Cancer Res Treat.
2023 Jan;55(1):112-122. 10.4143/crt.2022.381.
Real-World Study of Osimertinib in Korean Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor T790M Mutation–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Lung and Esophageal Cancer Clinic, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 5Division of Pulmonology, Allergy and Critical care medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 6Department of Pulmonology and Critical care medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 7Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea
- 8Divi-sion of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 9Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 10Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 11Department of Pulmonology, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 12Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea
- 13Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 14Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 15Department of Internal Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- 16Division of Pulmonology, Allergy and Critical care medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 17Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 18Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea
- 19Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Eunpyeong St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 20Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2537997
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2022.381
Abstract
- Purpose
Although osimertinib is the standard-of-care treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation–positive non–small cell lung cancer, real-world evidence on the efficacy of osimertinib is not enough to reflect the complexity of the entire course of treatment. Herein, we report on the use of osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M mutation–positive non–small cell lung cancer who had previously received EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment in Korea.
Materials and Methods
Patients with confirmed EGFR T790M after disease progression of prior EGFR-TKI were enrolled and administered osimertinib 80 mg daily. The primary effectiveness outcome was progression-free survival, with time-to-treatment discontinuation, treatment and adverse effects leading to treatment discontinuation, and overall survival being the secondary endpoints.
Results
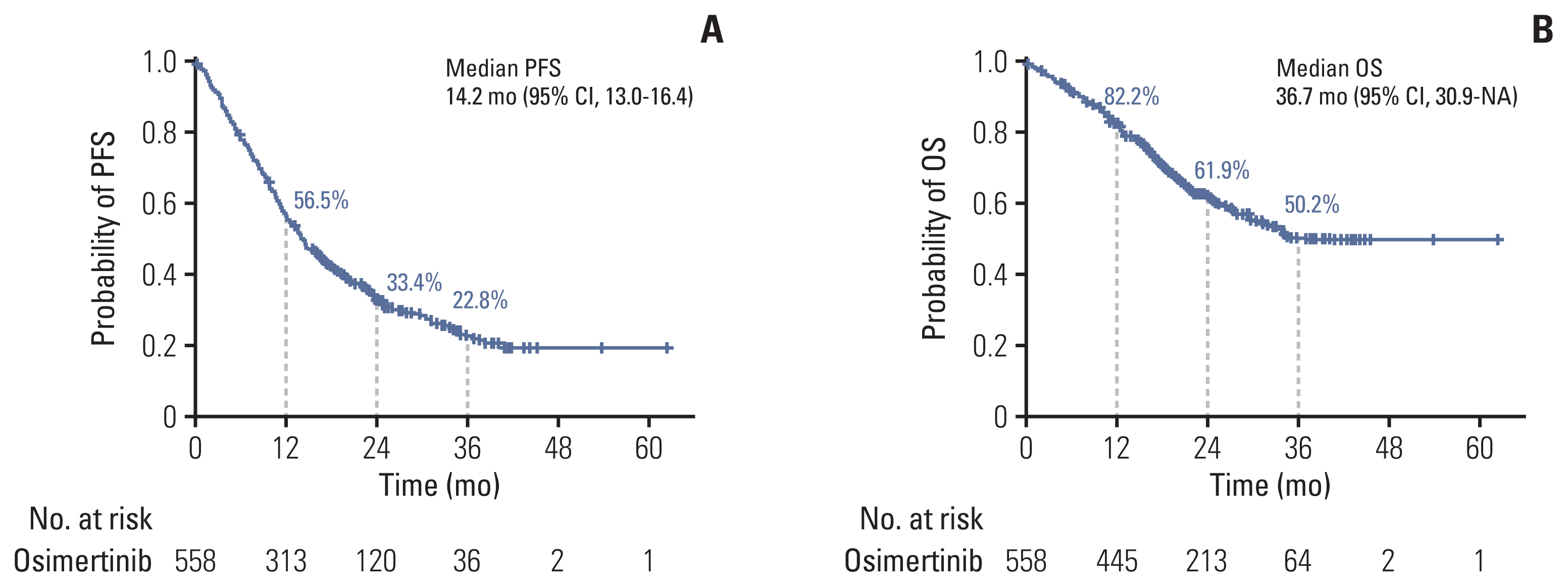
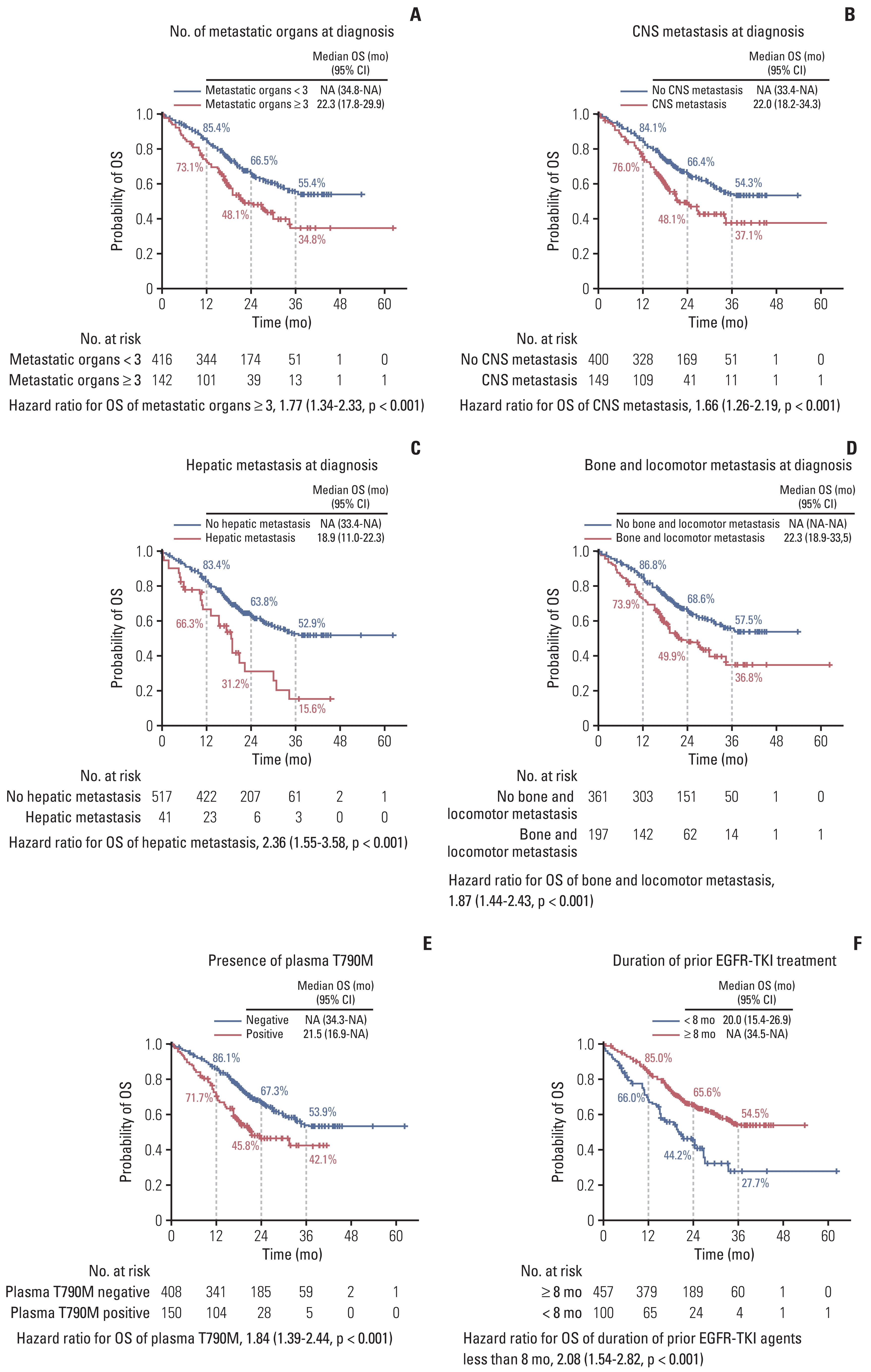
A total of 558 individuals were enrolled, and 55.2% had investigator-assessed responses. The median progression-free survival was 14.2 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 13.0 to 16.4), and the median time-to-treatment discontinuation was 15.0 months (95% CI, 14.1 to 15.9). The median overall survival was 36.7 months (95% CI, 30.9 to not reached). The benefit with osimertinib was consistent regardless of the age, sex, smoking history, and primary EGFR mutation subtype. However, hepatic metastases at the time of diagnosis, the presence of plasma EGFR T790M, and the shorter duration of prior EGFR-TKI treatment were poor predictors of osimertinib treatment. Ten patients (1.8%), including three with pneumonitis, had to discontinue osimertinib due to severe adverse effects.
Conclusion
Osimertinib demonstrated its clinical effectiveness and survival benefit for EGFR T790M mutation–positive in Korean patients with no new safety signals.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020; 70:7–30.2. Santarpia M, Liguori A, Karachaliou N, Gonzalez-Cao M, Daffina MG, D’Aveni A, et al. Osimertinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: design, development and place in therapy. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 2017; 8:109–25.3. Cho BC, Kim DW, Park K, Lee JS, Yoo SS, Kang JH, et al. Real-world use of osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer: ASTRIS study Korean subgroup analysis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020; 36:477–82.4. Majeed U, Manochakian R, Zhao Y, Lou Y. Targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: current advances and future trends. J Hematol Oncol. 2021; 14:108.5. Lee JG, Kim HC, Choi CM. Recent trends of lung cancer in Korea. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2021; 84:89–95.6. Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, O’Byrne K, Hirsh V, Mok T, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:3327–34.7. Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:2380–8.8. Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:123–32.9. Wu SG, Shih JY. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018; 17:38.10. Oh DK, Ji WJ, Kim WS, Choi CM, Yoon SK, Rho JK, et al. Efficacy, safety, and resistance profile of osimertinib in T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer in real-world practice. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0210225.11. Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014; 4:1046–61.12. Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS, et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:629–40.
Article13. Marinis F, Wu YL, de Castro G Jr, Chang GC, Chen YM, Cho BC, et al. ASTRIS: a global real-world study of osimertinib in >3000 patients with EGFR T790M positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2019; 15:3003–14.14. Lee JC, Hung JY, Kim YC, Chang GC, Yoo SS, Yang SH, et al. Real-world treatment patterns in patients with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC receiving a first-line, first-or second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor in South Korea and Taiwan. Asian Pac J Cancer Biol. 2021; 6:123–32.15. Hochmair MJ, Morabito A, Hao D, Yang CT, Soo RA, Yang JC, et al. Sequential afatinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: final analysis of the GioTag study. Future Oncol. 2020; 16:2799–808.16. Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Mok TS, Han JY, Ahn MJ, Delmonte A, Ramalingam SS, et al. Osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed for patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC and progression on a prior EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: AURA3 overall survival analysis. Ann Oncol. 2020; 31:1536–44.17. Blumenthal GM, Gong Y, Kehl K, Mishra-Kalyani P, Goldberg KB, Khozin S, et al. Analysis of time-to-treatment discontinuation of targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy in clinical trials of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2019; 30:830–8.18. Lim JU. Management of oligometastasis and oligoprogression in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive NSCLC in the era of third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021; 22:e786–92.19. Wu YL, Planchard D, Lu S, Sun H, Yamamoto N, Kim DW, et al. Pan-Asian adapted Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a CSCO-ESMO initiative endorsed by JSMO, KSMO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann Oncol. 2019; 30:171–210.20. Choi MG, Choi CM, Lee DH, Kim SW, Yoon S, Kim WS, et al. Different prognostic implications of hepatic metastasis according to front-line treatment in non-small cell lung cancer: a real-world retrospective study. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021; 10:2551–61.21. Zheng D, Ye X, Zhang MZ, Sun Y, Wang JY, Ni J, et al. Plasma EGFR T790M ctDNA status is associated with clinical outcome in advanced NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:20913.22. Yu HA, Suzawa K, Jordan E, Zehir A, Ni A, Kim R, et al. Concurrent alterations in EGFR-mutant lung cancers associated with resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors and characterization of MTOR as a mediator of resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2018; 24:3108–18.23. Chen M, Xu Y, Zhao J, Zhong W, Zhang L, Bi Y, et al. Concurrent driver gene mutations as negative predictive factors in epidermal growth factor receptor-positive non-small cell lung cancer. EBioMedicine. 2019; 42:304–10.24. Ramalingam SS, Cheng Y, Zhou C, Ohe Y, Imamura F, Cho BC, et al. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29(Suppl 8):VIII740.25. Kim ES, Melosky B, Park K, Yamamoto N, Yang JC. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: outcomes in Asian populations. Future Oncol. 2021; 17:2395–408.26. Lorenzi M, Ferro A, Cecere F, Scattolin D, Del Conte A, Follador A, et al. First-line osimertinib in patients with EGFR− mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: outcome and safety in the real world: FLOWER study. Oncologist. 2021; 27:87–8.27. Ohe Y, Kato T, Sakai F, Kusumoto M, Endo M, Saito Y, et al. Real-world use of osimertinib for epidermal growth factor receptor T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020; 50:909–19.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Real-World Analysis of the Efficacy of Rebiopsy and EGFR Mutation Test of Tissue and Plasma Samples in Drug-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Rare Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in Korean Patients with EGFR-mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- A Phase II Trial of Osimertinib in the Second-Line Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with the EGFR T790M Mutation, Detected from Circulating Tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 2
- Assessment of Anti-tumor Efficacy of Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients by Liquid Biopsy Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid, Plasma, or Pleural Effusion
- Osimertinib Combined with Systemic Chemotherapy for EGFR Mutant, T790M-Negative, Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Who Develop Leptomeningeal Metastases with Extracranial Progression to Prior EGFR TKI