Korean J healthc assoc Infect Control Prev.
2021 Jun;26(1):31-38. 10.14192/kjicp.2021.26.1.31.
Comparison of the Microbiological Efficacy of Disinfection Using Ultraviolet and Hydrogen Peroxide System for Carbapenemaseproducing Enterobacteriaceae in a Healthcare Setting
- Affiliations
-
- 1Office for Infection Control, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2516942
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14192/kjicp.2021.26.1.31
Abstract
- Background
This study aimed to compare the efficacy of microbiological disinfection between the ultraviolet-C (UV-C) device and aerosolized hydrogen peroxide (aHP) system in a healthcare setting.
Methods
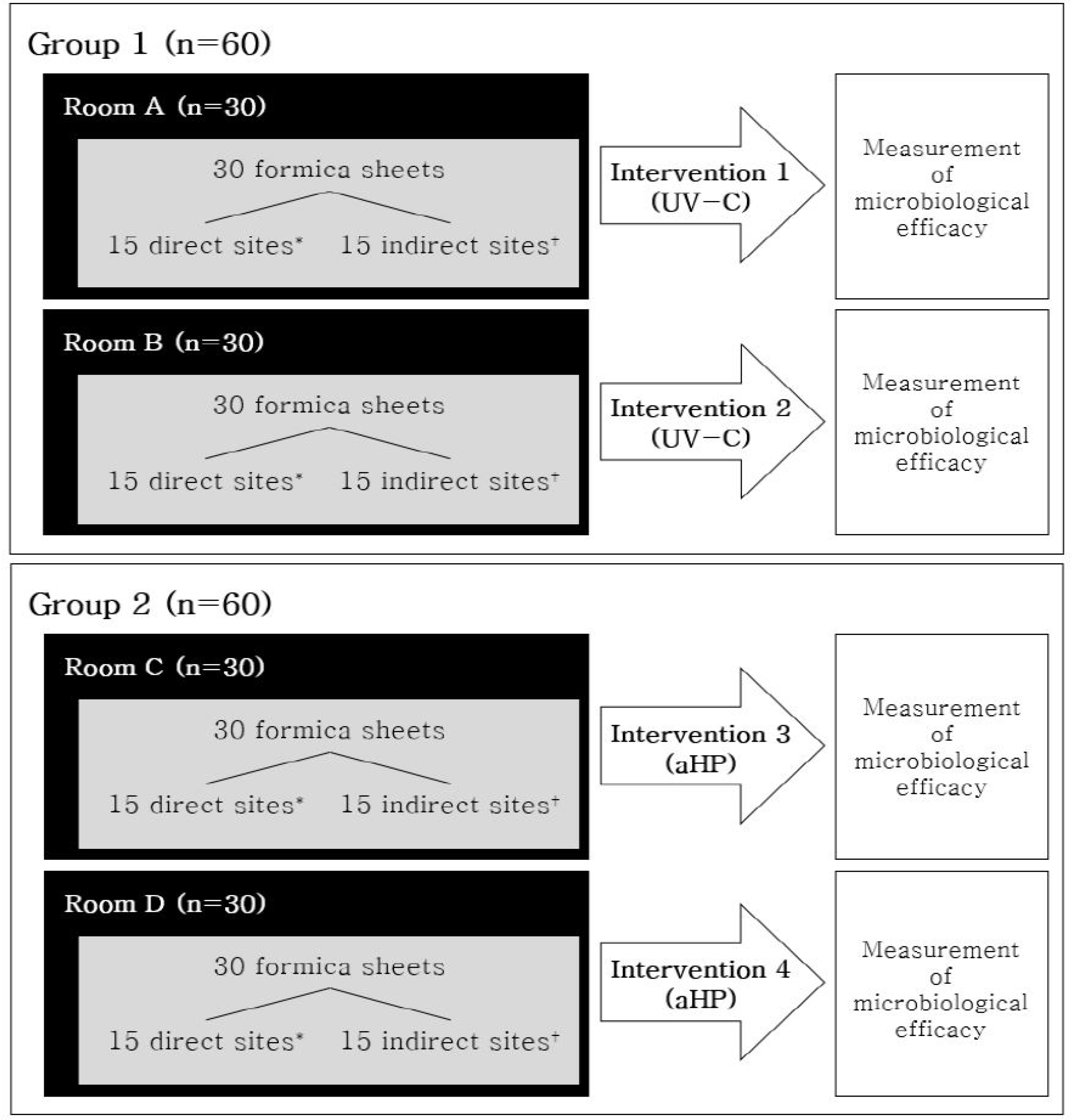
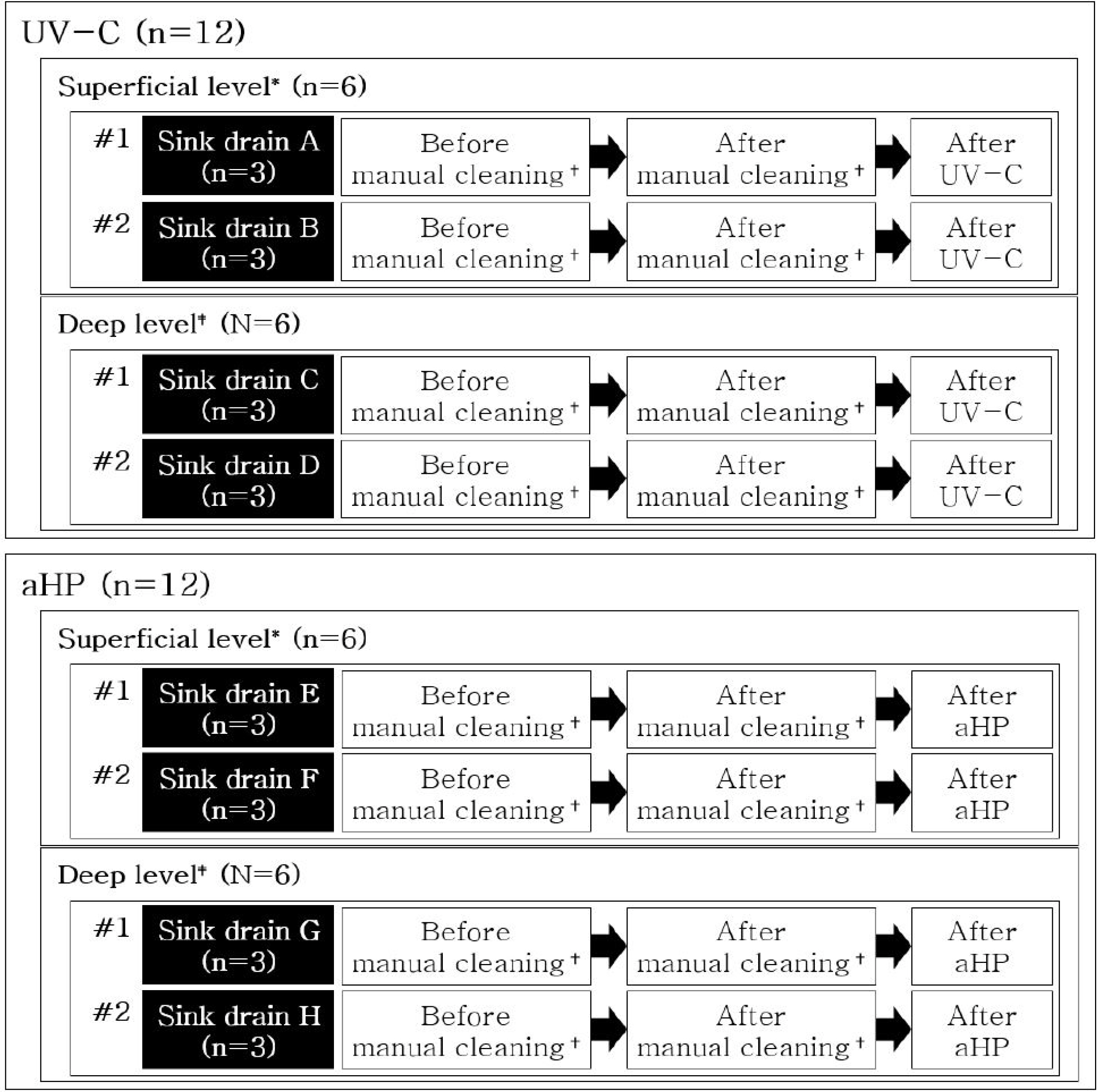
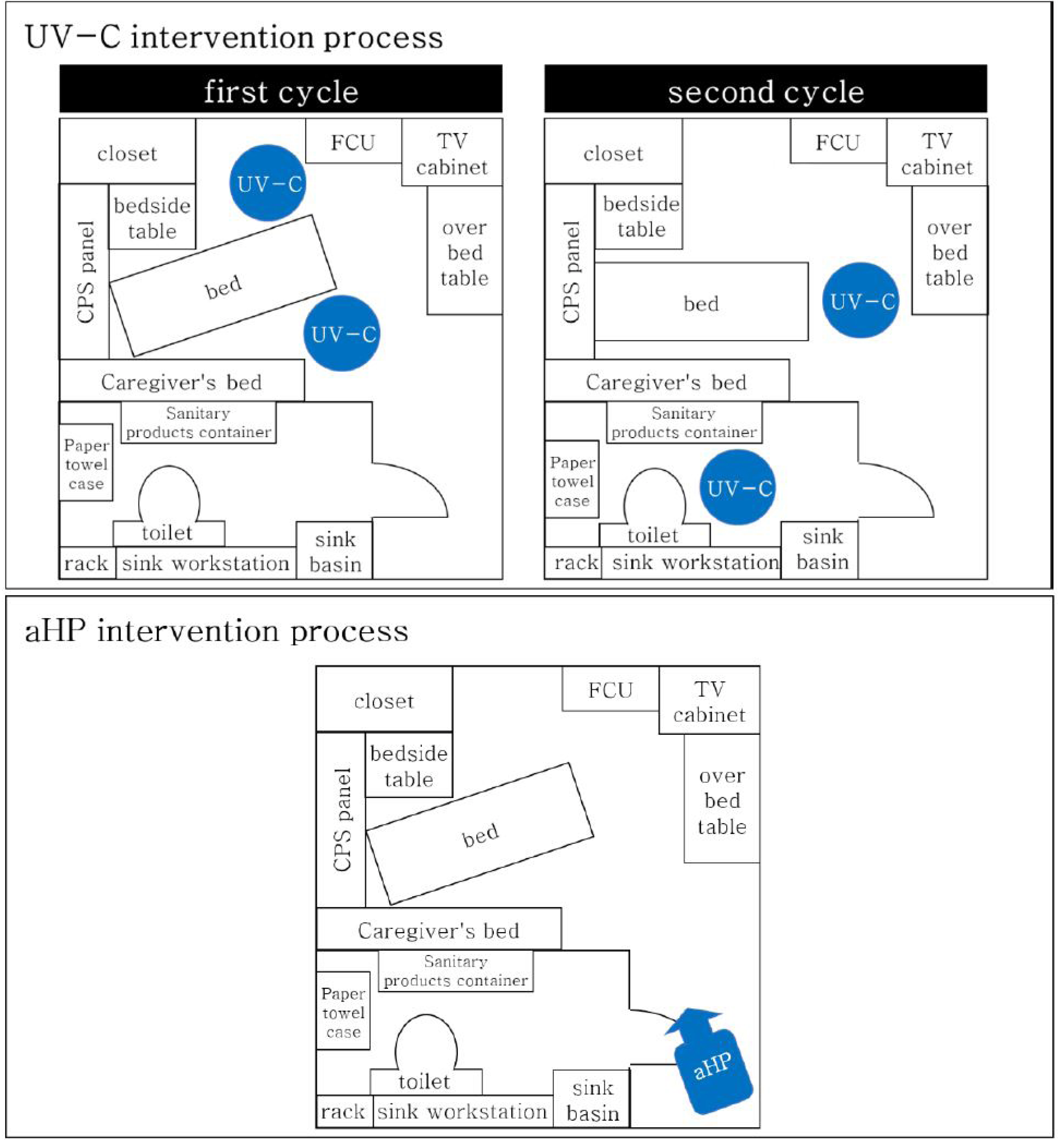
Four rooms were installed with two UV-C devices and two aHP systems. Thirty formica sheets contaminated with carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) were placed in each room. After intervention, the median log 10 reduction and modified decontamination rates were compared between the two methods using Rodac plates. Eight sink drains in the rooms previously occupied by a patient with CPE were sampled separately before and after the interventions.
Results
The median log10 reduction was 5.52 and 5.37 after the UV-C (n=60) and aHP (n=60) interventions, respectively (P=0.86), whereas the modified decontamination rate was 50% and 45%, respectively (P=0.71). At the UV-direct sites, UV-C showed higher median log 10 reduction (5.91 vs. 5.61, P=0.002) and modified decontamination rate (83% vs. 53%, P=0.03) than those of aHP. Conversely, at UV-indirect sites, aHP showed higher median log 10 reduction (4.63 vs. 5.07%, P=0.02) and modified decontamination rate (17% vs. 37%, P=0.01) than those of UV-C. After the intervention, carbapenemase-resistant Gram-negative bacilli decreased further in five of the seven sink drains disinfected by sodium.
Conclusion
Both UV-C and aHP reduced the bacterial contamination in the rooms. The aHP was significantly more effective than UV-C at the UV-indirect sites, and the converse was true for the UV-direct sites. Application of the intervention to disinfect the sink drains resulted in additional bacterial decontamination. Considering the features of the machines and the results of this study, healthcare facilities can choose either UV-C or aHP for decontamination.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Hydrogen Peroxide as a Disinfection and Sterilization Tool
Jin-Hong Yoo
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2021;26(1):1-2. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2021.26.1.1.Efficacy of Disinfection Using Activated Ionized Hydrogen Peroxide System for Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales and Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci
Keon Young Lee, Jin Young Kang, Un Young Choi, Jae Hee Lee, Nam Hee Ryu, Miri Hyun, Hyun Ah Kim, Ji Yeon Lee
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2023;28(1):99-105. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2023.28.1.99.
Reference
-
1. Lee E, Lee S, Bahk H, Kim S, Lee H. 2018; Analysis of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) surveillance results for 2017 in Korea: comparison with the surveillance results of the previous 5 years (2012-2016). Public Health Wkly Rep. 11:1586–94.2. Nordmann P, Cuzon G, Naas T. 2009; The real threat of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Lancet Infect Dis. 9:228–36. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70054-4.
Article3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Facility guidance for control of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE). Facility guidance for control of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE). https://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/cre/CRE-guidance-508.pdf . Updated on Novemver 2015.4. Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (KCDC). Guideline for control of healthcare-associated infectious diseases (VRSA, CRE). Guideline for control of healthcare-associated infectious diseases (VRSA, CRE). http://www.jcdm.or.kr/modules/user/file/2020_%EC%9D%98%EB%A3%8C%EA%B4%80%EB%A0%A8%EA%B0%90%EC%97%BC%EB%B3%91_%EA%B4%80%EB%A6%AC%EC%A7%80%EC%B9%A8.pdf . Updated on January 2020.5. Carling PC, Parry MF, Bruno-Murtha LA, Dick B. 2010; Improving environmental hygiene in 27 intensive care units to decrease multidrug-resistant bacterial transmission. Crit Care Med. 38:1054–9. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181cdf705. PMID: 20081531.
Article6. Marra AR, Schweizer ML, Edmond MB. 2018; No-touch disinfection methods to decrease multidrug-resistant organism infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 39:20–31. DOI: 10.1017/ice.2017.226. PMID: 29144223.
Article7. Weber DJ, Rutala WA, Anderson DJ, Chen LF, Sickbert-Bennett EE, Boyce JM. 2016; Effectiveness of ultraviolet devices and hydrogen peroxide systems for terminal room decontamination: focus on clinical trials. Am J Infect Control. 44(5 Suppl):e77–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajic.2015.11.015. PMID: 27131140. PMCID: PMC7132689.
Article8. Havill NL, Moore BA, Boyce JM. 2012; Comparison of the microbiological efficacy of hydrogen peroxide vapor and ultraviolet light processes for room decontamination. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 33:507–12. DOI: 10.1086/665326. PMID: 22476278.
Article9. Dancer SJ, White L, Robertson C. 2008; Monitoring environmental cleanliness on two surgical wards. Int J Environ Health Res. 18:357–64. DOI: 10.1080/09603120802102465. PMID: 18821374.
Article10. Boyce JM, Havill NL, Moore BA. 2011; Terminal decontamination of patient rooms using an automated mobile UV light unit. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 32:737–42. DOI: 10.1086/661222. PMID: 21768755.
Article11. Rutala WA, Weber DJ. Carrico R, editor. 2009. Cleaning, disinfection and sterilization. APIC text of infection control and epidemiology. 3rd ed. Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology;Washington, DC: p. 21:1–21:27.12. Huslage K, Rutala WA, Gergen MF, Sickbert-Bennett EE, Weber DJ. 2013; Microbial assessment of high-, medium-, and low-touch hospital room surfaces. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 34:211–2. DOI: 10.1086/669092. PMID: 23295570.
Article13. Nerandzic MM, Cadnum JL, Pultz MJ, Donskey CJ. 2010; Evaluation of an automated ultraviolet radiation device for decontamination of Clostridium difficile and other healthcare-associated pathogens in hospital rooms. BMC Infect Dis. 10:197. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-197. PMID: 20615229. PMCID: PMC2910020.
Article14. Boyce JM. 2016; Modern technologies for improving cleaning and disinfection of environmental surfaces in hospitals. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 5:10. DOI: 10.1186/s13756-016-0111-x. PMID: 27069623. PMCID: PMC4827199.
Article15. Doll M, Morgan DJ, Anderson D, Bearman G. 2015; Touchless technologies for decontamination in the hospital: a review of hydrogen peroxide and UV devices. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 17:498. DOI: 10.1007/s11908-015-0498-1. PMID: 26252970.
Article16. Kizny Gordon AE, Mathers AJ, Cheong EYL, Gottlieb T, Kotay S, Walker AS, et al. 2017; The hospital water environment as a reservoir for carbapenem-resistant organisms causing hospital-acquired infections-a systematic review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis. 64:1435–44. DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix132. PMID: 28200000.
Article17. Clarivet B, Grau D, Jumas-Bilak E, Jean-Pierre H, Pantel A, Parer S, et al. 2016; Persisting transmission of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae due to an environmental reservoir in a university hospital, France, 2012 to 2014. Euro Surveill. 21:30213. DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2016.21.17.30213. PMID: 27168586.
Article18. Swan JS, Deasy EC, Boyle MA, Russell RJ, O'Donnell MJ, Coleman DC. 2016; Elimination of biofilm and microbial contamination reservoirs in hospital washbasin U-bends by automated cleaning and disinfection with electrochemically activated solutions. J Hosp Infect. 94:169–74. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2016.07.007. PMID: 27485396.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Disinfection Using Activated Ionized Hydrogen Peroxide System for Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales and Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci
- A Case of Hydrogen Peroxide Induced Proctocolitis
- A simple and effective method for addition silicone impression disinfection
- Roles of clinical microbiology in hospital environmental cleaning and disinfection: a narrative review
- A Case of Hydrogen Peroxidese Induced Proctitis.