J Stroke.
2023 Sep;25(3):371-377. 10.5853/jos.2023.00668.
Intravenous Tenecteplase for Acute Ischemic Stroke Within 4.5–24 Hours of Onset (ROSE-TNK): A Phase 2, Randomized, Multicenter Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, China
- 2Department of Neurology, Liaoning Health Industry Group Fukuang General Hospital, Fushun, China
- 3Department of Neurology, Lvshunkou Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Dalian, China
- 4Department of Neurology, Liaoning Health Industry Group Fuxinkuang General Hospital, Fuxin, China
- 5Department of Neurology, Haicheng Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Haicheng, China
- 6Department of Neurology, Huludao Second People’s Hospital, Huludao, China
- 7Department of Neurology, Beipiao Central Hospital, Beipiao, China
- 8Department of Neurology, Xiuyan County Central People’s Hospital, Anshan, China
- 9Department of Neurology, Linghai Dalinghe Hospital, Jinzhou, China
- 10Department of Neurology, Fuxin Central Hospital, Fuxin, China
- 11Department of Neurology, Anshan Changda Hospital, Anshan, China
- 12Department of Neurology, General Hospital of Benxi Iron & Steel Industry Group of Liaoning Health Industry Group, Benxi, China
- 13Department of Neurology, Benxi Central Hospital, Benxi, China
- 14Department of Neurology, Tieling County Central Hospital, Tieling, China Background
- KMID: 2546438
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2023.00668
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
Intravenous tenecteplase (TNK) efficacy has not been well demonstrated in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) beyond 4.5 hours after onset. This study aimed to determine the effect of intravenous TNK for AIS within 4.5 to 24 hours of onset.
Methods
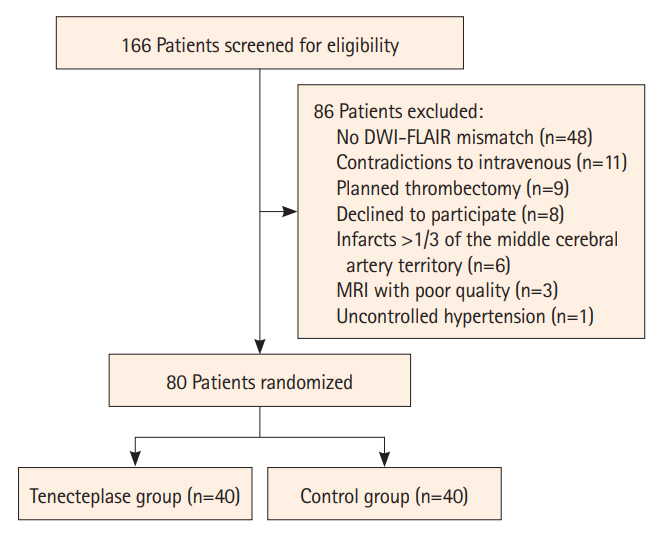
In this pilot trial, eligible AIS patients with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI)-fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) mismatch were randomly allocated to intravenous TNK (0.25 mg/kg) or standard care within 4.5–24 hours of onset. The primary endpoint was excellent functional outcome at 90 days (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] score of 0–1). The primary safety endpoint was symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH).
Results
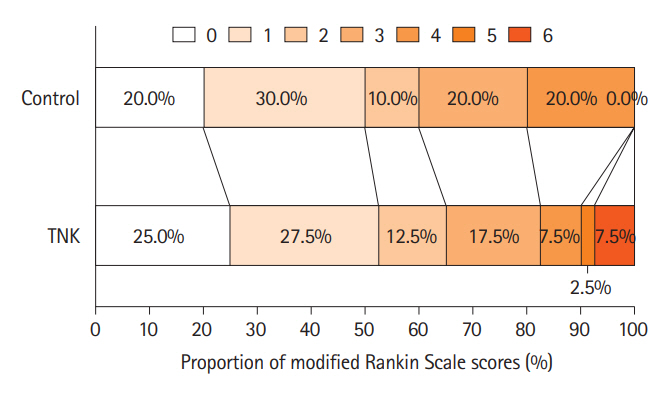
Of the randomly assigned 80 patients, the primary endpoint occurred in 52.5% (21/40) of TNK group and 50.0% (20/40) of control group, with no significant difference (unadjusted odds ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval 0.46–2.66; P=0.82). More early neurological improvement occurred in TNK group than in control group (11 vs. 3, P=0.03), but no significant differences were found in other secondary endpoints, such as mRS 0–2 at 90 days, shift analysis of mRS at 90 days, and change in National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score at 24 hours and 7 days. There were no cases of sICH in this trial; however, asymptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 3 of the 40 patients (7.5%) in the TNK group.
