Endocrinol Metab.
2023 Feb;38(1):156-173. 10.3803/EnM.2022.1516.
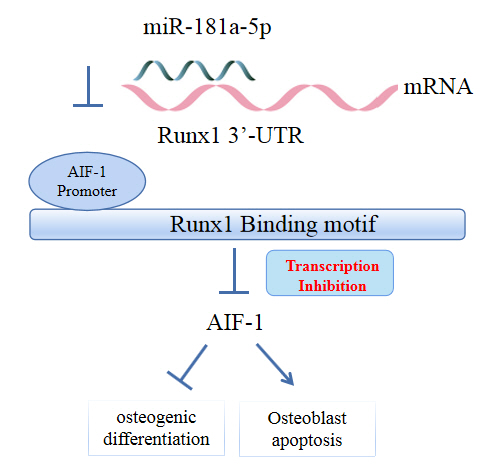
MicroRNA-181a-5p Curbs Osteogenic Differentiation and Bone Formation Partially Through Impairing Runx1-Dependent Inhibition of AIF-1 Transcription
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 2Department of Nephrology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- KMID: 2539829
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1516
Abstract
- Background
Evidence has revealed the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs) in modulating osteogenic differentiation, implying the promise of miRNA-based therapies for treating osteoporosis. This study investigated whether miR-181a-5p influences osteogenic differentiation and bone formation and aimed to establish the mechanisms in depth.
Methods
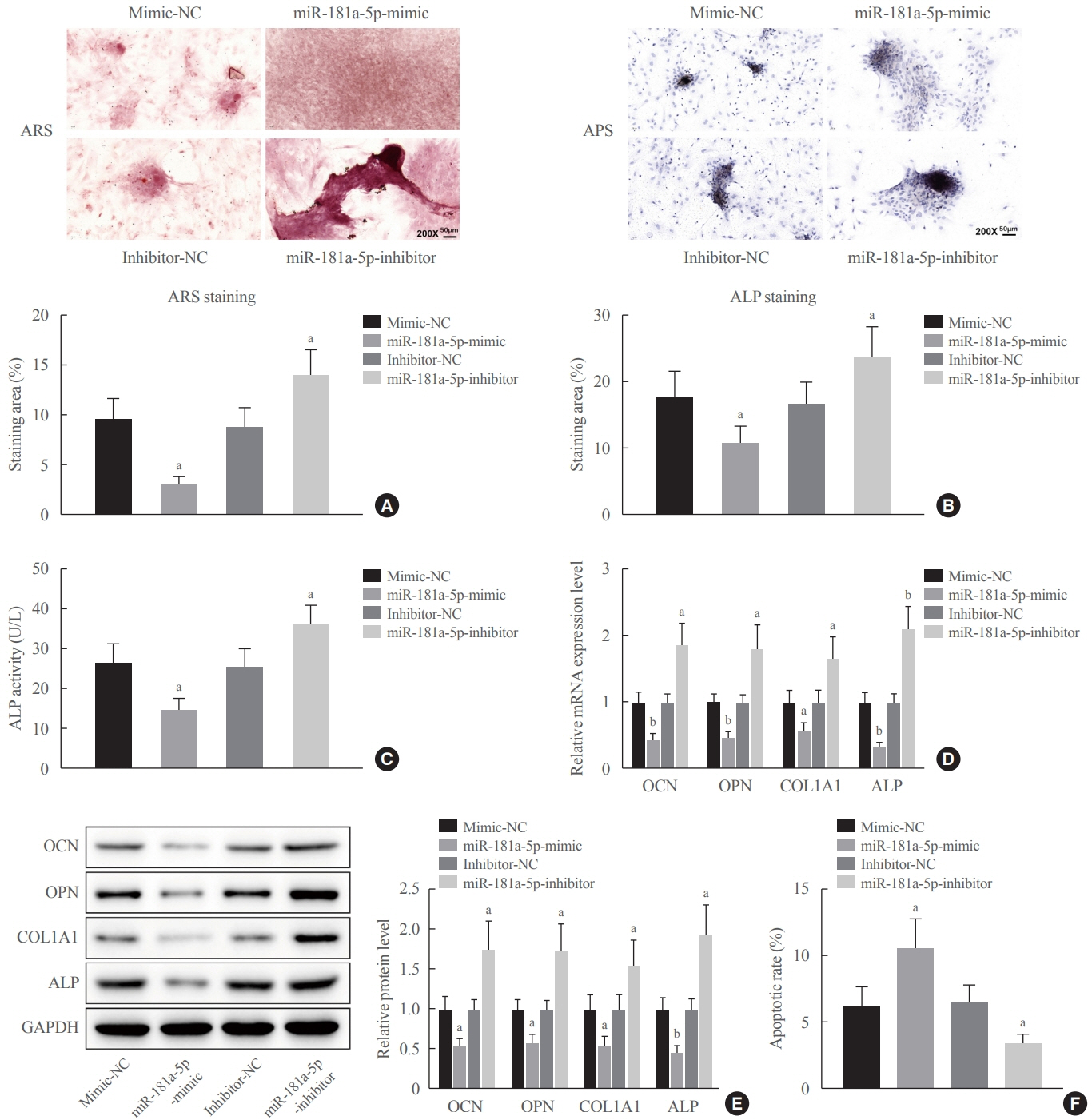
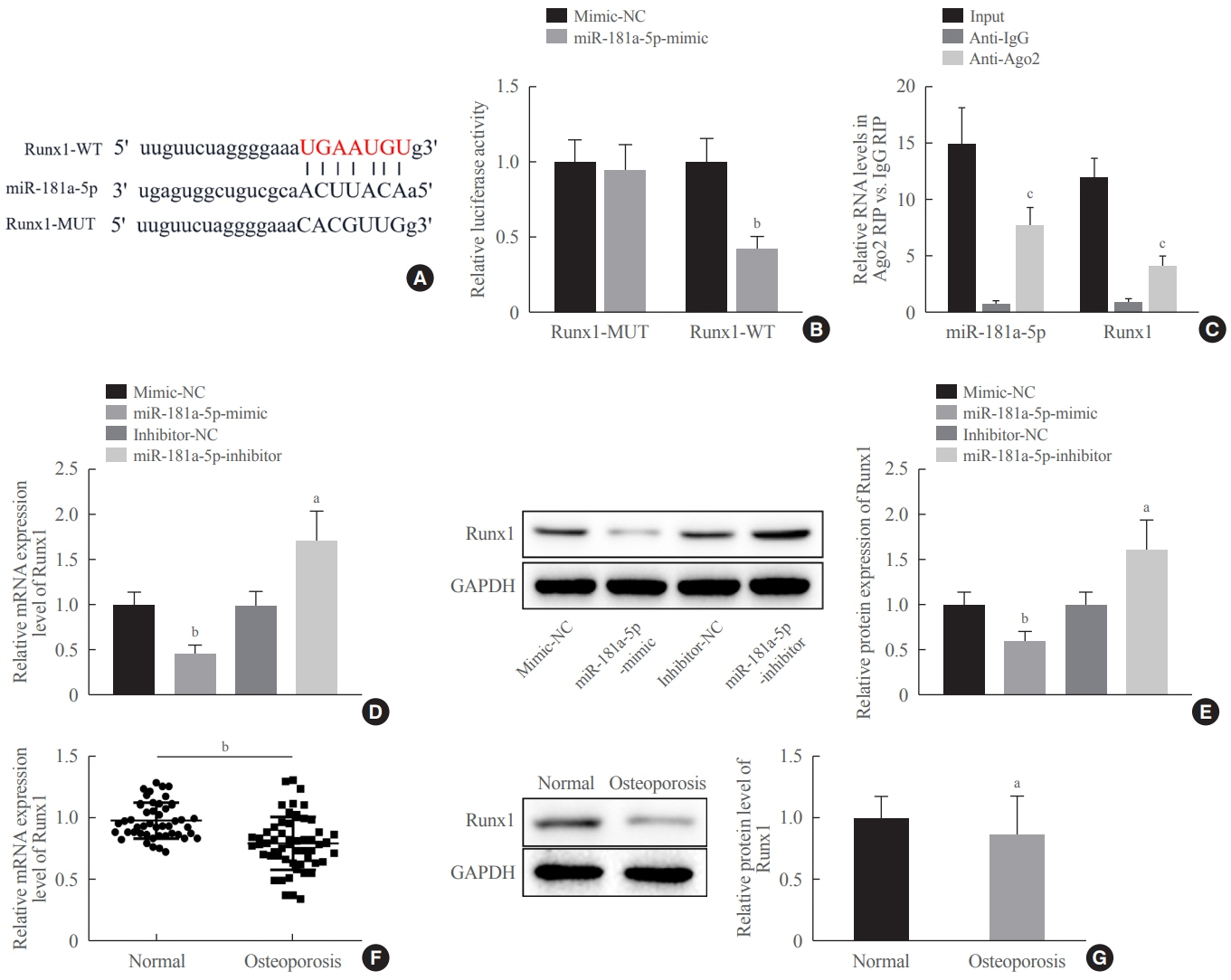
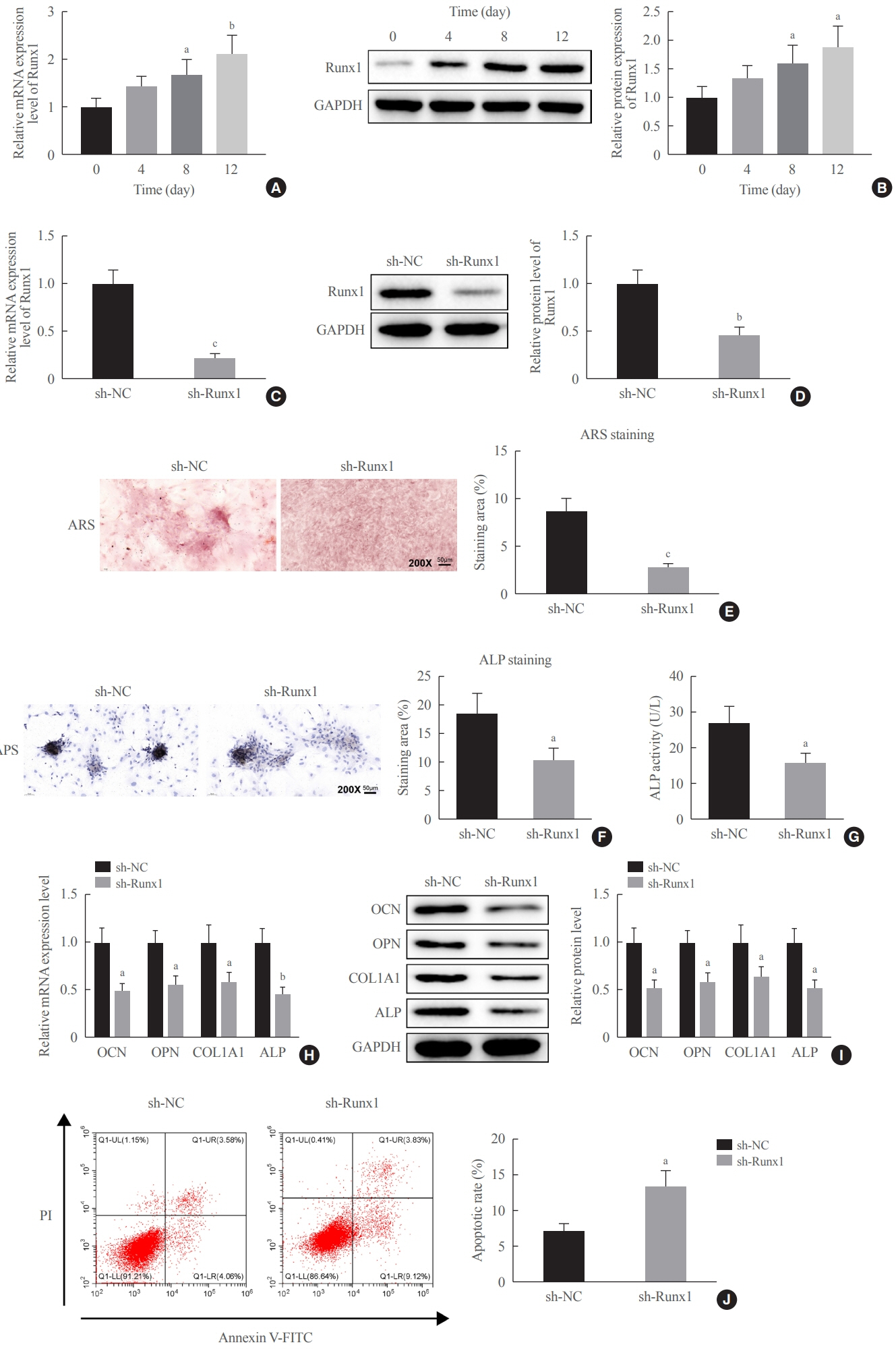
Clinical serum samples were obtained from osteoporosis patients, and MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with osteogenic induction medium (OIM) to induce osteogenic differentiation. miR-181a-5p-, Runt-related transcription factor 1 (Runx1)-, and/or allograft inflammatory factor-1 (AIF-1)-associated oligonucleotides or vectors were transfected into MC3T3-E1 cells to explore their function in relation to the number of calcified nodules, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining and activity, expression levels of osteogenesis-related proteins, and apoptosis. Luciferase activity, RNA immunoprecipitation, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were employed to validate the binding relationship between miR-181a-5p and Runx1, and the transcriptional regulatory relationship between Runx1 and AIF-1. Ovariectomy (OVX)-induced mice were injected with a miR-181a-5p antagonist for in vivo verification.
