Diabetes Metab J.
2021 Sep;45(5):708-718. 10.4093/dmj.2020.0117.
Screening Tools Based on Nomogram for Diabetic Kidney Diseases in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1ADR Monitoring Department, Henan Medical Products Administration & Center for ADR Monitoring of Henan, Zhengzhou, China
- 2Zhengzhou University Affiliated Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 4Department of Infection Control, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 5Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, College of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 6Department of Nephrology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- KMID: 2520853
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0117
Abstract
- Background
The influencing factors of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were explored to develop and validate a DKD diagnostic tool based on nomogram approach for patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 2,163 in-hospital patients with diabetes diagnosed from March 2015 to March 2017 were enrolled. Specified logistic regression models were used to screen the factors and establish four different diagnostic tools based on nomogram according to the final included variables. Discrimination and calibration were used to assess the performance of screening tools.
Results
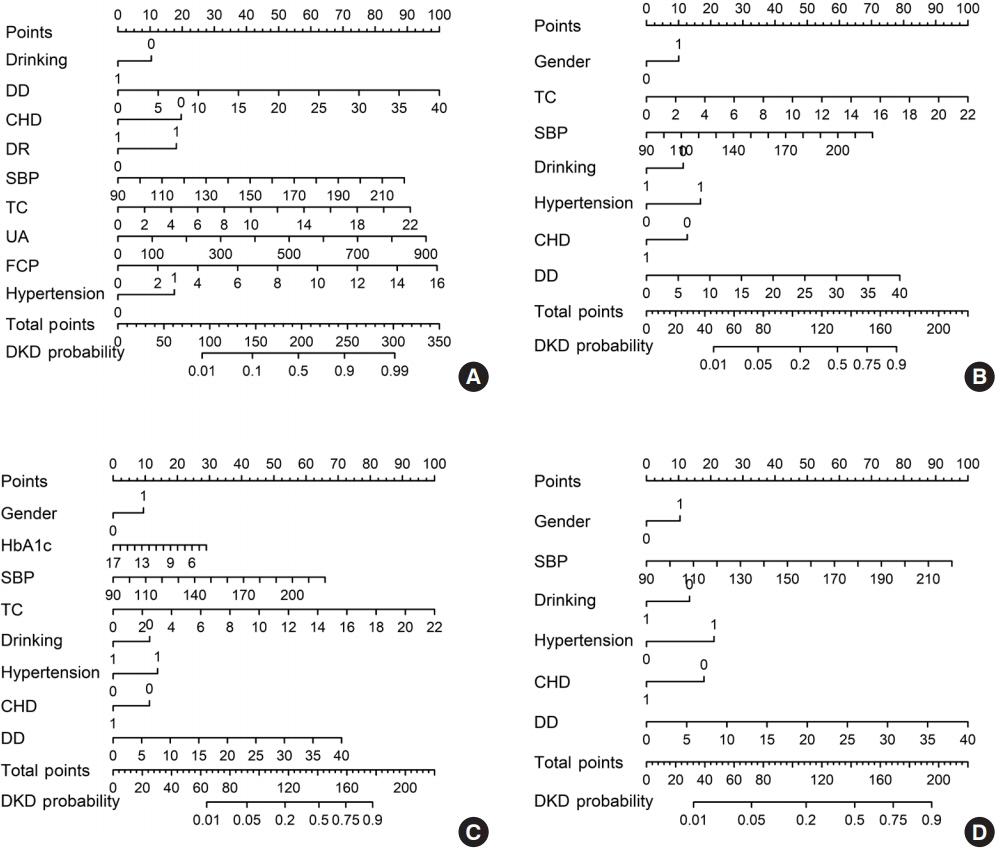
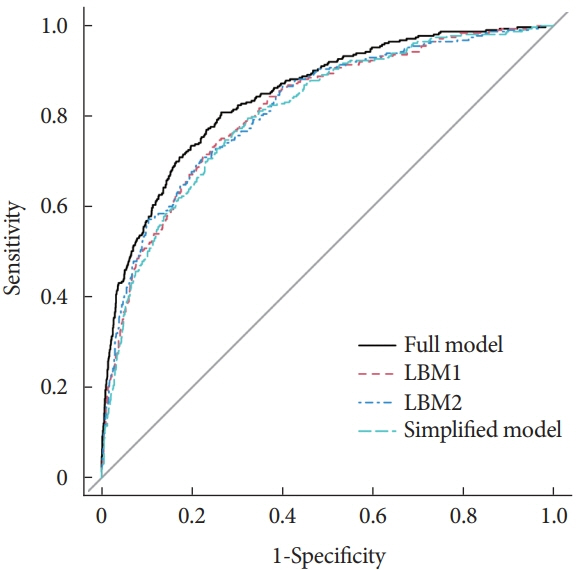
Among the 2,163 participants with diabetes (1,227 men and 949 women), 313 patients (194 men and 120 women) were diagnosed with DKD. Four different screening equations (full model, laboratory-based model 1 [LBM1], laboratory-based model 2 [LBM2], and simplified model) showed good discriminations and calibrations. The C-indexes were 0.8450 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.8202 to 0.8690) for full model, 0.8149 (95% CI, 0.7892 to 0.8405) for LBM1, 0.8171 (95% CI, 0.7912 to 0.8430) for LBM2, and 0.8083 (95% CI, 0.7824 to 0.8342) for simplified model. According to Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, good agreement between the predicted and observed DKD events in patients with diabetes was observed for full model (χ2=3.2756, P=0.9159), LBM1 (χ2=7.749, P=0.4584), LBM2 (χ2=10.023, P=0.2634), and simplified model (χ2=12.294, P=0.1387).
Conclusion
LBM1, LBM2, and simplified model exhibited excellent predictive performance and availability and could be recommended for screening DKD cases among Chinese patients with diabetes.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lewis G, Maxwell AP. Risk factor control is key in diabetic nephropathy. Practitioner. 2014; 258:13–7.2. KDOQI. Guideline 2: management of hyperglycemia and general diabetes care in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007; 49(2 Suppl 2):S62–73.3. World Health Organization. WHO Global report on diabetes. Geneva: WHO;2016.4. Liu M, Wang J, He Y, Jiang B, Wu L, Wang Y, et al. Awareness, treatment and control of type 2 diabetes among Chinese elderly and its changing trend for past decade. BMC Public Health. 2016; 16:278.
Article5. Quan J, Li TK, Pang H, Choi CH, Siu SC, Tang SY, et al. Diabetes incidence and prevalence in Hong Kong, China during 2006-2014. Diabet Med. 2017; 34:902–8.
Article6. Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, Huang Z, Zhang D, Deng Q, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA. 2017; 317:2515–23.
Article7. Grimes DA. The nomogram epidemic: resurgence of a medical relic. Ann Intern Med. 2008; 149:273–5.
Article8. Balachandran VP, Gonen M, Smith JJ, DeMatteo RP. Nomograms in oncology: more than meets the eye. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:e173–80.
Article9. Perloff D, Grim C, Flack J, Frohlich ED, Hill M, McDonald M, et al. Human blood pressure determination by sphygmomanometry. Circulation. 1993; 88:2460–70.
Article10. Liu LS; Writing Group of 2010 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. 2010 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011; 39:579–615.11. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32 Suppl 1:S62–7.12. KDOQI. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007; 49:S12–154.13. Yang L, Shen W, Sakamoto N. Population-based study evaluating and predicting the probability of death resulting from thyroid cancer and other causes among patients with thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:468–74.
Article14. Steyerberg EW, Harrell FE Jr, Borsboom GJ, Eijkemans MJ, Vergouwe Y, Habbema JD. Internal validation of predictive models: efficiency of some procedures for logistic regression analysis. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001; 54:774–81.15. Harrell FE. Regression modeling strategies: with applications to linear models, logistic and ordinal regression, and survival analysis. Cham: Springer International Publishing;2015.16. Yang X, Li J, Hu D, Chen J, Li Y, Huang J, et al. Predicting the 10-year risks of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in Chinese population: the China-PAR Project (Prediction for ASCVD Risk in China). Circulation. 2016; 134:1430–40.17. Collins GS, Reitsma JB, Altman DG, Moons KG. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): the TRIPOD statement. BMJ. 2015; 350:g7594.
Article18. Steyerberg EW. Clinical prediction models: a practical approach to development, validation, and updating. New York: Springer;2008.19. Hosmer DW, Lemesbow S. Goodness of fit tests for the multiple logistic regression model. Commun Stat Theory Methods. 1980; 9:1043–69.
Article20. Steyerberg EW, Vickers AJ, Cook NR, Gerds T, Gonen M, Obuchowski N, et al. Assessing the performance of prediction models: a framework for traditional and novel measures. Epidemiology. 2010; 21:128–38.21. D’Agostino RB, Nam BH. Evaluation of the performance of survival analysis models: discrimination and calibration measures. Handb Stat. 2003; 23:1–25.22. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 9th ed. Brussels: IDF;2019.23. Chinese Diabetes Society; National Offic for Primary Diabetes Care. National guidelines for the prevention and control of diabetes in primary care (2018). Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2018; 57:885–93.24. Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L, Wang W, Liu B, Liu J, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2012; 379:815–22.
Article25. Lu B, Song X, Dong X, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Wen J, et al. High prevalence of chronic kidney disease in population-based patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in downtown Shanghai. J Diabetes Complications. 2008; 22:96–103.
Article26. Guo K, Zhang L, Zhao F, Lu J, Pan P, Yu H, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and associated factors in Chinese individuals with type 2 diabetes: cross-sectional study. J Diabetes Complications. 2016; 30:803–10.
Article27. Luk AO, Li X, Zhang Y, Guo X, Jia W, Li W, et al. Quality of care in patients with diabetic kidney disease in Asia: the Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) Registry. Diabet Med. 2016; 33:1230–9.
Article28. Nelson RG, Grams ME, Ballew SH, Sang Y, Azizi F, Chadban SJ, et al. Development of risk prediction equations for incident chronic kidney disease. JAMA. 2019; 322:2104–14.
Article29. Wu M, Lu J, Zhang L, Liu F, Chen S, Han Y, et al. A non-laboratory-based risk score for predicting diabetic kidney disease in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:102550–8.
Article30. Jiang W, Wang J, Shen X, Lu W, Wang Y, Li W, et al. Establishment and validation of a risk prediction model for early diabetic kidney disease based on a systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 cohorts. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:925–33.
Article31. Al-Rubeaan K, Youssef AM, Subhani SN, Ahmad NA, Al-Sharqawi AH, Al-Mutlaq HM, et al. Diabetic nephropathy and its risk factors in a society with a type 2 diabetes epidemic: a Saudi National Diabetes Registry-based study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e88956.
Article32. Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria, blood pressure and diabetic renal disease: origin and development of ideas. Diabetologia. 1999; 42:263–85.
Article33. Tseng CH. Correlation of uric acid and urinary albumin excretion rate in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Taiwan. Kidney Int. 2005; 68:796–801.
Article34. Unnikrishnan RI, Rema M, Pradeepa R, Deepa M, Shanthirani CS, Deepa R, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic nephropathy in an urban South Indian population: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES 45). Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:2019–24.
Article35. Hall ME, do Carmo JM, da Silva AA, Juncos LA, Wang Z, Hall JE. Obesity, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2014; 7:75–88.
Article36. Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR, et al. Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int. 2003; 63:225–32.
Article37. Park JY, Kim HK, Chung YE, Kim SW, Hong SK, Lee KU. Incidence and determinants of microalbuminuria in Koreans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:530–4.
Article38. Gall MA, Hougaard P, Borch-Johnsen K, Parving HH. Risk factors for development of incipient and overt diabetic nephropathy in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: prospective, observational study. BMJ. 1997; 314:783–8.
Article39. Ravid M, Brosh D, Ravid-Safran D, Levy Z, Rachmani R. Main risk factors for nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus are plasma cholesterol levels, mean blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. Arch Intern Med. 1998; 158:998–1004.
Article