Conclusion
This phase 2, randomized, multicenter study suggests that intravenous TNK within 4.5–24 hours of onset may be safe and feasible in AIS patients with a DWI-FLAIR mismatch.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019; 50:e344–e418.2. Berge E, Whiteley W, Audebert H, De Marchis GM, Fonseca AC, Padiglioni C, et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines on intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Eur Stroke J. 2021; 6:I–LXII.3. Logallo N, Novotny V, Assmus J, Kvistad CE, Alteheld L, Rønning OM, et al. Tenecteplase versus alteplase for management of acute ischaemic stroke (NOR-TEST): a phase 3, randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017; 16:781–788.4. Menon BK, Buck BH, Singh N, Deschaintre Y, Almekhlafi MA, Coutts SB, et al. Intravenous tenecteplase compared with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in Canada (AcT): a pragmatic, multicentre, open-label, registry-linked, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2022; 400:161–169.5. Wang Y, Li S, Pan Y, Li H, Parsons MW, Campbell BCV, et al. Tenecteplase versus alteplase in acute ischaemic cerebrovascular events (TRACE-2): a phase 3, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2023; 401:645–654.6. Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Churilov L, Yassi N, Kleinig TJ, Dowling RJ, et al. Tenecteplase versus alteplase before thrombectomy for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:1573–1582.7. Bivard A, Zhao H, Churilov L, Campbell BCV, Coote S, Yassi N, et al. Comparison of tenecteplase with alteplase for the early treatment of ischaemic stroke in the Melbourne Mobile Stroke Unit (TASTE-A): a phase 2, randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol. 2022; 21:520–527.8. Ma H, Campbell BCV, Parsons MW, Churilov L, Levi CR, Hsu C, et al. Thrombolysis guided by perfusion imaging up to 9 hours after onset of stroke. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:1795–1803.9. Thomalla G, Simonsen CZ, Boutitie F, Andersen G, Berthezene Y, Cheng B, et al. MRI-guided thrombolysis for stroke with unknown time of onset. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:611–622.10. Kate M, Wannamaker R, Kamble H, Riaz P, Gioia LC, Buck B, et al. Penumbral imaging-based thrombolysis with tenecteplase is feasible up to 24 hours after symptom onset. J Stroke. 2018; 20:122–130.11. Coutts SB, Dubuc V, Mandzia J, Kenney C, Demchuk AM, Smith EE, et al. Tenecteplase-tissue-type plasminogen activator evaluation for minor ischemic stroke with proven occlusion. Stroke. 2015; 46:769–774.12. Liu L, Chen W, Zhou H, Duan W, Li S, Huo X, et al. Chinese Stroke Association guidelines for clinical management of cerebrovascular disorders: executive summary and 2019 update of clinical management of ischaemic cerebrovascular diseases. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2020; 5:159–176.13. Chinese Society of Neurology, Chinese Stroke Society. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018. Chin J Neurol. 2018; 51:666–682.14. Kharitonova T, Mikulik R, Roine RO, Soinne L, Ahmed N, Wahlgren N; Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke Investigators. Association of early National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale improvement with vessel recanalization and functional outcome after intravenous thrombolysis in ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2011; 42:1638–1643.15. Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Dávalos A, Guidetti D, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1317–1329.16. Katsanos AH, Psychogios K, Turc G, Sacco S, de Sousa DA, De Marchis GM, et al. Off-label use of tenecteplase for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022; 5:e224506.17. Mahawish K, Gommans J, Kleinig T, Lallu B, Tyson A, Ranta A. Switching to tenecteplase for stroke thrombolysis: real-world experience and outcomes in a regional stroke network. Stroke. 2021; 52:e590–e593.18. Tsivgoulis G, Katsanos AH, Christogiannis C, Faouzi B, Mavridis D, Dixit AK, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis with tenecteplase for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2022; 92:349–357.19. Ma P, Zhang Y, Chang L, Li X, Diao Y, Chang H, et al. Tenecteplase vs. alteplase for the treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol. 2022; 269:5262–5271.20. Thomalla G, Boutitie F, Ma H, Koga M, Ringleb P, Schwamm LH, et al. Intravenous alteplase for stroke with unknown time of onset guided by advanced imaging: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet. 2020; 396:1574–1584.21. Thomalla G, Cheng B, Ebinger M, Hao Q, Tourdias T, Wu O, et al. DWI-FLAIR mismatch for the identification of patients with acute ischaemic stroke within 4·5 h of symptom onset (PREFLAIR): a multicentre observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2011; 10:978–986.22. Koga M, Yamamoto H, Inoue M, Asakura K, Aoki J, Hamasaki T, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase at 0.6 mg/kg for stroke with unknown time of onset: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke. 2020; 51:1530–1538.23. Albers GW, Campbell BC, Lansberg MG, Broderick J, Butcher K, Froehler MT, et al. A phase III, prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of thrombolysis in imaging-eligible, late-window patients to assess the efficacy and safety of tenecteplase (TIMELESS): rationale and design. Int J Stroke. 2023; 18:237–241.24. Roaldsen MB, Lindekleiv H, Eltoft A, Jusufovic M, Søyland MH, Petersson J, et al. Tenecteplase in wake-up ischemic stroke trial: protocol for a randomized-controlled trial. Int J Stroke. 2021; 16:990–994.25. Campbell BCV, Ma H, Ringleb PA, Parsons MW, Churilov L, Bendszus M, et al. Extending thrombolysis to 4·5-9 h and wake-up stroke using perfusion imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet. 2019; 394:139–147.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Penumbral Imaging-Based Thrombolysis with Tenecteplase Is Feasible up to 24 Hours after Symptom Onset
- Replacing Alteplase with Tenecteplase: Is the Time Ripe?
- Outcome Evaluation of Intravenous Infusion of Urokinase for Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Reperfusion therapy in acute ischemic stroke
- Treatment for Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Presenting beyond Six Hours of Ischemic Symptom Onset : Effectiveness of Intravenous Direct Thrombin Inhibitor, Argatroban