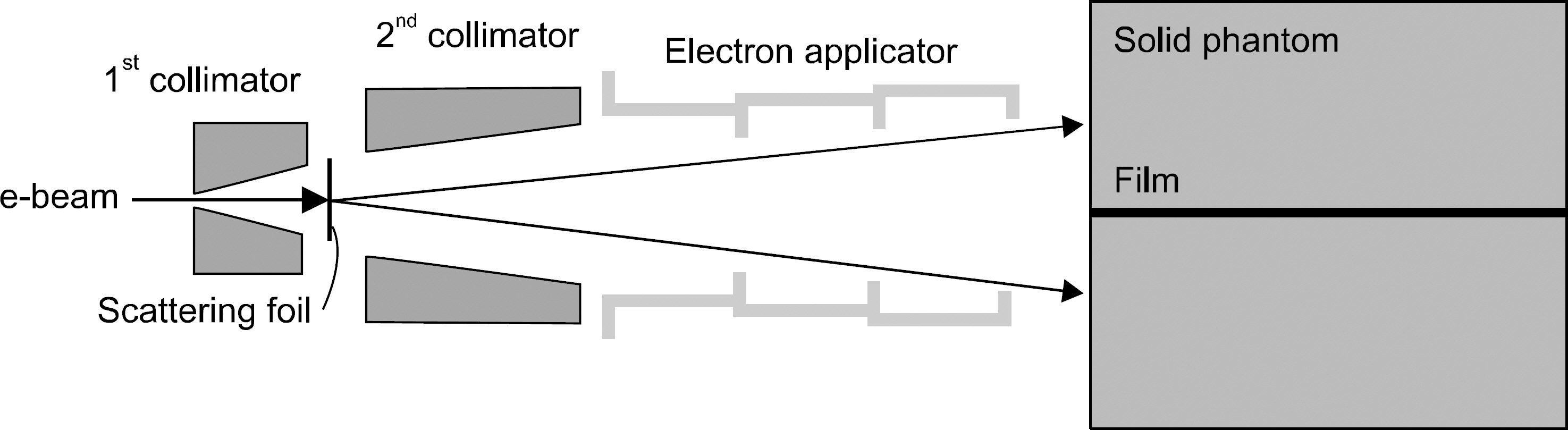
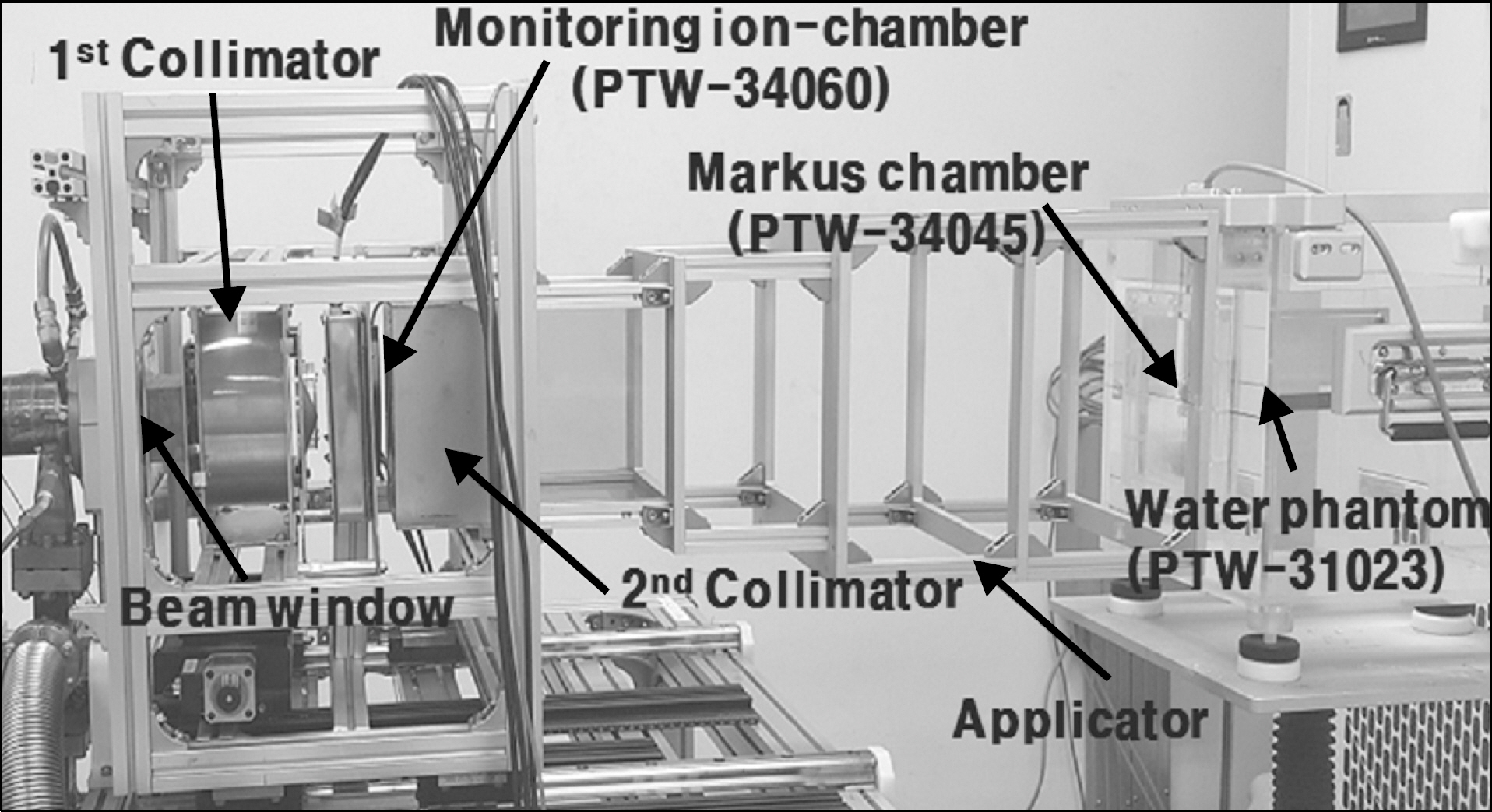
Measurement of Energy Parameters for Electron Gun Heater Currents and Output Dose Rate for Electron Beams from a Prototype Linac
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center, Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea. physics7@empas.com
- KMID: 2161935
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.1.25
Abstract
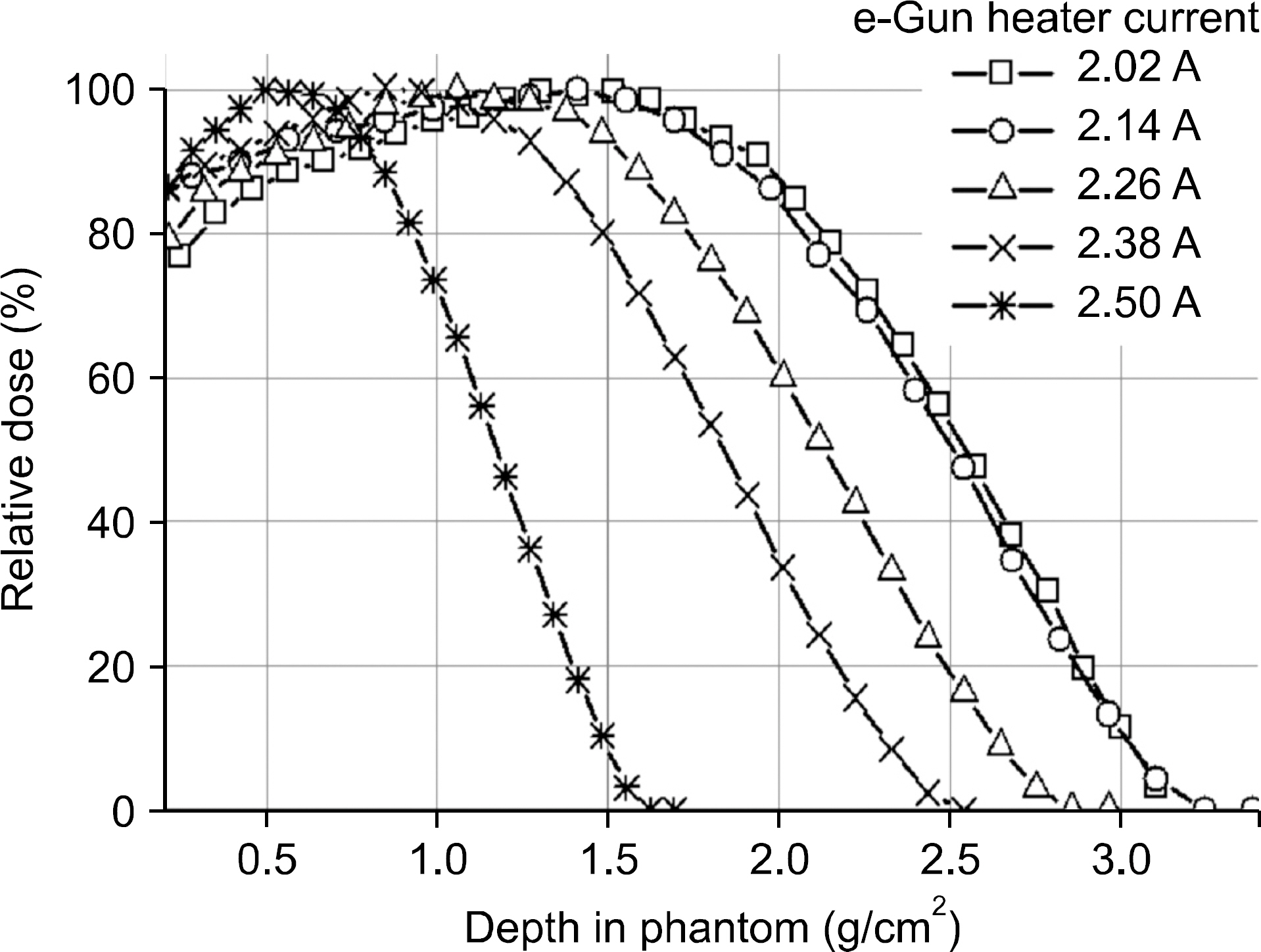
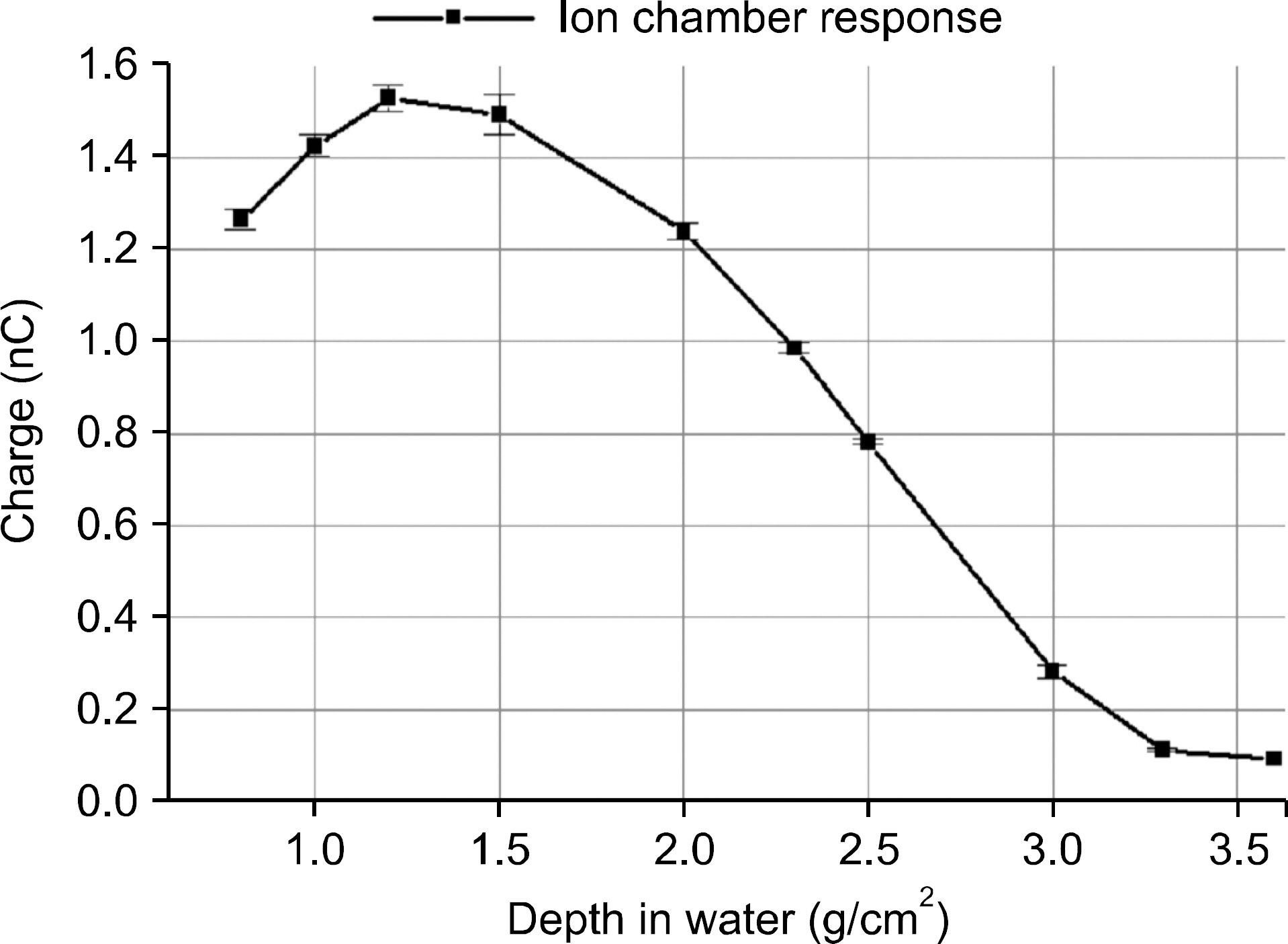
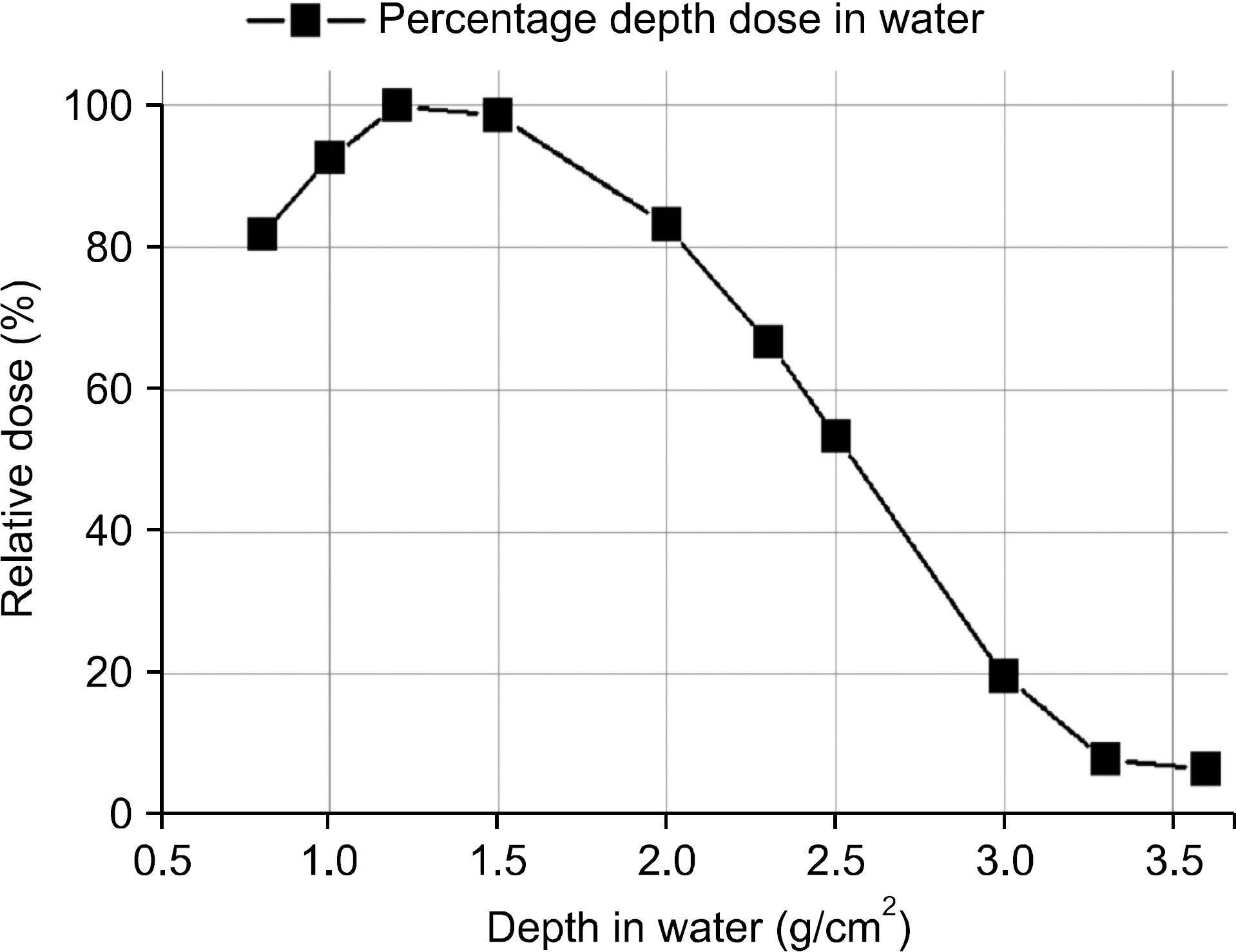
- The dosimetric characteristics were experimentally evaluated for electron beams from the prototype linac developed for radiotherapy units. This paper focuses on the electron beam output and energy variations as a function of electron gun heater current. The electron energy was derived from its mean and most probable energies measured by film dosimetry. The electron beam output at the maximum electron energy was measured with the plane parallel ionization chamber in water using TRS-398 dosimetry protocol. The mean energy and the most probable energy of the electron beam were 6.54~3.31 MeV and 5.94~2.80 MeV at electron gun current of 2.02~2.50 A respectively. The output dose rate for an electron beam of mean energy 6.54 MeV was 5.41 Gy/min ±1.5% at the reference depth in water.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Development of a Wide Dose-Rate Range Electron Beam Irradiation System for Pre-Clinical Studies and Multi-Purpose Applications Using a Research Linear Accelerator
Kyoung Won Jang, Manwoo Lee, Heuijin Lim, Sang Koo Kang, Sang Jin Lee, Jung Kee Kim, Young Min Moon, Jin Young Kim, Dong Hyeok Jeong
Prog Med Phys. 2020;31(2):9-19. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.2.9.High-Dose-Rate Electron-Beam Dosimetry Using an Advanced Markus Chamber with Improved Ion-Recombination Corrections
Dong Hyeok Jeong, Manwoo Lee, Heuijin Lim, Sang Koo Kang, Kyoung Won Jang
Prog Med Phys. 2020;31(4):145-152. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.145.Electron Energy Distribution for a Research Electron LINAC
Heuijin Lim, Manwoo Lee, Jungyu Yi, Sang Koo Kang, Me Young Kim, Dong Hyeok Jeong
Prog Med Phys. 2017;28(2):49-53. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2017.28.2.49.Initial Dosimetry of a Prototype Ultra-High Dose Rate Electron-Beam Irradiator for FLASH RT Preclinical Studies
Hyun Kim, Heuijin Lim, Sang Koo Kang, Sang Jin Lee, Tae Woo Kang, Seung Wook Kim, Wung-Hoa Park, Manwoo Lee, Kyoung Won Jang, Dong Hyeok Jeong
