Effects of Microbiota on the Treatment of Obesity with the Natural Product Celastrol in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, Center for Global Health, School of Public Health, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
- 2Key Laboratory of Modern Toxicology of Ministry of Education, School of Public Health, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
- KMID: 2513036
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0124
Abstract
Background Obesity has become one of the most serious issues threatening the health of humankind, and we conducted this study to examine whether and how celastrol protects against obesity.
Methods We fed male Sprague-Dawley rats a high-fat diet and administered celastrol to obese rats for 3 weeks. By recording body weight (BW) and other measures, we identified the effective dose of celastrol for obesity treatment. Feces were collected to perform 16S rRNA sequencing, and hypothalami were extracted for transcriptome sequencing. We then treated leptin knockout rats with celastrol and explored the changes in energy metabolism. Male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice were used to test the acute toxicity of celastrol.
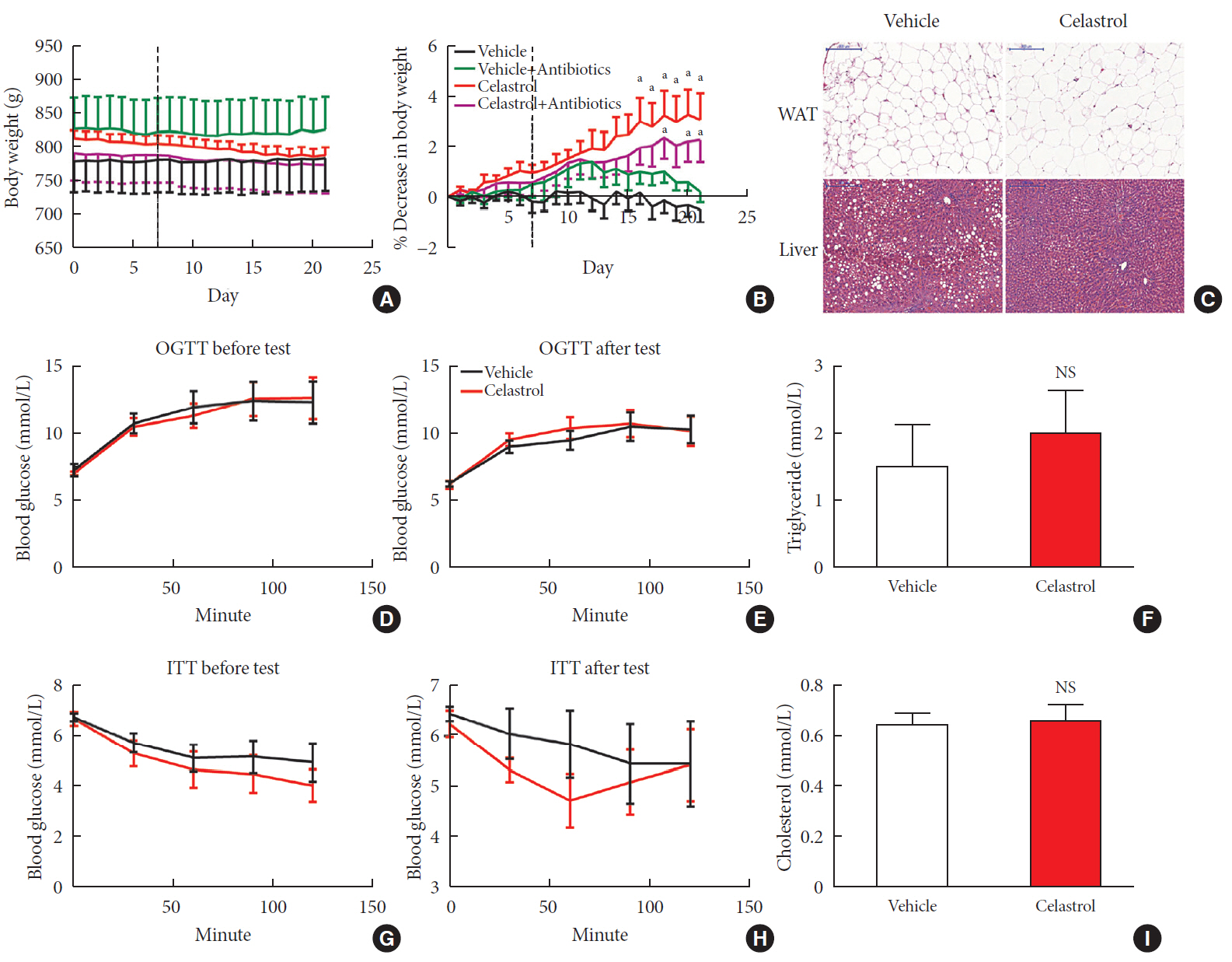
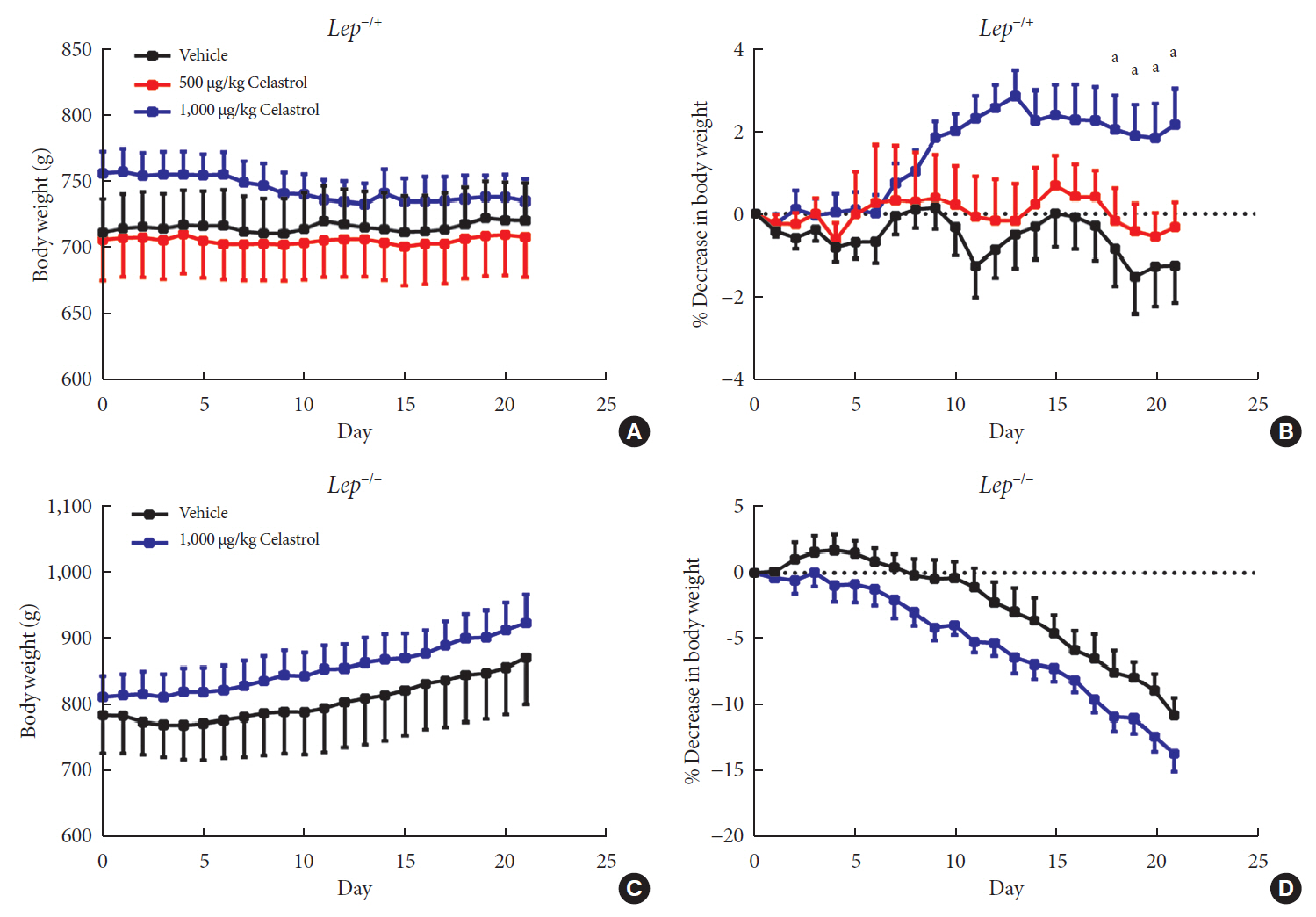
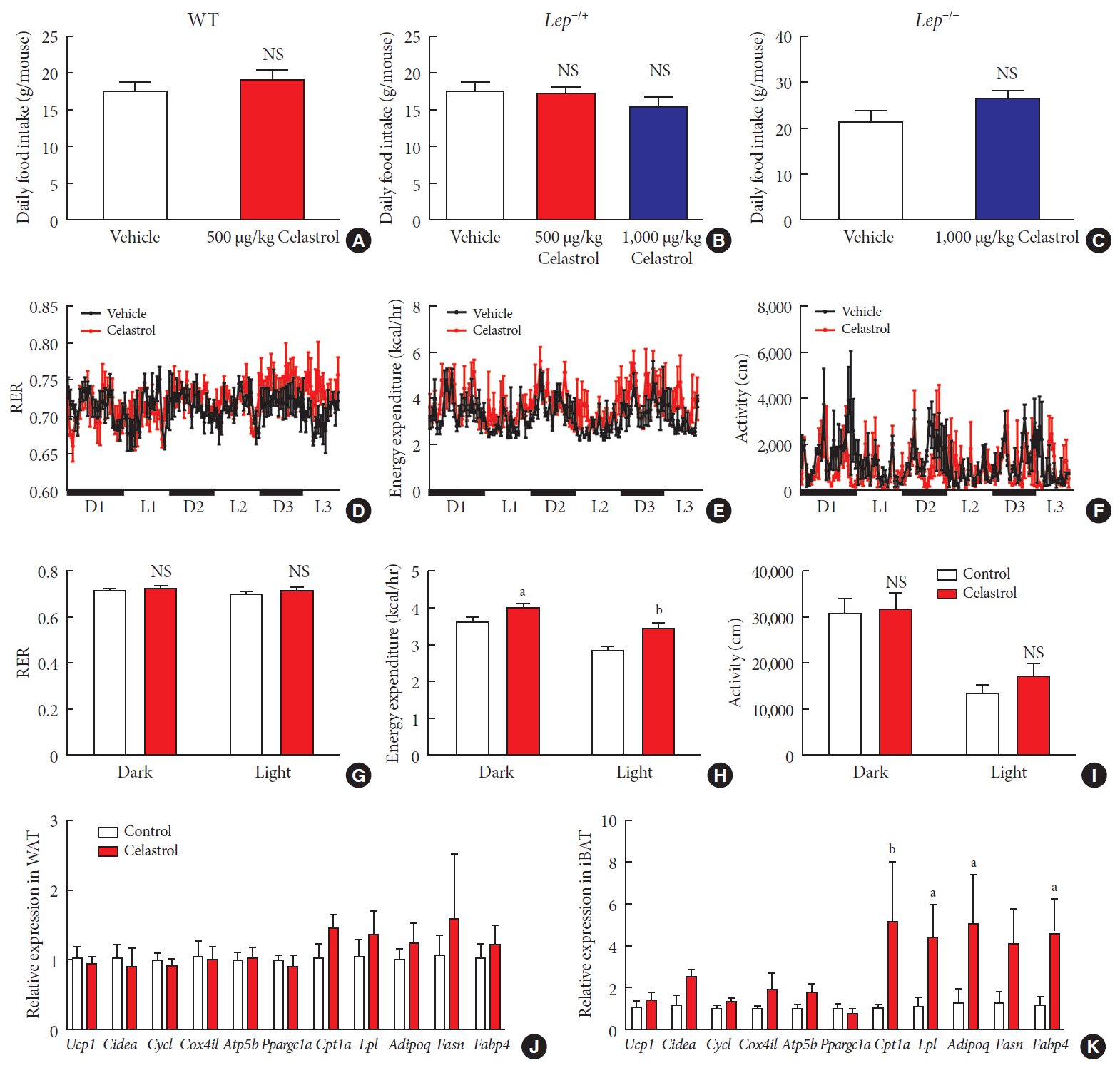
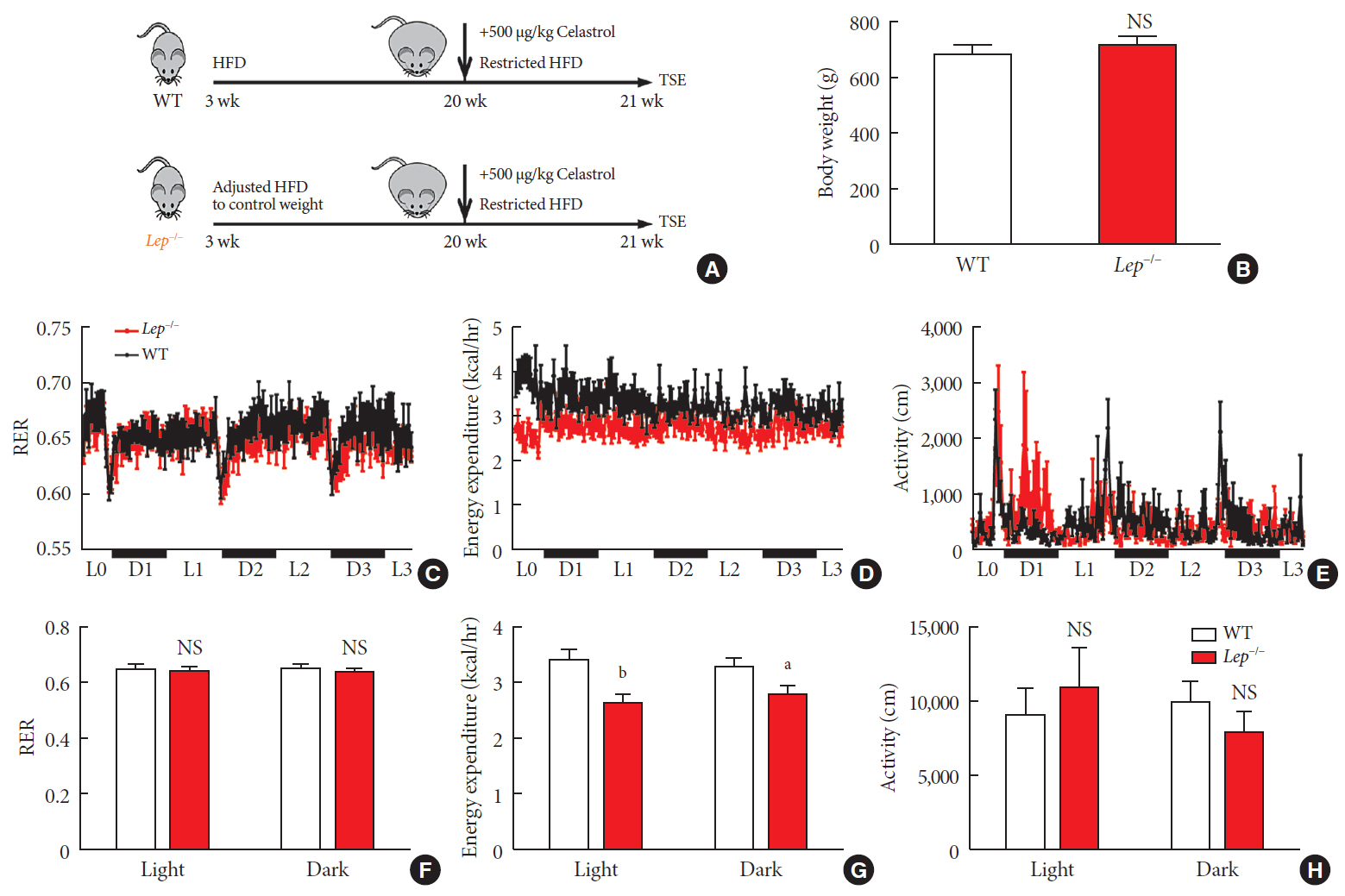
Results We observed that celastrol reduced BW and promoted energy expenditure at a dose of 500 µg/kg BW but that food intake was not changed after administration. The diversity of the gut microbiota was improved, with an increased ratio of
Bacteroidetes toFirmicutes , and the gut microbiota played an important role in the anti-obesity effects of celastrol. Hypothalamic transcriptome analysis showed a significant enrichment of the leptin signaling pathway, and we found that celastrol significantly enhanced energy expenditure, which was mediated by the leptin signaling pathway. Acute lethal toxicity of celastrol was not observed at doses ranging from 0 to 62.5 mg/kg BW.Conclusion Our study revealed that celastrol decreased the BW of obese rats by enhancing energy expenditure but not by suppressing food intake and that this effect was mediated by the improvement of the gut microbiota and the activation of the hypothalamic leptin signaling pathway.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yoshimoto S, Loo TM, Atarashi K, Kanda H, Sato S, Oyadomari S, Iwakura Y, Oshima K, Morita H, Hattori M, Honda K, Ishikawa Y, Hara E, Ohtani N. Obesity-induced gut microbial metabolite promotes liver cancer through senescence secretome. Nature. 2013; 499:97–101.
Article2. Tseng YH, Cypess AM, Kahn CR. Cellular bioenergetics as a target for obesity therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010; 9:465–482.
Article3. Al-Najim W, Docherty NG, le Roux CW. food intake and eating behavior after bariatric surgery. Physiol Rev. 2018; 98:1113–1141.
Article4. Cone RD. Studies on the physiological functions of the melanocortin system. Endocr Rev. 2006; 27:736–749.
Article5. Sohn JW, Elmquist JK, Williams KW. Neuronal circuits that regulate feeding behavior and metabolism. Trends Neurosci. 2013; 36:504–512.
Article6. Gropp E, Shanabrough M, Borok E, Xu AW, Janoschek R, Buch T, Plum L, Balthasar N, Hampel B, Waisman A, Barsh GS, Horvath TL, Bruning JC. Agouti-related peptide-expressing neurons are mandatory for feeding. Nat Neurosci. 2005; 8:1289–1291.
Article7. Paz-Filho G, Mastronardi CA, Licinio J. Leptin treatment: facts and expectations. Metabolism. 2015; 64:146–156.
Article8. Saltiel AR. New therapeutic approaches for the treatment of obesity. Sci Transl Med. 2016; 8:323rv2.
Article9. Chang CJ, Lin CS, Lu CC, Martel J, Ko YF, Ojcius DM, Tseng SF, Wu TR, Chen YY, Young JD, Lai HC. Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:7489.
Article10. Wu TR, Lin CS, Chang CJ, Lin TL, Martel J, Ko YF, Ojcius DM, Lu CC, Young JD, Lai HC. Gut commensal Parabacteroides goldsteinii plays a predominant role in the anti-obesity effects of polysaccharides isolated from Hirsutella sinensis. Gut. 2019; 68:248–262.
Article11. Zhang Z, Zhang H, Li B, Meng X, Wang J, Zhang Y, Yao S, Ma Q, Jin L, Yang J, Wang W, Ning G. Berberine activates thermogenesis in white and brown adipose tissue. Nat Commun. 2014; 5:5493.
Article12. Kannaiyan R, Shanmugam MK, Sethi G. Molecular targets of celastrol derived from Thunder of God Vine: potential role in the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2011; 303:9–20.
Article13. Guo L, Luo S, Du Z, Zhou M, Li P, Fu Y, Sun X, Huang Y, Zhang Z. Targeted delivery of celastrol to mesangial cells is effective against mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:878.
Article14. Liu J, Lee J, Salazar Hernandez MA, Mazitschek R, Ozcan U. Treatment of obesity with celastrol. Cell. 2015; 161:999–1011.
Article15. Greenhill C. Celastrol identified as a leptin sensitizer and potential novel treatment for obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015; 11:444.
Article16. Ma X, Xu L, Alberobello AT, Gavrilova O, Bagattin A, Skarulis M, Liu J, Finkel T, Mueller E. Celastrol protects against obesity and metabolic dysfunction through activation of a HSF1-PGC1α transcriptional axis. Cell Metab. 2015; 22:695–708.
Article17. Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, Griffin NW, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Ilkayeva O, Semenkovich CF, Funai K, Hayashi DK, Lyle BJ, Martini MC, Ursell LK, Clemente JC, Van Treuren W, Walters WA, Knight R, Newgard CB, Heath AC, Gordon JI. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science. 2013; 341:1241214.
Article18. Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature. 2006; 444:1027–1031.
Article19. Zhao L, Zhang F, Ding X, Wu G, Lam YY, Wang X, Fu H, Xue X, Lu C, Ma J, Yu L, Xu C, Ren Z, Xu Y, Xu S, Shen H, Zhu X, Shi Y, Shen Q, Dong W, Liu R, Ling Y, Zeng Y, Wang X, Zhang Q, Wang J, Wang L, Wu Y, Zeng B, Wei H, Zhang M, Peng Y, Zhang C. Gut bacteria selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes. Science. 2018; 359:1151–1156.
Article20. Xu S, Zhu X, Li H, Hu Y, Zhou J, He D, Feng Y, Lu L, Du G, Hu Y, Liu T, Wang Z, Ding G, Chen J, Gao S, Wu F, Xue Z, Li Y, Fan G. The 14th Ile residue is essential for leptin function in regulating energy homeostasis in rat. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:28508.
Article21. Suárez-Zamorano N, Fabbiano S, Chevalier C, Stojanovic O, Colin DJ, Stevanovic A, Veyrat-Durebex C, Tarallo V, Rigo D, Germain S, Ilievska M, Montet X, Seimbille Y, Hapfelmeier S, Trajkovski M. Microbiota depletion promotes browning of white adipose tissue and reduces obesity. Nat Med. 2015; 21:1497–1501.
Article22. Callahan BJ, Sankaran K, Fukuyama JA, McMurdie PJ, Holmes SP. Bioconductor Workflow for Microbiome Data Analysis: from raw reads to community analyses. Version 2. F1000Res. 2016; 5:1492.23. Love MI, Anders S, Kim V, Huber W. RNA-seq workflow: gene-level exploratory analysis and differential expression. F1000Res. 2015; 4:1070.
Article24. Basso N, Soricelli E, Castagneto-Gissey L, Casella G, Albanese D, Fava F, Donati C, Tuohy K, Angelini G, La Neve F, Severino A, Kamvissi-Lorenz V, Birkenfeld AL, Bornstein S, Manco M, Mingrone G. Insulin resistance, microbiota, and fat distribution changes by a new model of vertical sleeve gastrectomy in obese rats. Diabetes. 2016; 65:2990–3001.
Article25. Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, Roe BA, Affourtit JP, Egholm M, Henrissat B, Heath AC, Knight R, Gordon JI. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature. 2009; 457:480–484.
Article26. Cani PD, Bibiloni R, Knauf C, Waget A, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM, Burcelin R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes. 2008; 57:1470–1481.
Article27. Grasset E, Puel A, Charpentier J, Collet X, Christensen JE, Terce F, Burcelin R. A specific gut microbiota dysbiosis of type 2 diabetic mice induces GLP-1 resistance through an enteric NO-dependent and gut-brain axis mechanism. Cell Metab. 2017; 25:1075–1090.
Article28. Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:292–295.
Article29. Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M, Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Gorgun CZ, Hotamisligil GS. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 2006; 313:1137–1140.
Article30. Angulo MA, Butler MG, Cataletto ME. Prader-Willi syndrome: a review of clinical, genetic, and endocrine findings. J Endocrinol Invest. 2015; 38:1249–1263.
Article31. Bray GA, Fruhbeck G, Ryan DH, Wilding JP. Management of obesity. Lancet. 2016; 387:1947–1956.
Article32. Tremaroli V, Backhed F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature. 2012; 489:242–249.
Article33. Zhao L. The gut microbiota and obesity: from correlation to causality. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013; 11:639–647.
Article34. Martinez I, Stegen JC, Maldonado-Gomez MX, Eren AM, Siba PM, Greenhill AR, Walter J. The gut microbiota of rural papua new guineans: composition, diversity patterns, and ecological processes. Cell Rep. 2015; 11:527–538.35. Murphy EF, Cotter PD, Healy S, Marques TM, O'Sullivan O, Fouhy F, Clarke SF, O'Toole PW, Quigley EM, Stanton C, Ross PR, O'Doherty RM, Shanahan F. Composition and energy harvesting capacity of the gut microbiota: relationship to diet, obesity and time in mouse models. Gut. 2010; 59:1635–1642.
Article36. Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006; 444:1022–1023.37. Semova I, Carten JD, Stombaugh J, Mackey LC, Knight R, Farber SA, Rawls JF. Microbiota regulate intestinal absorption and metabolism of fatty acids in the zebrafish. Cell Host Microbe. 2012; 12:277–288.
Article38. Murphy EF, Cotter PD, Hogan A, O'Sullivan O, Joyce A, Fouhy F, Clarke SF, Marques TM, O'Toole PW, Stanton C, Quigley EM, Daly C, Ross PR, O'Doherty RM, Shanahan F. Divergent metabolic outcomes arising from targeted manipulation of the gut microbiota in diet-induced obesity. Gut. 2013; 62:220–226.
Article39. Hwang I, Park YJ, Kim YR, Kim YN, Ka S, Lee HY, Seong JK, Seok YJ, Kim JB. Alteration of gut microbiota by vancomycin and bacitracin improves insulin resistance via glucagon-like peptide 1 in diet-induced obesity. FASEB J. 2015; 29:2397–2411.40. Reijnders D, Goossens GH, Hermes GD, Neis EP, van der Beek CM, Most J, Holst JJ, Lenaerts K, Kootte RS, Nieuwdorp M, Groen AK, Olde Damink SW, Boekschoten MV, Smidt H, Zoetendal EG, Dejong CH, Blaak EE. Effects of gut microbiota manipulation by antibiotics on host metabolism in obese humans: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Cell Metab. 2016; 24:63–74.
Article41. Hartstra AV, Bouter KE, Backhed F, Nieuwdorp M. Insights into the role of the microbiome in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015; 38:159–165.
Article42. Perry RJ, Peng L, Barry NA, Cline GW, Zhang D, Cardone RL, Petersen KF, Kibbey RG, Goodman AL, Shulman GI. Acetate mediates a microbiome-brain-β-cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome. Nature. 2016; 534:213–217.
Article43. Frederich RC, Hamann A, Anderson S, Lollmann B, Lowell BB, Flier JS. Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat Med. 1995; 1:1311–1314.
Article44. Kootte RS, Levin E, Salojarvi J, Smits LP, Hartstra AV, Udayappan SD, Hermes G, Bouter KE, Koopen AM, Holst JJ, Knop FK, Blaak EE, Zhao J, Smidt H, Harms AC, Hankemeijer T, Bergman JJGHM, Romijn HA, Schaap FG, Olde Damink SWM, Ackermans MT, Dallinga-Thie GM, Zoetendal E, de Vos WM, Serlie MJ, Stroes ESG, Groen AK, Nieuwdorp M. Improvement of insulin sensitivity after lean donor feces in metabolic syndrome is driven by baseline intestinal microbiota composition. Cell Metab. 2017; 26:611–619.
Article45. Everard A, Lazarevic V, Derrien M, Girard M, Muccioli GG, Neyrinck AM, Possemiers S, Van Holle A, Francois P, de Vos WM, Delzenne NM, Schrenzel J, Cani PD. Responses of gut microbiota and glucose and lipid metabolism to prebiotics in genetic obese and diet-induced leptin-resistant mice. Diabetes. 2011; 60:2775–2786.
Article46. Leshan RL, Greenwald-Yarnell M, Patterson CM, Gonzalez IE, Myers MG Jr. Leptin action through hypothalamic nitric oxide synthase-1-expressing neurons controls energy balance. Nat Med. 2012; 18:820–823.
Article47. Pfuhlmann K, Schriever SC, Baumann P, Kabra DG, Harrison L, Mazibuko-Mbeje SE, Contreras RE, Kyriakou E, Simonds SE, Tiganis T, Cowley MA, Woods SC, Jastroch M, Clemmensen C, De Angelis M, Schramm KW, Sattler M, Messias AC, Tschop MH, Pfluger PT. Celastrol-induced weight loss is driven by hypophagia and independent from UCP1. Diabetes. 2018; 67:2456–2465.
Article48. Finan B, Yang B, Ottaway N, Smiley DL, Ma T, Clemmensen C, Chabenne J, Zhang L, Habegger KM, Fischer K, Campbell JE, Sandoval D, Seeley RJ, Bleicher K, Uhles S, Riboulet W, Funk J, Hertel C, Belli S, Sebokova E, Conde-Knape K, Konkar A, Drucker DJ, Gelfanov V, Pfluger PT, Muller TD, Perez-Tilve D, DiMarchi RD, Tschop MH. A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents. Nat Med. 2015; 21:27–36.
Article