.14316/pmp.2016.27.1.25.
Article14. Buaphad P, Kim YJ, Cha SS, Lee BC, Cha HK, Ha JH, et al. 2016. 6/9 MeV S-band standing wave accelerating structure for container X-ray inspection system at RTX. Paper presented at: Proceedings of IPAC2016; 2016 May 8-13. Busan, Korea: 1924–1926.15. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). 1987. IAEA TRS-277. Absorbed dose determination in photon and electron beams. IAEA;Vienna: DOI: 10.1016/s0167-8140(01)80920-8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- FLASH Radiotherapy: A FLASHing Idea to Preserve Neurocognitive Function
- Measurement of Energy Parameters for Electron Gun Heater Currents and Output Dose Rate for Electron Beams from a Prototype Linac
- FLASH radiotherapy: bridging revolutionary mechanisms and clinical frontiers in cancer treatment – a narrative review
- High Energy Electron Dosimetry by Alanine/ESR Spectroscopy
- Field size and dose distribution of electron beam