Prog Med Phys. 2023;34(3):33-39. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2023.34.3.33.
Reference
-
References
1. David IT, John BT. Backtothefuture: thehistoryanddevel-opmentoftheclinicallinearaccelerator.PhysMedBiol. 51:R343–R362. 2006.2. www.kirams.re.kr/khima3. Kim S, Kang SK, Rhee DJ, et al. :. MeasurementofElectron BeamOutputforthe PrototypeCompactLinac,Progressin MedicalPhysics. 26(1):1–5. 2015.4. Yi J, Lee M, Lee M, et al. :. FabricationandHighpowerRF testofaC-bandStanding-waveAcceleratingStructurefor MedicalApplication,ICABU(InternationalConferenceonAccele-ratorsandBeamUtilizations)Proceeding. 134–134. 2015.5. Scott EVB. AnIntroductiontoMassSpectrometry, Widner University, PA, USA. 1998.6. TRS-277. AbsorbedDoseDeterminationinPhotonand ElectronBeams: AnInternationalCodeofPractice. International Atomic Energy Agency;Vienna: 1997.7. Li A, Wen D, Chen , et al. :. Astudyofdosimetrycharacteristics ofGAFDM-1260radiochromicFilms,RadPhysChem. 57:103–113. 2000.8. TRS-398. Absorbeddosedeterminationinexternalbeamra-diotherapy: aninternationalcodeofpracticefordosimetrybased onstandardsofabsorbeddosetowater. International Atomic Energy Agency;Vienna: 2000.9. Zink K, Wulff J. MonteCarlocalculationsofbeamqualitycor-rectionfactors for electron dosimetry with a parallel-plate Roos chamber,PhysMedBiol. 53:1595–1607. 2008.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Measurement of Electron Beam Output for the Prototype Compact Linac
- A study on dose distribution of small irradiation field in the electron therapy
- Field size and dose distribution of electron beam
- Comparison of Electron Beam Dosimetries by Means of Several Kinds of Dosimeters
- A Study on the Effect of Field Shaping on Dose Distribution of Electron Beams