Int J Thyroidol.
2019 Nov;12(2):127-131. 10.11106/ijt.2019.12.2.127.
A Case of Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia in a Thyroid Cancer Patient Receiving Lenvatinib
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mj080332@gmail.com
- KMID: 2465066
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2019.12.2.127
Abstract
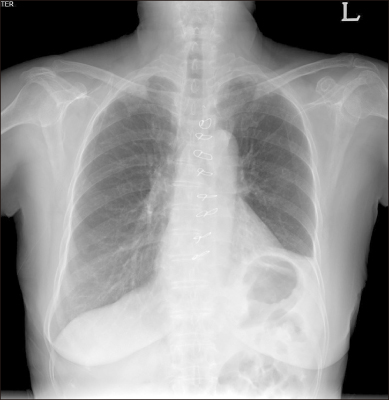
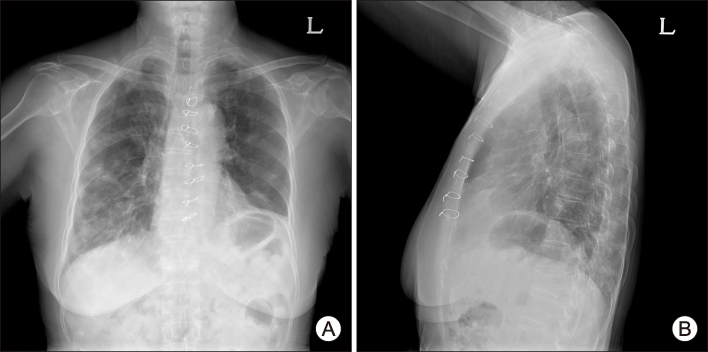
- Lenvatinib is a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for use in patients with iodine-131-refractory thyroid cancer. The common adverse events of lenvatinib include hypertension, proteinuria, fatigue, and diarrhea. To date, no report on Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in patients receiving lenvatinib has been published. Here, we present a case of severe PCP that led to the death of a 79-year-old woman who was diagnosed with poorly differentiated thyroid cancer and received lenvatinib. The development of PCP should be considered when patients taking lenvatinib show clinical symptoms of pneumonia, and regular chest X-ray follow-up is needed for patients receiving lenvatinib.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Valerio L, Pieruzzi L, Giani C, Agate L, Bottici V, Lorusso L, et al. Targeted therapy in thyroid cancer: state of the art. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2017; 29(5):316–324.
Article2. Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, Robinson B, Brose MS, Elisei R, et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372(7):621–630.
Article3. Thomas CF Jr, Limper AH. Pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350(24):2487–2498.
Article4. Truong J, Ashurst JV. Pneumocystis (Carinii) jiroveci pneumonia. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing;2019.5. French JD, Bible K, Spitzweg C, Haugen BR, Ryder M. Leveraging the immune system to treat advanced thyroid cancers. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 5(6):469–481.
Article6. Tasaka S, Tokuda H. Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in non-HIV-infected patients in the era of novel immunosuppressive therapies. J Infect Chemother. 2012; 18(6):793–806.
Article7. Liu Y, Su L, Jiang SJ, Qu H. Risk factors for mortality from pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) in non-HIV patients: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(35):59729–59739.
Article8. Ibrahimpasic T, Ghossein R, Shah JP, Ganly I. Poorly differentiated carcinoma of the thyroid gland: current status and future prospects. Thyroid. 2019; 29(3):311–321.
Article9. Shah RR. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced interstitial lung disease: clinical features, diagnostic challenges, and therapeutic dilemmas. Drug Saf. 2016; 39(11):1073–1091.
Article10. Kotani K, Enomoto M, Okada M, Yoshida K, Motoyama H, Fujii H, et al. Interstitial pneumonia suspected during regorafenib administration and exacerbated by subsequent therapy with lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2019; 12(4):355–360.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of Hypertension and Proteinuria after Treatment with Lenvatinib for Radioiodine Refractory Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: a Case Report
- Lung Related Complications in Patients with Advanced Thyroid Cancer during Lenvatinib Therapy: Case Series and Literature Review
- A Clinical Study of 15 Cases of Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia
- A Case of Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia Associated with Cytomegalovirus Lung Infection
- Two Autopsy Cases of Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia