Int J Thyroidol.
2022 May;15(1):42-48. 10.11106/ijt.2022.15.1.42.
Lung Related Complications in Patients with Advanced Thyroid Cancer during Lenvatinib Therapy: Case Series and Literature Review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2530125
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2022.15.1.42
Abstract
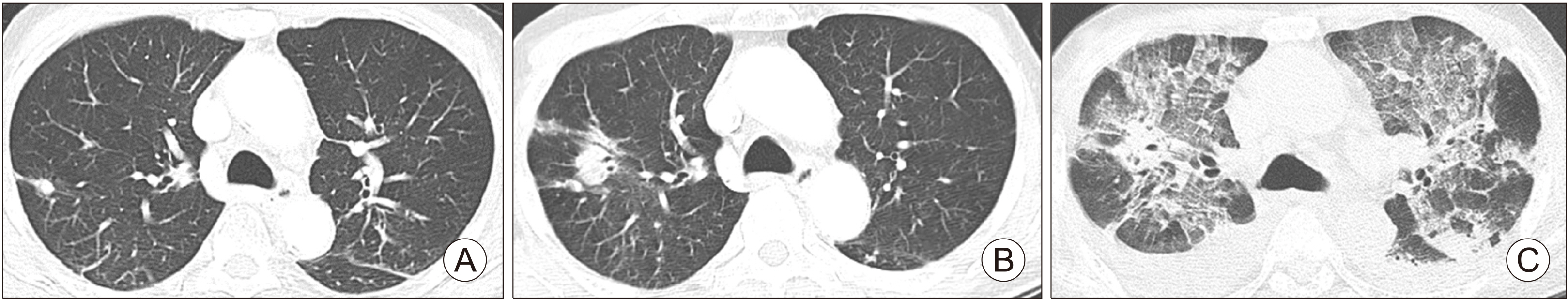
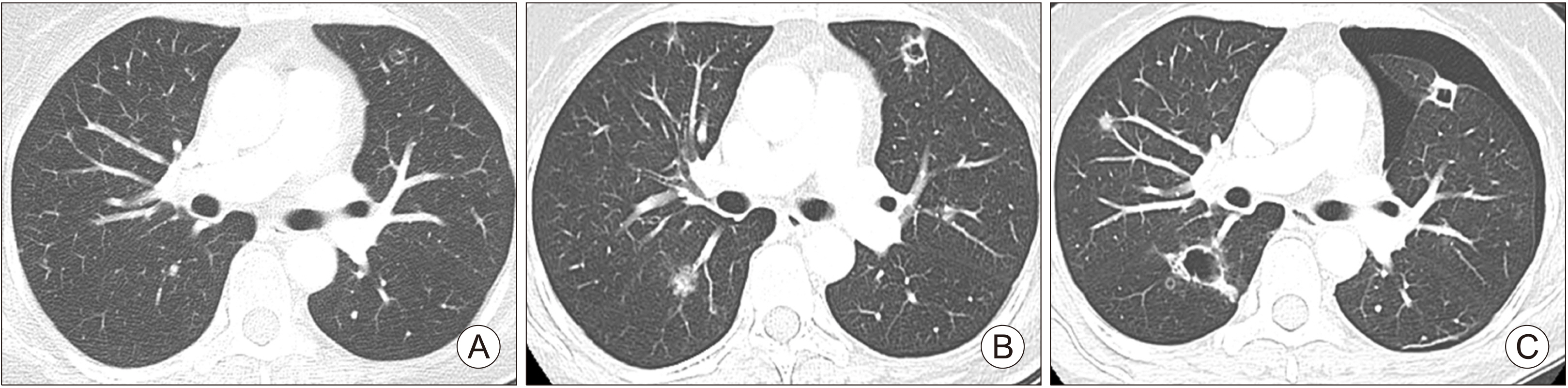
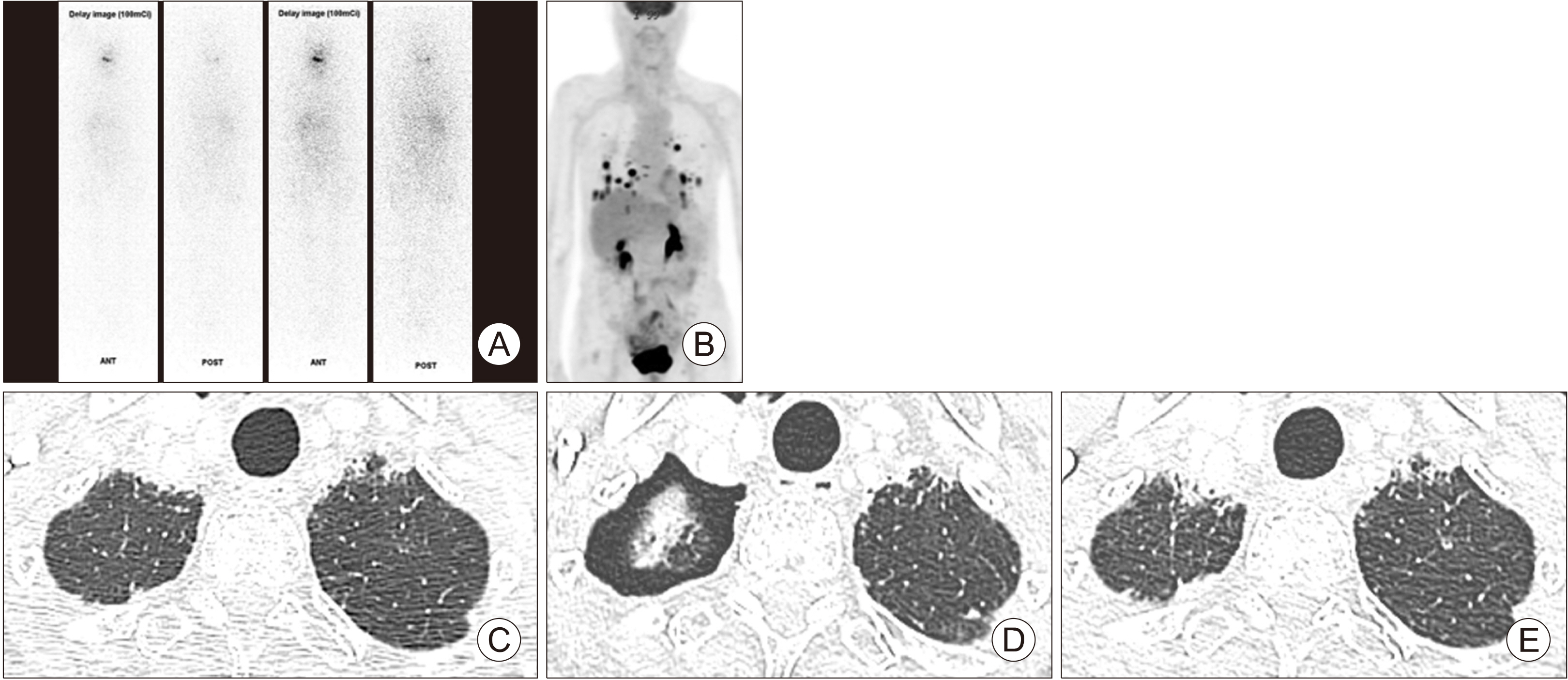
- Lenvatinib prolongs the survival of patients with advanced thyroid cancer. At initiation of lenvatinib therapy, advanced thyroid cancer patients frequently have lung metastasis and are vulnerable to pulmonary complications due to concealed lung damage caused by previous therapies including radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. Among 24 patients treated with lenvatinib, pulmonary events were observed in three patients with lung metastasis, including one with interstitial lung disease (ILD) and two with pneumothorax. One patient who was previously treated with 750 mCi RAI developed uncontrolled ILD after lenvatinib therapy and died of respiratory failure. Two pneumothorax cases had previous cavitation of metastatic lung nodules. Pneumothorax resolved spontaneously in both patients. Pulmonary events in patients with lung metastases treated with lenvatinib are uncommon and manageable in most cases, but may be fatal if detection and management are delayed. Special attention should be given to patients with lung metastasis treated with high cumulative dose of RAI therapy or cavitary changes that develop after lenvatinib therapy.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Fugazzola L, Elisei R, Fuhrer D, Jarzab B, Leboulleux S, Newbold K, et al. 2019; 2019 European Thyroid Association guidelines for the treatment and follow-up of advanced radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. Eur Thyroid J. 8(5):227–45. DOI: 10.1159/000502229. PMID: 31768334. PMCID: PMC6873012.
Article2. Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, Robinson B, Brose MS, Elisei R, et al. 2015; Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 372(7):621–30. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406470. PMID: 25671254.
Article3. Oh HS, Shin DY, Kim M, Park SY, Kim TH, Kim BH, et al. 2019; Extended real-world observation of patients treated with sorafenib for radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma and impact of lenvatinib salvage treatment: a Korean multicenter study. Thyroid. 29(12):1804–10. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2019.0246. PMID: 31592739.
Article4. Ruegemer JJ, Hay ID, Bergstralh EJ, Ryan JJ, Offord KP, Gorman CA. 1988; Distant metastases in differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a multivariate analysis of prognostic variables. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 67(3):501–8. DOI: 10.1210/jcem-67-3-501. PMID: 3410936.
Article5. Berdelou A, Borget I, Godbert Y, Nguyen T, Garcia ME, Chougnet CN, et al. 2018; Lenvatinib for the treatment of radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer in real-life practice. Thyroid. 28(1):72–8. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2017.0205. PMID: 29048237.
Article6. Kazzaz FI, Cabanillas ME, Bashoura L, Shannon VR, Faiz SA. 2019; Bilateral spontaneous pneumothoraces in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Respir Med Case Rep. 26:197–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.01.006. PMID: 30705818. PMCID: PMC6348391.
Article7. Yamazaki H, Iwasaki H, Suganuma N, Toda S, Masudo K, Nakayama H, et al. 2019; Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma diagnosed after treatment of lenvatinib for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2019:19–0085. DOI: 10.1530/EDM-19-0085. PMID: 31600721. PMCID: PMC6790905.
Article8. Lorusso L, Pieruzzi L, Biagini A, Sabini E, Valerio L, Giani C, et al. 2016; Lenvatinib and other tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of radioiodine refractory, advanced, and progressive thyroid cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 9:6467–77. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S84625. PMID: 27799794. PMCID: PMC5079697.
Article9. Ancker OV, Kruger M, Wehland M, Infanger M, Grimm D. 2019; Multikinase inhibitor treatment in thyroid cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21(1):10. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21010010. PMID: 31861373. PMCID: PMC6982227.
Article10. Aydemirli MD, Kapiteijn E, Ferrier KRM, Ottevanger PB, Links TP, van der Horst-Schrivers ANA, et al. 2020; Effectiveness and toxicity of lenvatinib in refractory thyroid cancer: Dutch real-life data. Eur J Endocrinol. 182(2):131–8. DOI: 10.1530/EJE-19-0763. PMID: 31751307.
Article11. Blevins DP, Dadu R, Hu M, Baik C, Balachandran D, Ross W, et al. 2014; Aerodigestive fistula formation as a rare side effect of antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 24(5):918–22. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2012.0598. PMID: 24635127. PMCID: PMC4026371.
Article12. Guan Y, Meng J, Zhao H, Hu Y, Yan X, Zhao SH, et al. 2014; Fatal interstitial lung disease after addition of sorafenib to a patient with lung adenocarcinoma who had failed to improve with erlotinib alone. Case Rep Oncol. 7(1):273–6. DOI: 10.1159/000362402. PMID: 24926256. PMCID: PMC4036133.
Article13. Nervo A, Ragni A, Gallo M, Ferraris A, Fonio P, Piovesan A, et al. 2020; Symptomatic biliary disorders during lenvatinib treatment for thyroid cancer: an underestimated problem. Thyroid. 30(2):229–36. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2019.0355. PMID: 31854230.
Article14. Terbuch A, Tiu C, Candilejo IM, Scaranti M, Curcean A, Bar D, et al. 2020; Radiological patterns of drug-induced interstitial lung disease (DILD) in early-phase oncology clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res. 26(18):4805–13. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-0454. PMID: 32332017.
Article15. Kashiwabara K, Semba H, Fujii S, Tsumura S. 2017; Outcome in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with successful rechallenge after recovery from epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced interstitial lung disease. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 79(4):705–10. DOI: 10.1007/s00280-017-3261-5. PMID: 28258422.
Article16. Takeda H, Nishikawa H, Iguchi E, Matsuda F, Kita R, Kimura T, et al. 2012; Sorafenib-induced acute interstitial pneumonia in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: report of three cases. Clin J Gastroenterol. 5(4):407–12. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-012-0339-9. PMID: 24672586. PMCID: PMC3961597.
Article17. Hotta K, Kiura K, Takigawa N, Yoshioka H, Harita S, Kuyama S, et al. 2010; Comparison of the incidence and pattern of interstitial lung disease during erlotinib and gefitinib treatment in Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer: the Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group experience. J Thorac Oncol. 5(2):179–84. DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181ca12e0. PMID: 20101144.
Article18. Schwaiblmair M, Behr W, Haeckel T, Markl B, Foerg W, Berghaus T. 2012; Drug induced interstitial lung disease. Open Respir Med J. 6:63–74. DOI: 10.2174/1874306401206010063. PMID: 22896776. PMCID: PMC3415629.
Article19. Sakurada T, Kakiuchi S, Tajima S, Horinouchi Y, Okada N, Nishisako H, et al. 2015; Characteristics of and risk factors for interstitial lung disease induced by chemotherapy for lung cancer. Ann Pharmacother. 49(4):398–404. DOI: 10.1177/1060028014566446. PMID: 25565405.
Article20. Komada F. 2018; Analysis of time-to-onset of interstitial lung disease after the administration of small molecule molecularly-targeted drugs. Yakugaku Zasshi. 138(2):229–35. DOI: 10.1248/yakushi.17-00194. PMID: 29386436.
Article21. Koma Y, Matsuoka H, Yoshimatsu H, Suzuki Y. 2012; Successful treatment with erlotinib after gefitinib-induced interstitial lung disease: a case report and literature review. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 50(10):760–4. DOI: 10.5414/CP201759. PMID: 22853866.
Article22. Kimura-Tsuchiya R, Sasaki E, Nakamura I, Suzuki S, Kawana S, Okouchi C, et al. 2018; A case of squamous cell carcinoma of unknown primary that responded to the multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib. Case Rep Oncol. 11(1):75–80. DOI: 10.1159/000486569. PMID: 29515414. PMCID: PMC5836208.
Article23. Kotani K, Enomoto M, Okada M, Yoshida K, Motoyama H, Fujii H, et al. 2019; Interstitial pneumonia suspected during regorafenib administration and exacerbated by subsequent therapy with lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin J Gastroenterol. 12(4):355–60. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-019-00983-x. PMID: 31020569.
Article24. Rall JE, Alpers JB, Lewallen CG, Sonenberg M, Berman M, Rawson RW. 1957; Radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis: a complication of radioiodine treatment of pulmonary metastases from cancer of the thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 17(11):1263–76. DOI: 10.1210/jcem-17-11-1263. PMID: 13475467.
Article25. Maniwa T, Nakagawa K, Isaka M, Ohde Y, Okumura T, Kondo H. 2011; Pneumothorax associated with treatment for pulmonary malignancy. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 13(3):257–61. DOI: 10.1510/icvts.2011.273201. PMID: 21700592.
Article26. Hendarsih E, Fadjari TH, Oehadian A. 2016; Chemotherapy-induced spontaneous pneumothorax: case series. Acta Med Indones. 48(2):134–8. PMID: 27550883.27. Lee HN, Chung WS, Jang HJ, Jee S, Tae K. 2020; Bilateral pneumothorax in a patient with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma and lung metastasis during lenvatinib therapy: a case report. Gland Surg. 9(5):1579–83. DOI: 10.21037/gs-20-462. PMID: 33224834. PMCID: PMC7667081.
Article28. Xie L, Xu J, Sun X, Tang X, Yan T, Yang R, et al. 2020; Anorexia, hypertension, pneumothorax, and hypothyroidism: potential signs of improved clinical outcome following apatinib in advanced osteosarcoma. Cancer Manag Res. 12:91–102. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S232823. PMID: 32021426. PMCID: PMC6956393.29. Datar S, Cabanillas M, Dadu R, Ost D, Grosu HB. 2020; Pulmonary cavitation in patients with thyroid cancer receiving antiangiogenic agents. BMC Cancer. 20(1):1181. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07693-5. PMID: 33267782. PMCID: PMC7709335.
Article30. Kawanishi Y, Kuwahara M, Utsunomiya M, Ishida N, Ishikawa Y, Hiroi M, et al. 2021; Pneumothorax during lenvatinib treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with lung metastasis. Clin J Gastroenterol. 14(1):288–92. DOI: 10.1007/s12328-020-01273-7. PMID: 33108567.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia in a Thyroid Cancer Patient Receiving Lenvatinib
- Management of Hypertension and Proteinuria after Treatment with Lenvatinib for Radioiodine Refractory Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: a Case Report
- BRAF/ MEK Inhibitors in Downstaging BRAFV600E Mutated Papillary Thyroid Cancer to Allow Resection: Case Report and Literature Review
- Adverse Events of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Thyroid Cancer
- Recent Improvements in the Treatment of High-Risk Thyroid Cancer