J Pathol Transl Med.
2021 Mar;55(2):125-131. 10.4132/jptm.2021.01.17.
MicroRNA-552 expression in colorectal cancer and its clinicopathological significance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2513898
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2021.01.17
Abstract
- Background
MicroRNA-552 (miR-552) has been reported to correlate with the development and progression of various cancers, including colorectal cancer (CRC). This study aimed to investigate miR-552 expression in cancer tissue samples compared to normal mucosal tissue and its role as a diagnostic or prognostic marker in CRC patients.
Methods
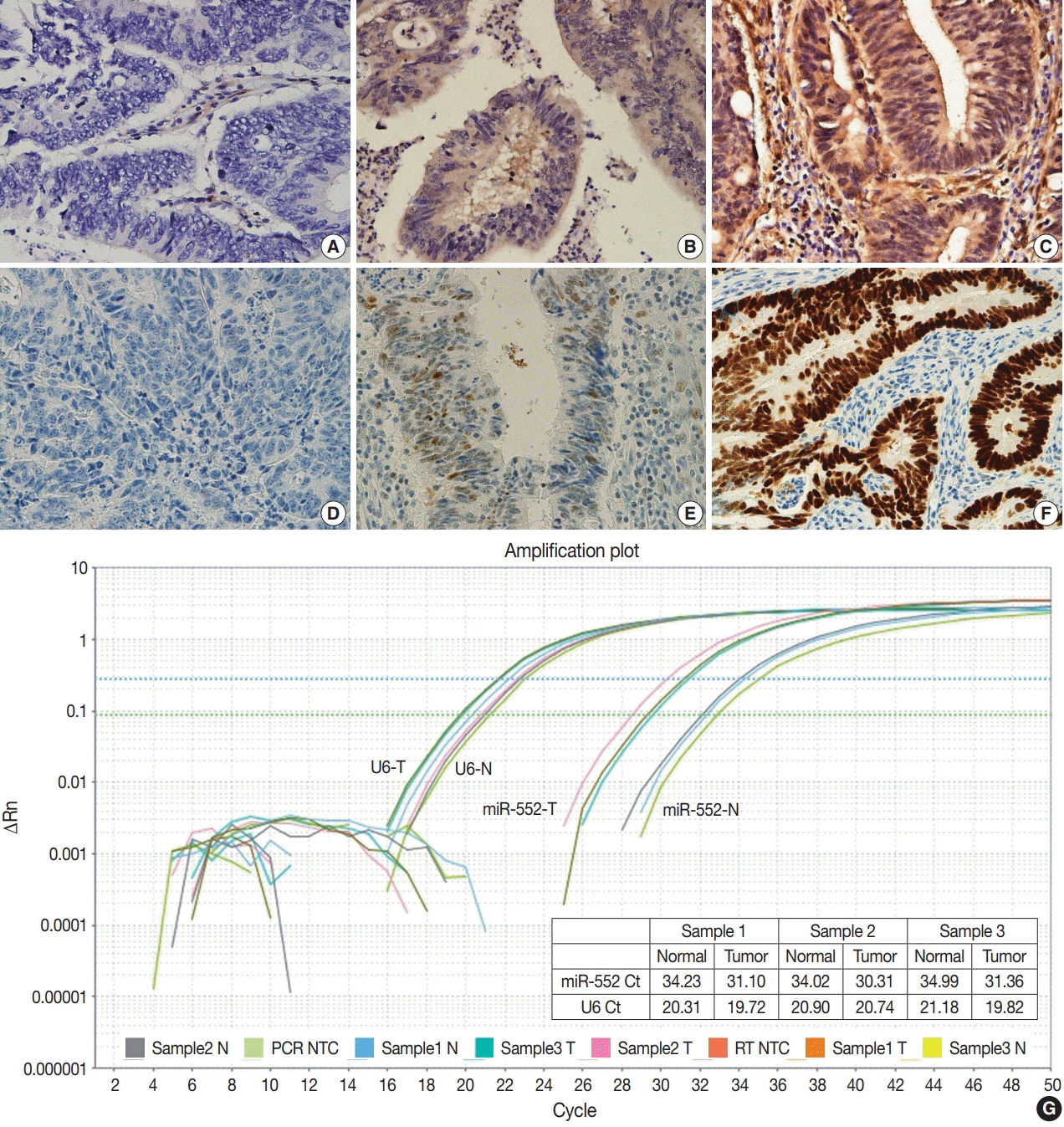
Normal mucosal tissues and primary cancer tissues from 80 surgically resected CRC specimens were used. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed for miR-552 and U6 small nuclear RNA to analyze miR-552 expression and its clinicopathological significance. Immunohistochemistry for p53 and phosphatase and tension homolog (PTEN) was performed to evaluate their association with miR-552 expression.
Results
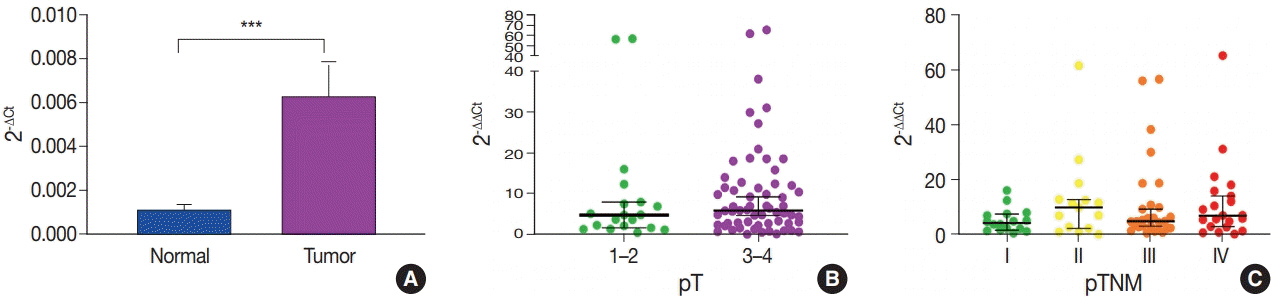
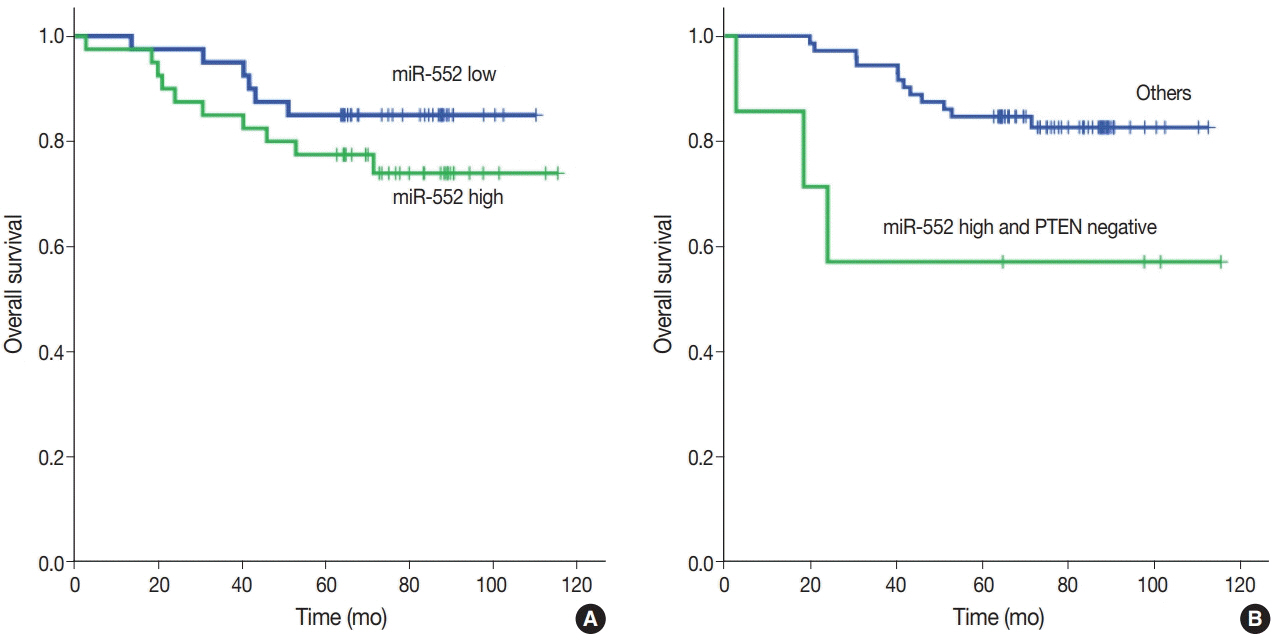
miR-552 expression was significantly higher in primary cancer tissues compared to normal mucosal tissues (p<.001). The expression level of miR552 was inversely correlated with that of PTEN (p=.068) and p53 (p=.004). Survival analysis showed that high miR-552 expression was associated with worse prognosis but this was not statistically significant (p=.255). However, patients with CRC having high miR-552 expression and loss of PTEN expression had significantly worse prognosis than others (p=.029).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that high miR-552 expression might be a potential diagnostic biomarker for CRC, and its combined analysis with PTEN expression can possibly be used as a prognostic marker.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424.
Article2. Hong S, Won YJ, Park YR, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2017. Cancer Res Treat. 2020; 52:335–50.
Article3. Markowitz SD, Bertagnolli MM. Molecular origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2449–60.4. Luo X, Burwinkel B, Tao S, Brenner H. MicroRNA signatures: novel biomarker for colorectal cancer? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011; 20:1272–86.
Article5. Koga Y, Yasunaga M, Takahashi A, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of exfoliated colonocytes isolated from feces for colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010; 3:1435–42.
Article6. Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 2005; 37:495–500.
Article7. Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993; 75:843–54.
Article8. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–97.9. Jeffrey SS. Cancer biomarker profiling with microRNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2008; 26:400–1.
Article10. Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101:2999–3004.
Article11. Ji J, Yamashita T, Wang XW. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activates microRNA-181 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biosci. 2011; 1:4.
Article12. Kim NH, Kim HS, Kim NG, et al. p53 and microRNA-34 are suppressors of canonical Wnt signaling. Sci Signal. 2011; 4:ra71.
Article13. Cai J, Guan H, Fang L, et al. MicroRNA-374a activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling to promote breast cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2013; 123:566–79.14. Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:857–66.
Article15. Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005; 435:834–8.
Article16. Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103:2257–61.
Article17. Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA-cancer connection: the beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:7390–4.
Article18. Hayes J, Peruzzi PP, Lawler S. MicroRNAs in cancer: biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol Med. 2014; 20:460–9.
Article19. Wang N, Liu W. Increased expression of miR-552 acts as a potential predictor biomarker for poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018; 22:412–6.20. Xia ZS, Wang L, Yu T, et al. MiR-5000-3p, miR-5009-3P and miR-552: potential microRNA biomarkers of side population cells in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 2014; 32:589–96.
Article21. Oberg AL, French AJ, Sarver AL, et al. miRNA expression in colon polyps provides evidence for a multihit model of colon cancer. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e20465.
Article22. Kwak B, Kim DU, Kim TO, Kim HS, Kim SW. MicroRNA-552 links Wnt signaling to p53 tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2018; 53:1800–8.
Article23. Cao J, Yan XR, Liu T, et al. MicroRNA-552 promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration by directly targeting DACH1 via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2017; 14:3795–802.24. Zhao W, Han T, Li B, Ma Q, Yang P, Li H. miR-552 promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating PTEN pathway. J Ovarian Res. 2019; 12:121.
Article25. Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, et al. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology. 2020; 76:182–8.
Article26. Weiser MR. AJCC 8th Edition: Colorectal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018; 25:1454–5.
Article27. Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc. 2008; 3:1101–8.
Article28. Hwang HJ, Nam SK, Park H, et al. Prediction of TP53 mutations by p53 immunohistochemistry and their prognostic significance in gastric cancer. J Pathol Transl Med. 2020; 54:378–86.29. Tong F, Ying Y, Pan H, Zhao W, Li H, Zhan X. MicroRNA-466 (miR-466) functions as a tumor suppressor and prognostic factor in colorectal cancer (CRC). Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018; 18:252–9.
Article30. Kim HK, Lim NJ, Jang SG, Lee GK. miR-592 and miR-552 can distinguish between primary lung adenocarcinoma and colorectal cancer metastases in the lung. Anticancer Res. 2014; 34:2297–302.31. Qu W, Wen X, Su K, Gou W. MiR-552 promotes the proliferation, migration and EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting AJAP1 expression. J Cell Mol Med. 2019; 23:1541–52.32. Chen T, Lei S, Zeng Z, et al. Linc00261 inhibits metastasis and the WNT signaling pathway of pancreatic cancer by regulating a miR-5525p/FOXO3 axis. Oncol Rep. 2020; 43:930–42.
Article33. Li C, Wang Z, Chen S, Zhang J, Qu K, Liu C. MicroRNA-552 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by downregulating WIF1. Int J Mol Med. 2018; 42:3309–17.
Article34. Maehama T, Dixon JE. The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:13375–8.
Article35. Xiong B, Cheng Y, Ma L, Zhang C. MiR-21 regulates biological behavior through the PTEN/PI-3 K/Akt signaling pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2013; 42:219–28.
Article36. Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002; 2:489–501.37. Brandmaier A, Hou SQ, Shen WH. Cell cycle control by PTEN. J Mol Biol. 2017; 429:2265–77.
Article38. Miyashita T, Reed JC. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell. 1995; 80:293–9.
Article39. Somasundaram K. Tumor suppressor p53: regulation and function. Front Biosci. 2000; 5:D424–37.
Article40. Han T, Zhang Y, Yang X, et al. miR-552 regulates liver tumor-initiating cell expansion and sorafenib resistance. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020; 19:1073–85.
Article41. Bi X, Lv X, Liu D, et al. METTL3-mediated maturation of miR126-5p promotes ovarian cancer progression via PTEN-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 2020 Sep 16 [Epub]. https://10.1038/s41417-020-00222-3.
Article42. Lee KS, Nam SK, Koh J, et al. Stromal expression of microRNA-21 in advanced colorectal cancer patients with distant metastases. J Pathol Transl Med. 2016; 50:270–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stromal Expression of MicroRNA-21 in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients with Distant Metastases
- Clinical Significance of p53 and Ki-67 Expression in Colorectal Cancer
- Prognostic Implications of MicroRNA-21 Overexpression in Invasive Ductal Carcinomas of the Breast
- Expression of RhoA in Colorectal Cancers and Its Clinicopathological Significance
- The Long Noncoding RNA DUXAP8 Facilitates the Malignant Progression of Colon Cancer via the microRNA-378a-3p/FOXQ1 Axis