Korean J Gastroenterol.
2021 Mar;77(3):123-131. 10.4166/kjg.2020.156.
Atorvastatin Induces FXR and CYP7A1 Activation as a Result of the Sequential Action of PPARγ/PGC-1α/HNF-4α in Hep3B Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong, Korea
- KMID: 2514088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2020.156
Abstract
- Background/Aims
PPARγ, farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and CYP7A1 are associated with solubility of bile. This study was performed to understand a mechanism and interactions of statin-induced PPARγ, PGC-1α and HNF-4α related to the statin-induced activation of FXR and CYP7A1, and verify whether the mevalonate pathway is involved in the mechanism.
Methods
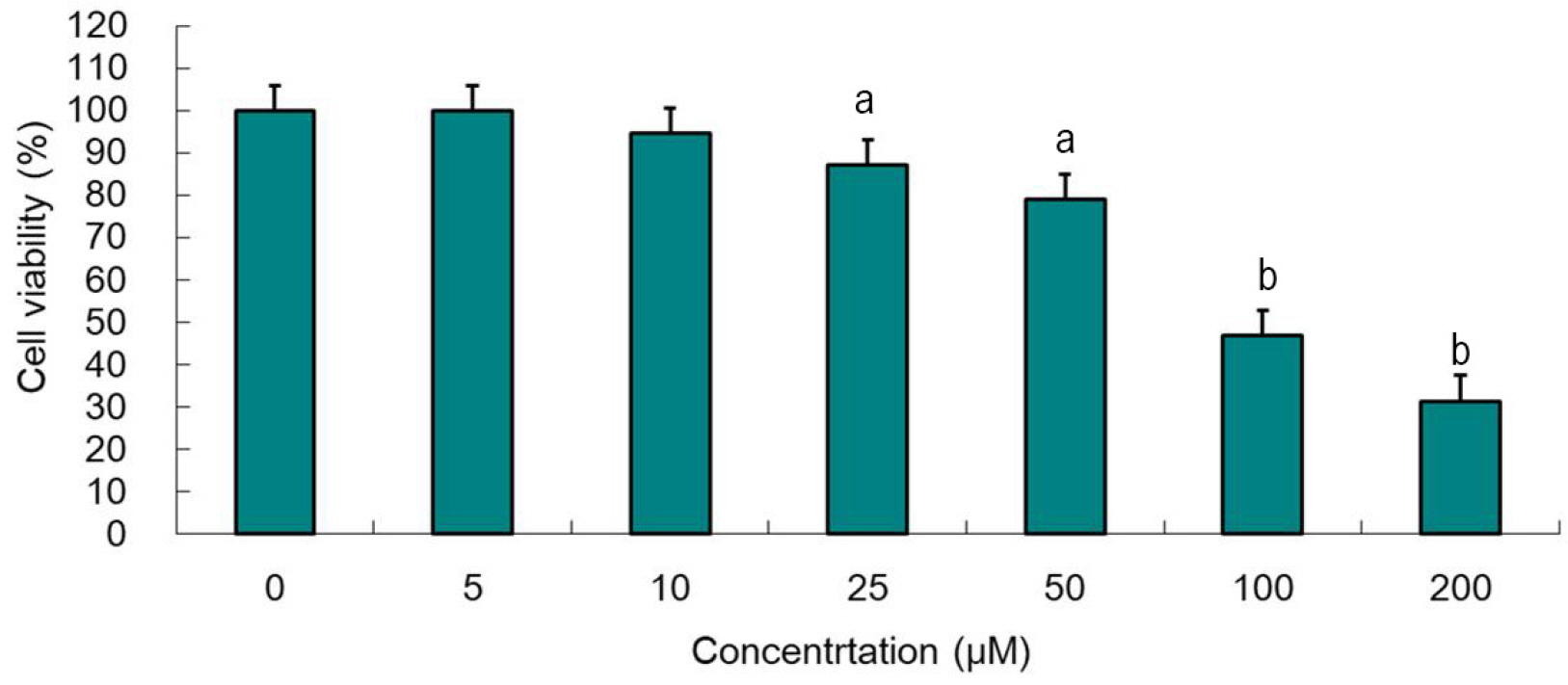
MTT assays were performed using cultured human Hep3B cells to determine the effect of atorvastatin on the cell proliferation. Expression levels of indicated proteins were measured using Western blotting assays by inhibiting the protein expression or not.
Results
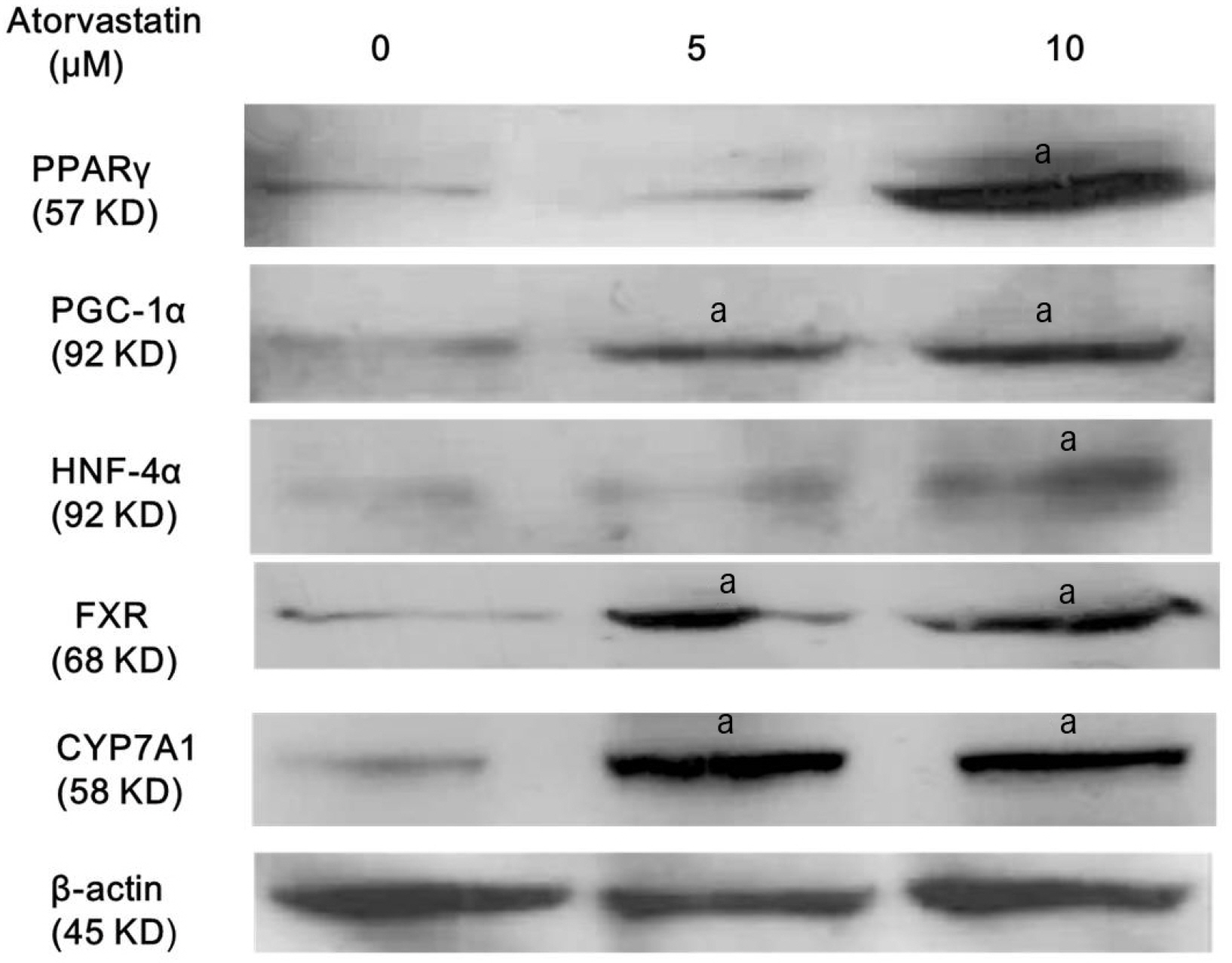
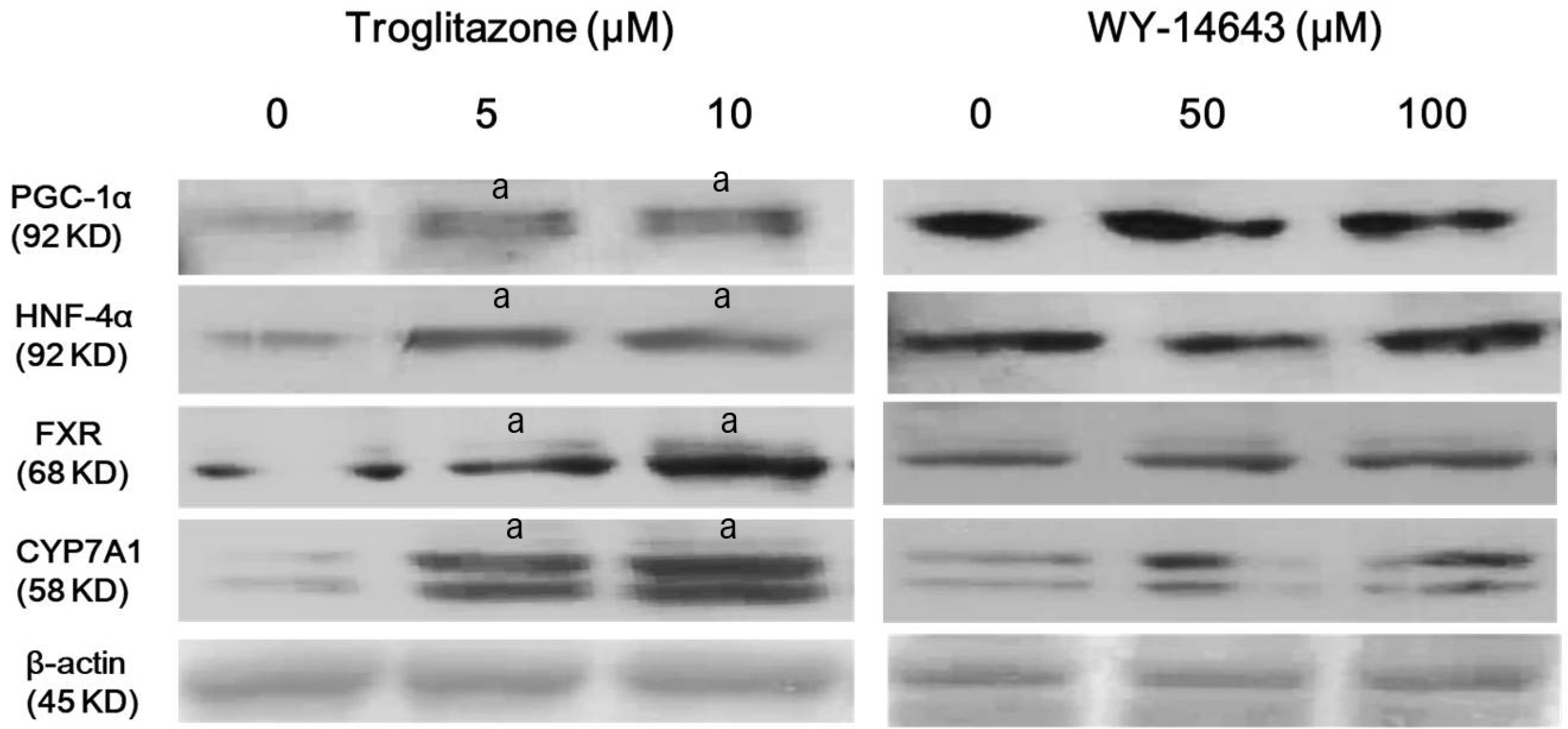
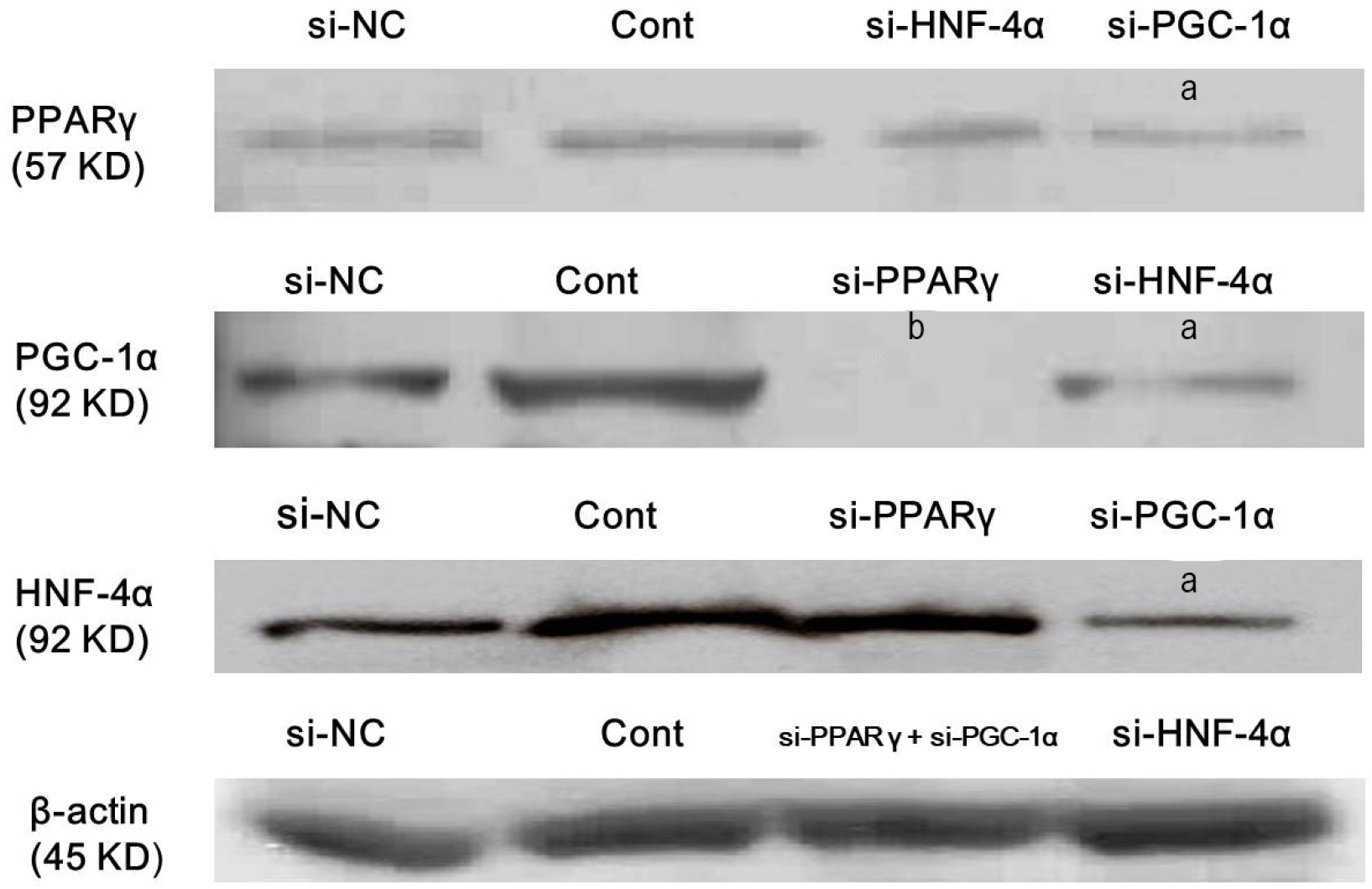
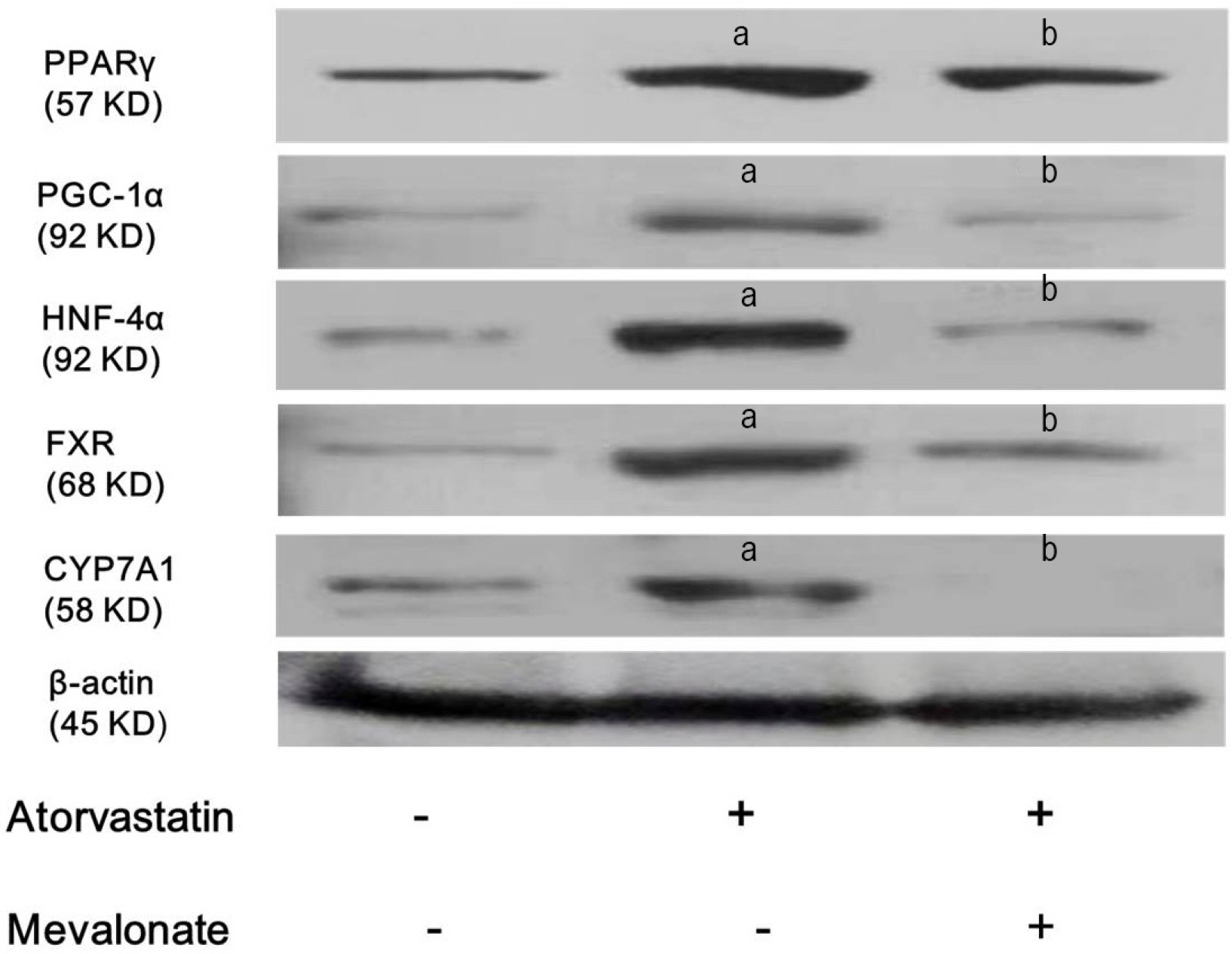
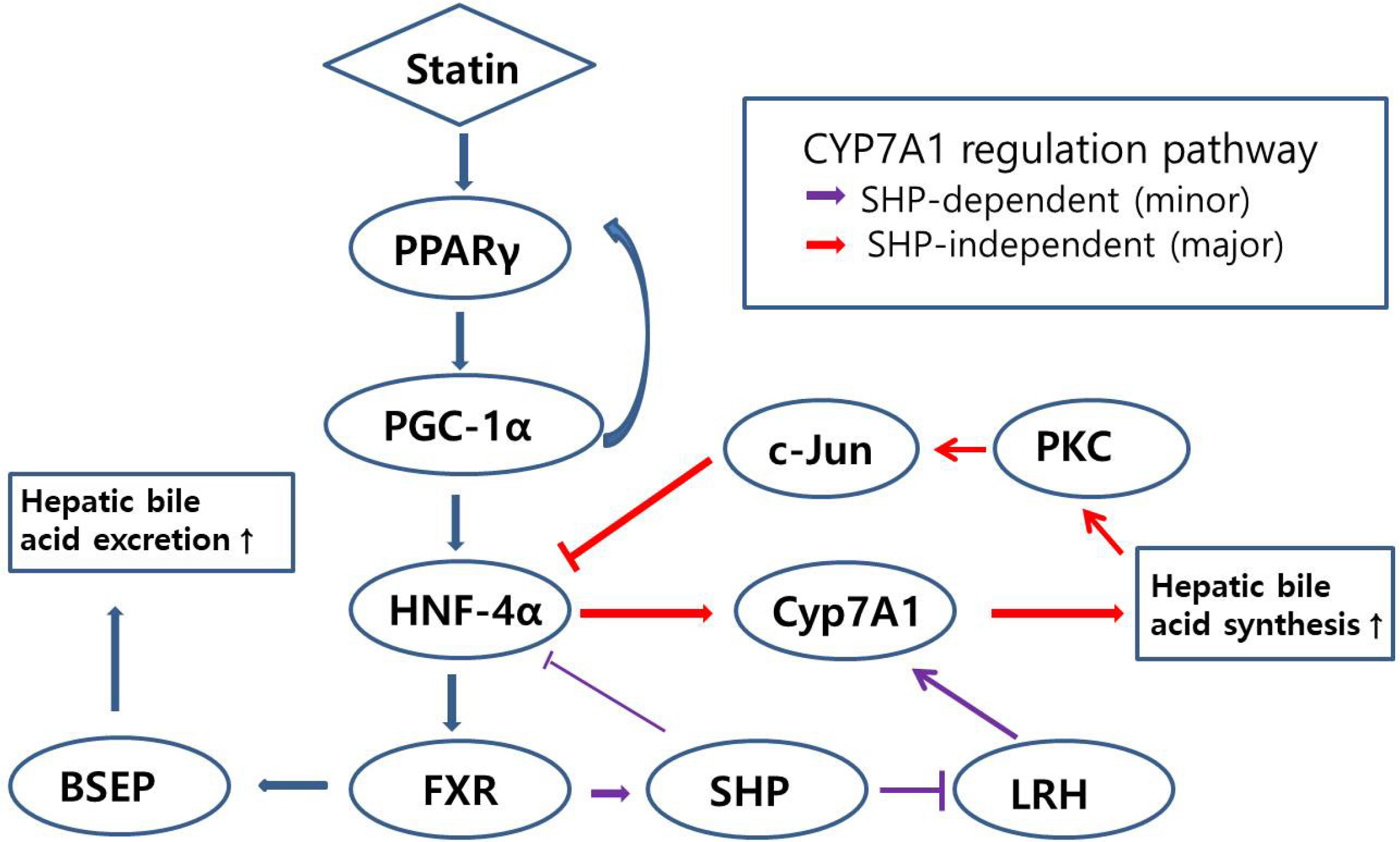
Atorvastatin increased expression of PPARγ, PGC-1α, HNF-4α, FXR, and CYP7A1 in Hep3B cells. PPARγ ligand of troglitazone upregulated the expression of PGC-1α, HNF-4α, FXR, and CYP7A1 in Hep3B cells. Silencing of PPARγ, PGC1α, and HNF4α using respective siRNA demonstrated that atorvastatin-induced FXR and CYP7A1 activation required sequential action of PPARγ /PGC-1α/HNF-4α. The silencing of PPARγ completely inhibited atorvastatin-induced PGC-1α expression, and the PGC1α silencing partially inhibited atorvastatin-induced PPARγ expression. The inhibition of HNF4α did not affect atorvastatin-induced PPARγ expression, but partially inhibited atorvastatin-induced PGC-1α expression. Besides, mevalonate completely reversed the effect of atorvastatin on PPARγ, PGC-1α, HNF-4α, FXR, and CYP7A1.
Conclusions
Atorvastatin induces FXR and CYP7A1 activation as a result of sequential action of PPARγ/PGC-1α/HNF-4α in human hepatocytes. We propose that atorvastatin enhances solubility of cholesterol in bile by simultaneously activating of FXR and CYP7A1.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gurusamy KS, Davidson BR. 2014; Gallstones. BMJ. 348:g2669. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g2669. PMID: 24755732. PMCID: PMC7919547.
Article2. Tazuma S. 2006; Gallstone disease: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and classification of biliary stones (common bile duct and intrahepatic). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 20:1075–1083. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2006.05.009. PMID: 17127189.3. Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ. 1999; Nuclear receptor regulation of cholesterol and bile acid metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 10:557–563. DOI: 10.1016/S0958-1669(99)00031-2. PMID: 10600692.
Article4. Trauner M, Halilbasic E. 2011; Nuclear receptors as new perspective for the management of liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 140:1120–1125. e1-12. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.044. PMID: 21334334.
Article5. Russell DW. 1999; Nuclear orphan receptors control cholesterol catabolism. Cell. 97:539–542. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80763-1. PMID: 10367881.
Article6. Dong SH, Lee J, Koh DH, Choi MH, Jang HJ, Kae SH. 2011; Pravastatin activates PPARalpha/PPARgamma expression in the liver and gallbladder epithelium of hamsters. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 10:185–190. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(11)60029-5. PMID: 21459726.7. Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, et al. 1999; Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 284:1362–1365. DOI: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1362. PMID: 10334992.
Article8. Wang H, Chen J, Hollister K, Sowers LC, Forman BM. 1999; Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol Cell. 3:543–553. DOI: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80348-2. PMID: 10360171.
Article9. Lee HK, Lee YK, Park SH, et al. 1998; Structure and expression of the orphan nuclear receptor SHP gene. J Biol Chem. 273:14398–14402. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14398. PMID: 9603951.10. Moschetta A, Bookout AL, Mangelsdorf DJ. 2004; Prevention of cholesterol gallstone disease by FXR agonists in a mouse model. Nat Med. 10:1352–1358. DOI: 10.1038/nm1138. PMID: 15558057.
Article11. Byun HW, Hong EM, Park SH, et al. 2014; Pravastatin activates the expression of farnesoid X receptor and liver X receptor alpha in Hep3B cells. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 13:65–73. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(14)60009-6. PMID: 24463082.
Article12. Wang W, Wong CW. 2010; Statins enhance peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha activity to regulate energy metabolism. J Mol Med (Berl). 88:309–317. DOI: 10.1007/s00109-009-0561-1. PMID: 19915805.13. Zhang Y, Castellani LW, Sinal CJ, Gonzalez FJ, Edwards PA. 2004; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) regulates triglyceride metabolism by activation of the nuclear receptor FXR. Genes Dev. 18:157–169. DOI: 10.1101/gad.1138104. PMID: 14729567. PMCID: PMC324422.14. Seo M, Inoue I, Ikeda M, et al. 2008; Statins activate human PPARalpha promoter and increase PPARalpha mRNA expression and activation in HepG2 cells. PPAR Res. 2008:316306. DOI: 10.1155/2008/316306. PMID: 19125197. PMCID: PMC2610383.15. Chiang JY, Kimmel R, Stroup D. 2001; Regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) transcription by the liver orphan receptor (LXRalpha). Gene. 262:257–265. DOI: 10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00518-7. PMID: 11179691.16. Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK, et al. 1999; Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 284:1365–1368. DOI: 10.1126/science.284.5418.1365. PMID: 10334993.
Article17. Lee FY, Lee H, Hubbert ML, Edwards PA, Zhang Y. 2006; FXR, a multipurpose nuclear receptor. Trends Biochem Sci. 31:572–580. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.08.002. PMID: 16908160.
Article18. Lee J, Hong EM, Jang JA, et al. 2016; Simvastatin induces apoptosis and suppresses insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in bile duct cancer cells. Gut Liver. 10:310–317. DOI: 10.5009/gnl15195. PMID: 26470769. PMCID: PMC4780463.
Article19. Shu N, Hu M, Ling Z, et al. 2016; The enhanced atorvastatin hepatotoxicity in diabetic rats was partly attributed to the upregulated hepatic Cyp3a and SLCO1B1. Sci Rep. 6:33072. DOI: 10.1038/srep33072. PMID: 27624558. PMCID: PMC5021965.
Article20. Wittenburg H, Lyons MA, Li R, Churchill GA, Carey MC, Paigen B. 2003; FXR and ABCG5/ABCG8 as determinants of cholesterol gallstone formation from quantitative trait locus mapping in mice. Gastroenterology. 125:868–881. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5085(03)01053-9. PMID: 12949731.
Article21. Chiang JY. 2004; Regulation of bile acid synthesis: pathways, nuclear receptors, and mechanisms. J Hepatol. 40:539–551. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2003.11.006. PMID: 15123373.
Article22. Russell DW. 2003; The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 72:137–174. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161712. PMID: 12543708.
Article23. Abrahamsson A, Gustafsson U, Ellis E, et al. 2005; Feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis in human liver: importance of HNF-4alpha for regulation of CYP7A1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 330:395–399. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.02.170. PMID: 15796896.24. Jung D, Kullak-Ublick GA. 2003; Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha: a key mediator of the effect of bile acids on gene expression. Hepatology. 37:622–631. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50100. PMID: 12601360.25. Sladek FM, Zhong WM, Lai E, Darnell JE Jr. 1990; Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 4:2353–2365. DOI: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. PMID: 2279702.
Article26. Rhee J, Inoue Y, Yoon JC, et al. 2003; Regulation of hepatic fasting response by PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1): requirement for hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha in gluconeogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100:4012–4017. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0730870100. PMID: 12651943. PMCID: PMC153039.27. Rhee J, Ge H, Yang W, et al. 2006; Partnership of PGC-1alpha and HNF4alpha in the regulation of lipoprotein metabolism. J Biol Chem. 281:14683–14690. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M512636200. PMID: 16574644.28. Lin J, Handschin C, Spiegelman BM. 2005; Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 1:361–370. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.05.004. PMID: 16054085.
Article29. Yoon JC, Puigserver P, Chen G, et al. 2001; Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Nature. 413:131–138. DOI: 10.1038/35093050. PMID: 11557972.
Article30. Dietrich CG, Martin IV, Porn AC, et al. 2007; Fasting induces basolateral uptake transporters of the SLC family in the liver via HNF4alpha and PGC1alpha. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 293:G585–G590. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00175.2007. PMID: 17640976.31. Dankel SN, Hoang T, Flågeng MH, Sagen JV, Mellgren G. 2010; cAMP-mediated regulation of HNF-4alpha depends on the level of coactivator PGC-1alpha. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803:1013–1019. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.05.008. PMID: 20670916.32. Habeos I, Ziros PG, Psyrogiannis A, Vagenakis AG, Papavassiliou AG. 2005; Statins and transcriptional regulation: the FXR connection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 334:601–605. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.06.129. PMID: 16009343.
Article33. Fu ZD, Cui JY, Klaassen CD. 2014; Atorvastatin induces bile acid-synthetic enzyme Cyp7a1 by suppressing FXR signaling in both liver and intestine in mice. J Lipid Res. 55:2576–2586. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M053124. PMID: 25278499. PMCID: PMC4242450.
Article34. Howe K, Sanat F, Thumser AE, Coleman T, Plant N. 2011; The statin class of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors demonstrate differential activation of the nuclear receptors PXR, CAR and FXR, as well as their downstream target genes. Xenobiotica. 41:519–529. DOI: 10.3109/00498254.2011.569773. PMID: 21476904.
Article35. Alawad AS, Levy C. 2016; FXR agonists: from bench to bedside, a guide for clinicians. Dig Dis Sci. 61:3395–3404. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-016-4334-8. PMID: 27734248.
Article36. Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R, Wright M, Spiegelman BM. 1998; A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell. 92:829–839. DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81410-5. PMID: 9529258.
Article37. Illingworth DR, Erkelens DW, Keller U, Thompson GR, Tikkanen MJ. 1994; Defined daily doses in relation to hypolipidaemic efficacy of lovastatin, pravastatin, and simvastatin. Lancet. 343:1554–1555. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(94)92945-9. PMID: 7911877.
Article38. Goldstein JL, Brown MS. 1990; Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 343:425–430. DOI: 10.1038/343425a0. PMID: 1967820.
Article39. Fan P, Zhang B, Kuroki S, Saku K. 2004; Pitavastatin, a potent hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitor, increases cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene expression in HepG2 cells. Circ J. 68:1061–1066. DOI: 10.1253/circj.68.1061. PMID: 15502389.
Article40. Li T, Chiang JY. 2007; A novel role of transforming growth factor beta1 in transcriptional repression of human cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene. Gastroenterology. 133:1660–1669. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.08.042. PMID: 17920062.41. Lee MS, Park JY, Freake H, Kwun IS, Kim Y. 2008; Green tea catechin enhances cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene expression in HepG2 cells. Br J Nutr. 99:1182–1185. DOI: 10.1017/S0007114507864816. PMID: 18533286.42. Shang Q, Pan L, Saumoy M, et al. 2006; The stimulatory effect of LXRalpha is blocked by SHP despite the presence of a LXRalpha binding site in the rabbit CYP7A1 promoter. J Lipid Res. 47:997–1004. DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M500449-JLR200. PMID: 16489206.43. Jiang W, Miyamoto T, Kakizawa T, et al. 2006; Inhibition of LXRalpha signaling by vitamin D receptor: possible role of VDR in bile acid synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:176–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.027. PMID: 17054913.44. Martínez-Jiménez CP, Castell JV, Gómez-Lechón MJ, Jover R. 2006; Transcriptional activation of CYP2C9, CYP1A1, and CYP1A2 by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha requires coactivators peroxisomal proliferator activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha and steroid receptor coactivator 1. Mol Pharmacol. 70:1681–1692. DOI: 10.1124/mol.106.025403. PMID: 16882880.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Melatonin-Induced PGC-1α Improves Angiogenic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Hindlimb Ischemia
- Role of HIF-1α in the Responses of Tumors to Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
- Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract and Gypenoside L enhance skeletal muscle differentiation and mitochondrial metabolism by activating the PGC-1α pathway in C2C12 myotubes
- Hypothermia protects against renal fibrosis after ischemia reperfusion injury
- Voluntary Wheel Running Exercise Improves Aging-Induced Sarcopenia via Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator-1α/Fibronectin Type III Domain-Containing Protein 5/Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway