Int J Thyroidol.
2018 Nov;11(2):78-81. 10.11106/ijt.2018.11.2.78.
Management of Hypertension and Proteinuria after Treatment with Lenvatinib for Radioiodine Refractory Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wongukim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2448975
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2018.11.2.78
Abstract
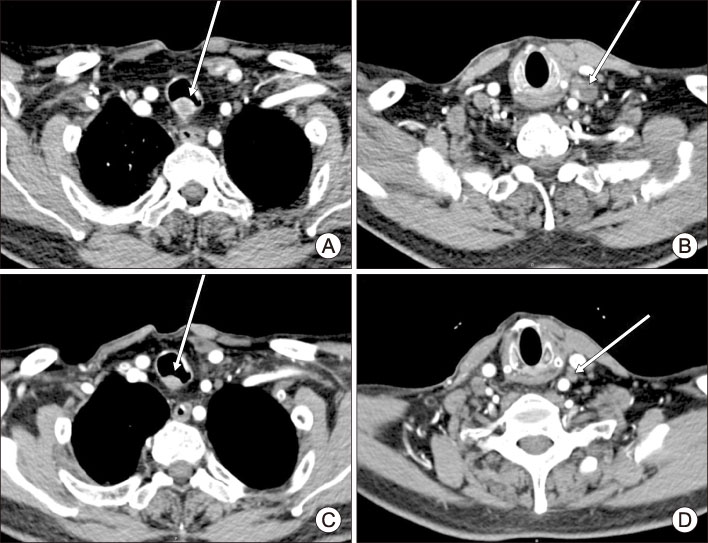
- Lenvatinib, an oral multi-kinase inhibitor, is a valuable treatment option for advanced differentiated thyroid carcinoma. However, severe treatment-related adverse events occur up to 30% of the patients receiving lenvatinib, making it a challenge for clinicians to maintain this drug and therefore affecting the outcome of therapy. Blood vessel related events, such as hypertension or proteinuria, are among the most frequent adverse events. We present a case of 65-year-old man with radioactive iodine refractory papillary thyroid carcinoma with cervical lymph node metastasis and tracheal invasion receiving lenvatinib who developed proteinuria and worsening of hypertension. Management with repeated dose reductions and using supportive medications allowed this patient to continue lenvatinib with his disease stably controlled. Early detection of patients at risk for these adverse events and cautious administration of lenvatinib at appropriate level are crucial in managing patients receiving lenvatinib.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tohyama O, Matsui J, Kodama K, Hata-Sugi N, Kimura T, Okamoto K, et al. Antitumor activity of lenvatinib (e7080): an angiogenesis inhibitor that targets multiple receptor tyrosine kinases in preclinical human thyroid cancer models. J Thyroid Res. 2014; 2014:638747.
Article2. Matsui J, Funahashi Y, Uenaka T, Watanabe T, Tsuruoka A, Asada M. Multi-kinase inhibitor E7080 suppresses lymph node and lung metastases of human mammary breast tumor MDA-MB-231 via inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor (VEGF-R) 2 and VEGF-R3 kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14(17):5459–5465.
Article3. Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, Robinson B, Brose MS, Elisei R, et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372(7):621–630.
Article4. Brose MS, Nutting CM, Jarzab B, Elisei R, Siena S, Bastholt L, et al. Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2014; 384(9940):319–328.
Article5. Kiyota N, Schlumberger M, Muro K, Ando Y, Takahashi S, Kawai Y, et al. Subgroup analysis of Japanese patients in a phase 3 study of lenvatinib in radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015; 106(12):1714–1721.
Article6. Eremina V, Cui S, Gerber H, Ferrara N, Haigh J, Nagy A, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor a signaling in the podocyte-endothelial compartment is required for mesangial cell migration and survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17(3):724–735.
Article7. Bollee G, Patey N, Cazajous G, Robert C, Goujon JM, Fakhouri F, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy secondary to VEGF pathway inhibition by sunitinib. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009; 24(2):682–685.
Article8. Haddad RI, Schlumberger M, Wirth LJ, Sherman EJ, Shah MH, Robinson B, et al. Incidence and timing of common adverse events in Lenvatinib-treated patients from the SELECT trial and their association with survival outcomes. Endocrine. 2017; 56(1):121–128.
Article9. Cavalieri S, Cosmai L, Genderini A, Nebuloni M, Tosoni A, Favales F, et al. Lenvatinib-induced renal failure: two first-time case reports and review of literature. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2018; 14(4):379–385.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Metastasis from Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma with Lenvatinib
- A Case of Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia in a Thyroid Cancer Patient Receiving Lenvatinib
- Augmentation of Radioiodine Uptake by Pulmonary Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated with Dabrafenib and Trametinib
- Management of Bleeding Induced by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Radioiodine Refractory Thyroid Cancer
- Recent Advances in Radioiodine Therapy for Thyroid Cancer