Results
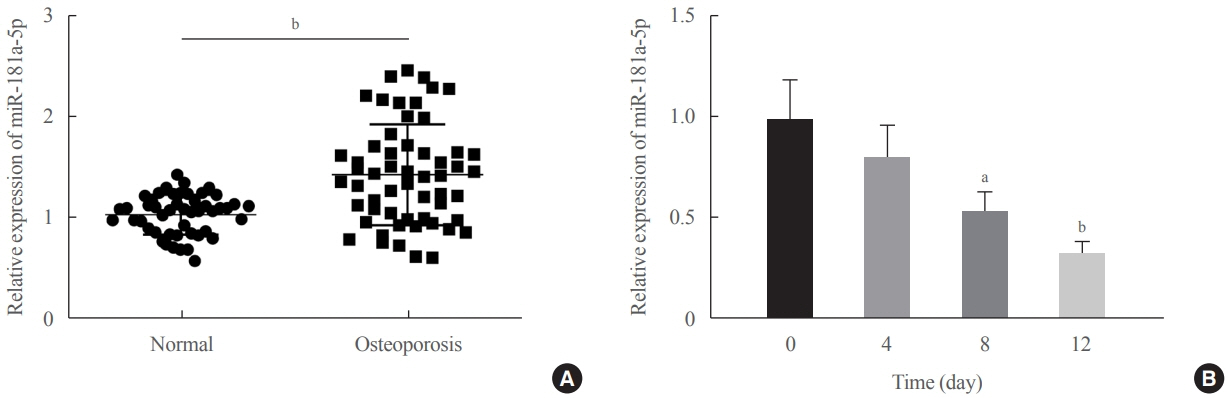
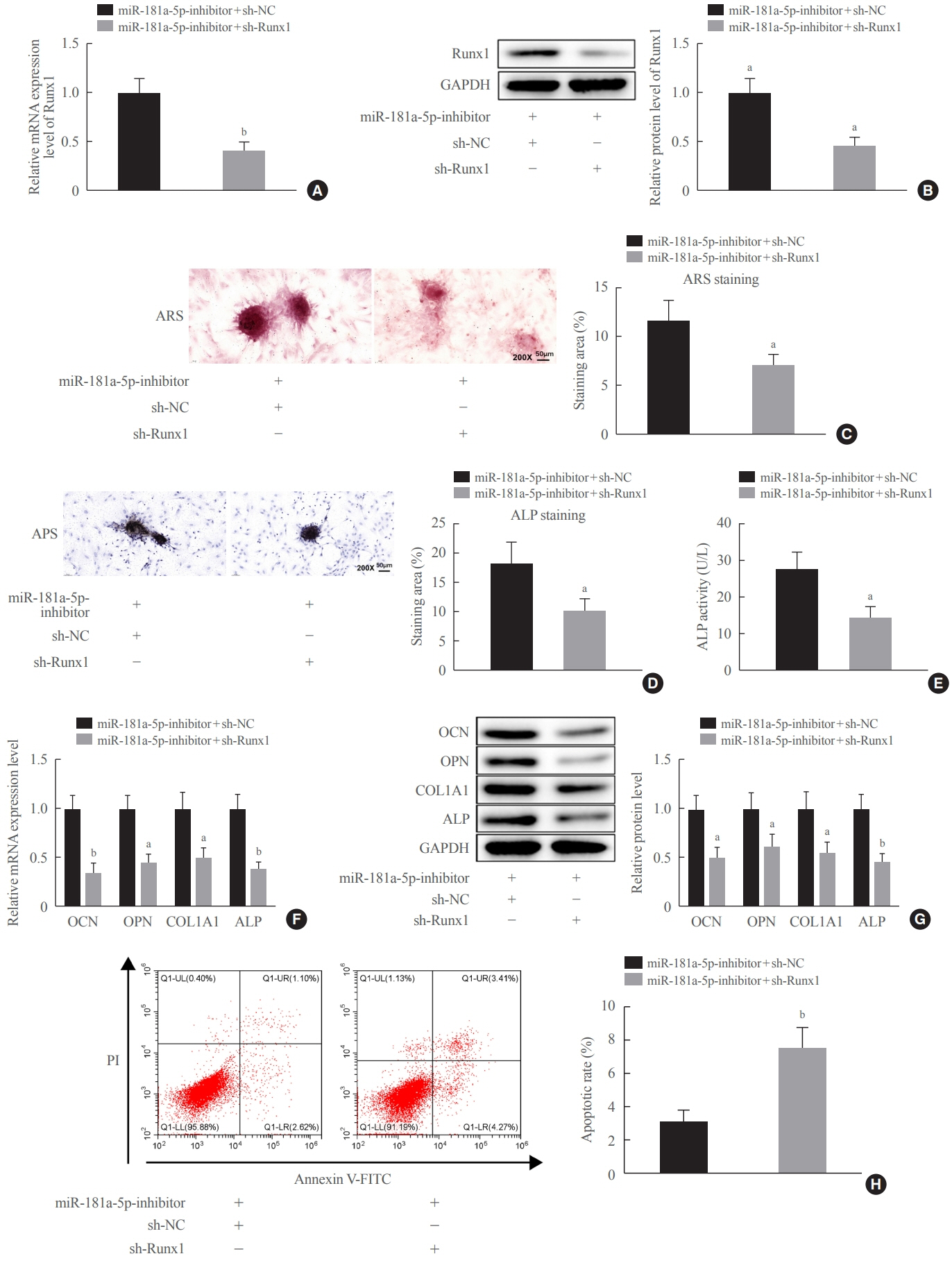
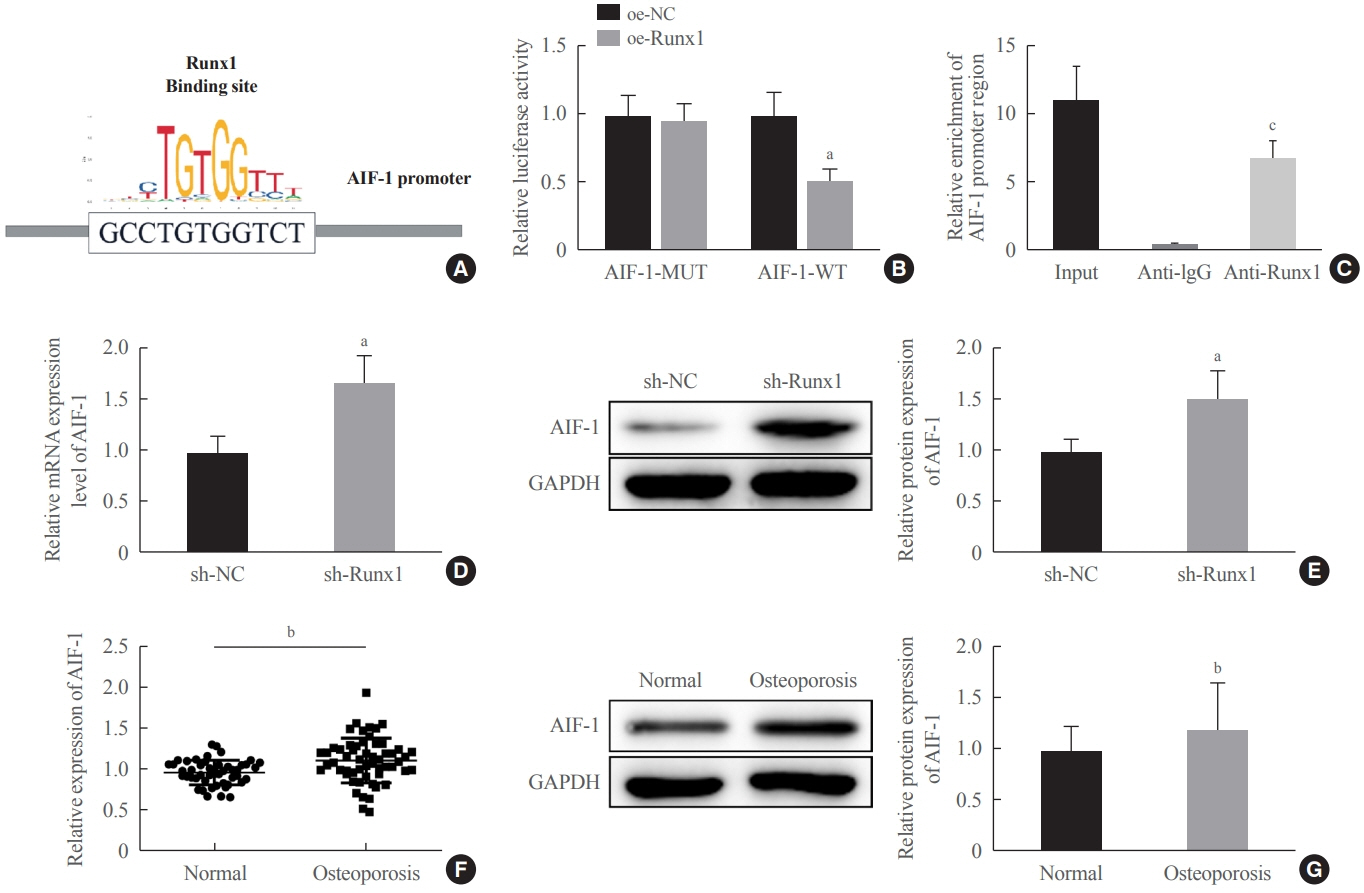
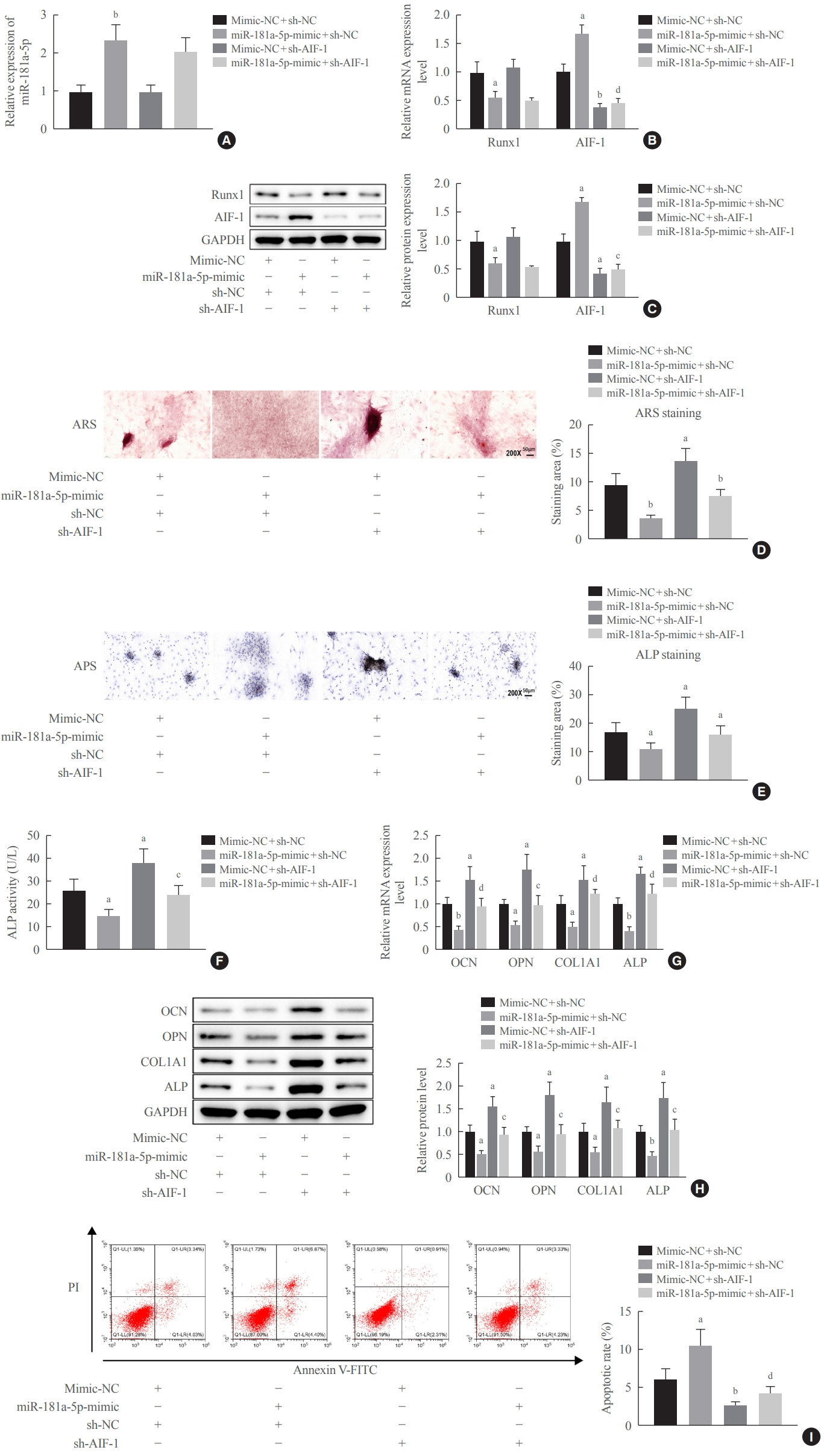
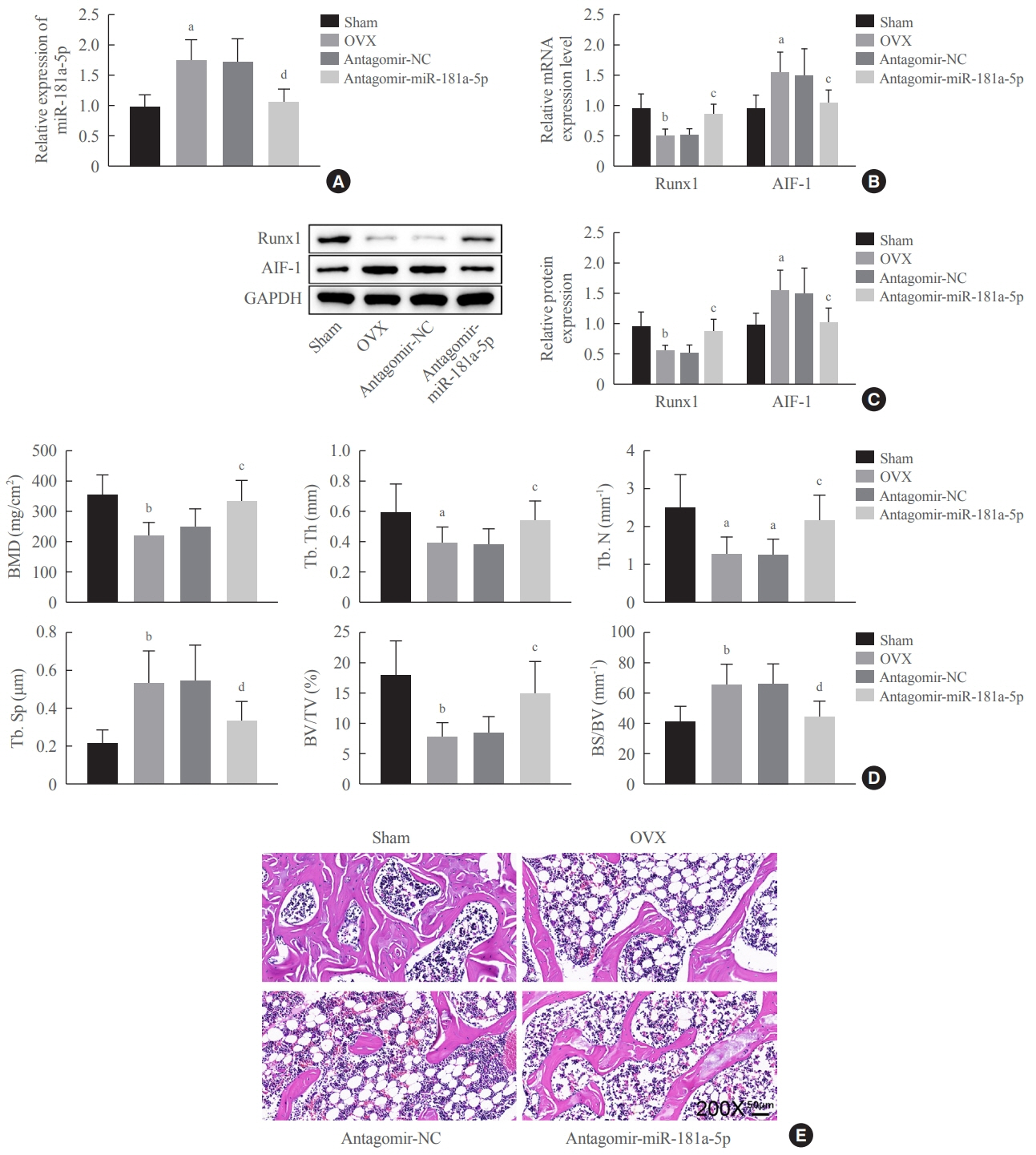
miR-181a-5p was highly expressed in the serum of osteoporosis patients. OIM treatment decreased miR-181a-5p and AIF-1 expression, but promoted Runx1 expression in MC3T-E1 cells. Meanwhile, upregulated miR-181a-5p suppressed OIM-induced increases in calcified nodules, ALP content, and osteogenesis-related protein expression. Mechanically, miR-181a-5p targeted Runx1, which acted as a transcription factor to negatively modulate AIF-1 expression. Downregulated Runx1 suppressed the miR-181a-5p inhibitor-mediated promotion of osteogenic differentiation, and downregulated AIF-1 reversed the miR-181a-5p mimic-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation. Tail vein injection of a miR-181a-5p antagonist induced bone formation in OVX-induced osteoporotic mice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, miR-181a-5p affects osteogenic differentiation and bone formation partially via the modulation of the Runx1/AIF-1 axis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Khosla S, Hofbauer LC. Osteoporosis treatment: recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 5:898–907.
Article2. Fuggle NR, Curtis EM, Ward KA, Harvey NC, Dennison EM, Cooper C. Fracture prediction, imaging and screening in osteoporosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019; 15:535–47.
Article3. Rachner TD, Khosla S, Hofbauer LC. Osteoporosis: now and the future. Lancet. 2011; 377:1276–87.
Article4. Eastell R, O’Neill TW, Hofbauer LC, Langdahl B, Reid IR, Gold DT, et al. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016; 2:16069.
Article5. Dirckx N, Moorer MC, Clemens TL, Riddle RC. The role of osteoblasts in energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019; 15:651–65.
Article6. Lewiecki EM. New targets for intervention in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7:631–8.
Article7. Lee WC, Guntur AR, Long F, Rosen CJ. Energy metabolism of the osteoblast: implications for osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2017; 38:255–66.
Article8. Hendrickx G, Boudin E, Van Hul W. A look behind the scenes: the risk and pathogenesis of primary osteoporosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015; 11:462–74.
Article9. Khraiwesh B, Arif MA, Seumel GI, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Reski R, et al. Transcriptional control of gene expression by microRNAs. Cell. 2010; 140:111–22.
Article10. Lu TX, Rothenberg ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; 141:1202–7.
Article11. Tang P, Xiong Q, Ge W, Zhang L. The role of microRNAs in osteoclasts and osteoporosis. RNA Biol. 2014; 11:1355–63.
Article12. Zhao W, Shen G, Ren H, Liang D, Yu X, Zhang Z, et al. Therapeutic potential of microRNAs in osteoporosis function by regulating the biology of cells related to bone homeostasis. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233:9191–208.
Article13. Wang Y, Wang K, Hu Z, Zhou H, Zhang L, Wang H, et al. MicroRNA-139-3p regulates osteoblast differentiation and apoptosis by targeting ELK1 and interacting with long noncoding RNA ODSM. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9:1107.
Article14. Liu Q, Guo Y, Wang Y, Zou X, Yan Z. miR-98-5p promotes osteoblast differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells by targeting CKIP-1. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 17:4797–802.
Article15. Waki T, Lee SY, Niikura T, Iwakura T, Dogaki Y, Okumachi E, et al. Profiling microRNA expression during fracture healing. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016; 17:83.
Article16. Zhu H, Chen H, Ding D, Wang S, Dai X, Zhu Y. The interaction of miR-181a-5p and sirtuin 1 regulated human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation and apoptosis. Bioengineered. 2021; 12:1426–35.
Article17. Shao B, Liao L, Yu Y, Shuai Y, Su X, Jing H, et al. Estrogen preserves Fas ligand levels by inhibiting microRNA-181a in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to maintain bone remodeling balance. FASEB J. 2015; 29:3935–44.
Article18. Yang YL, Yen CT, Pai CH, Chen HY, Yu SL, Lin CY, et al. A double negative loop comprising ETV6/RUNX1 and MIR181A1 contributes to differentiation block in t(12;21)-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0142863.
Article19. Tang CY, Wu M, Zhao D, Edwards D, McVicar A, Luo Y, et al. Runx1 is a central regulator of osteogenesis for bone homeostasis by orchestrating BMP and WNT signaling pathways. PLoS Genet. 2021; 17:e1009233.
Article20. Soung do Y, Kalinowski J, Baniwal SK, Jacome-Galarza CE, Frenkel B, Lorenzo J, et al. Runx1-mediated regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function. Mol Endocrinol. 2014; 28:546–53.
Article21. Compston JE, McClung MR, Leslie WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019; 393:364–76.
Article22. Bellavia D, Salamanna F, Raimondi L, De Luca A, Carina V, Costa V, et al. Deregulated miRNAs in osteoporosis: effects in bone metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019; 76:3723–44.
Article23. Papaioannou G, Mirzamohammadi F, Kobayashi T. MicroRNAs involved in bone formation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014; 71:4747–61.
Article24. Lian JB, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Hassan MQ, Gaur T, et al. MicroRNA control of bone formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012; 8:212–27.
Article25. Xu Y, Jin Y, Hong F, Ma Y, Yang J, Tang Y, et al. MiR-664-3p suppresses osteoblast differentiation and impairs bone formation via targeting Smad4 and osterix. J Cell Mol Med. 2021; 25:5025–37.
Article26. Okamoto H, Matsumi Y, Hoshikawa Y, Takubo K, Ryoke K, Shiota G. Involvement of microRNAs in regulation of osteoblastic differentiation in mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e43800.
Article27. Luo Y, Zhang Y, Miao G, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Huang Y. Runx1 regulates osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by inhibiting adipogenesis through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arch Oral Biol. 2019; 97:176–84.
Article28. Tang CY, Chen W, Luo Y, Wu J, Zhang Y, McVicar A, et al. Runx1 up-regulates chondrocyte to osteoblast lineage commitment and promotes bone formation by enhancing both chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. Biochem J. 2020; 477:2421–38.
Article29. Tang J, Xie J, Chen W, Tang C, Wu J, Wang Y, et al. Runt-related transcription factor 1 is required for murine osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Biol Chem. 2020; 295:11669–81.
Article30. Sikora M, Kopec B, Piotrowska K, Pawlik A. Role of allograft inflammatory factor-1 in pathogenesis of diseases. Immunol Lett. 2020; 218:1–4.
Article31. da Silva RL, Elizondo DM, Brandy NZ, Haddock NL, Boddie TA, de Oliveira LL, et al. Leishmania donovani infection suppresses allograft inflammatory factor-1 in monocytes and macrophages to inhibit inflammatory responses. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:946.
Article32. Elizondo DM, Brandy NZ, da Silva RL, Haddock NL, Kacsinta AD, de Moura TR, et al. Allograft inflammatory factor-1 governs hematopoietic stem cell differentiation into cDC1 and monocyte-derived dendritic cells through IRF8 and RelB in vitro. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:173.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of miR-34c-5p in Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Prolactin Inhibits BCL6 Expression in Breast Cancer Cells through a MicroRNA-339-5p-Dependent Pathway
- Extracellular Vesicles Carrying RUNX3 Promote Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells
- MicroRNA-103a-3p controls proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells
- Effects of Ascorbic Acid on Osteoblast Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells