Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Jul;52(3):867-885. 10.4143/crt.2019.606.
Caspase Recruitment Domain Containing Protein 9 Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Proliferation and Invasion via Inhibiting MAPK/p38 Pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Respiratory Medicine, The Affiliated Huadong Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, The Affiliated Huadong Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Pathology, The Affiliated Huadong Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- KMID: 2504466
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2019.606
Abstract
- Purpose
Caspase recruitment domain containing protein 9 (CARD9) has been demonstrated to be a pro-tumor factor in various cancers. However, our previous study found a significant decrease of CARD9 in malignant pleural effusion compared with benign pleural effusion. So we investigated the role of CARD9 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and its working mechanism.
Materials and Methods
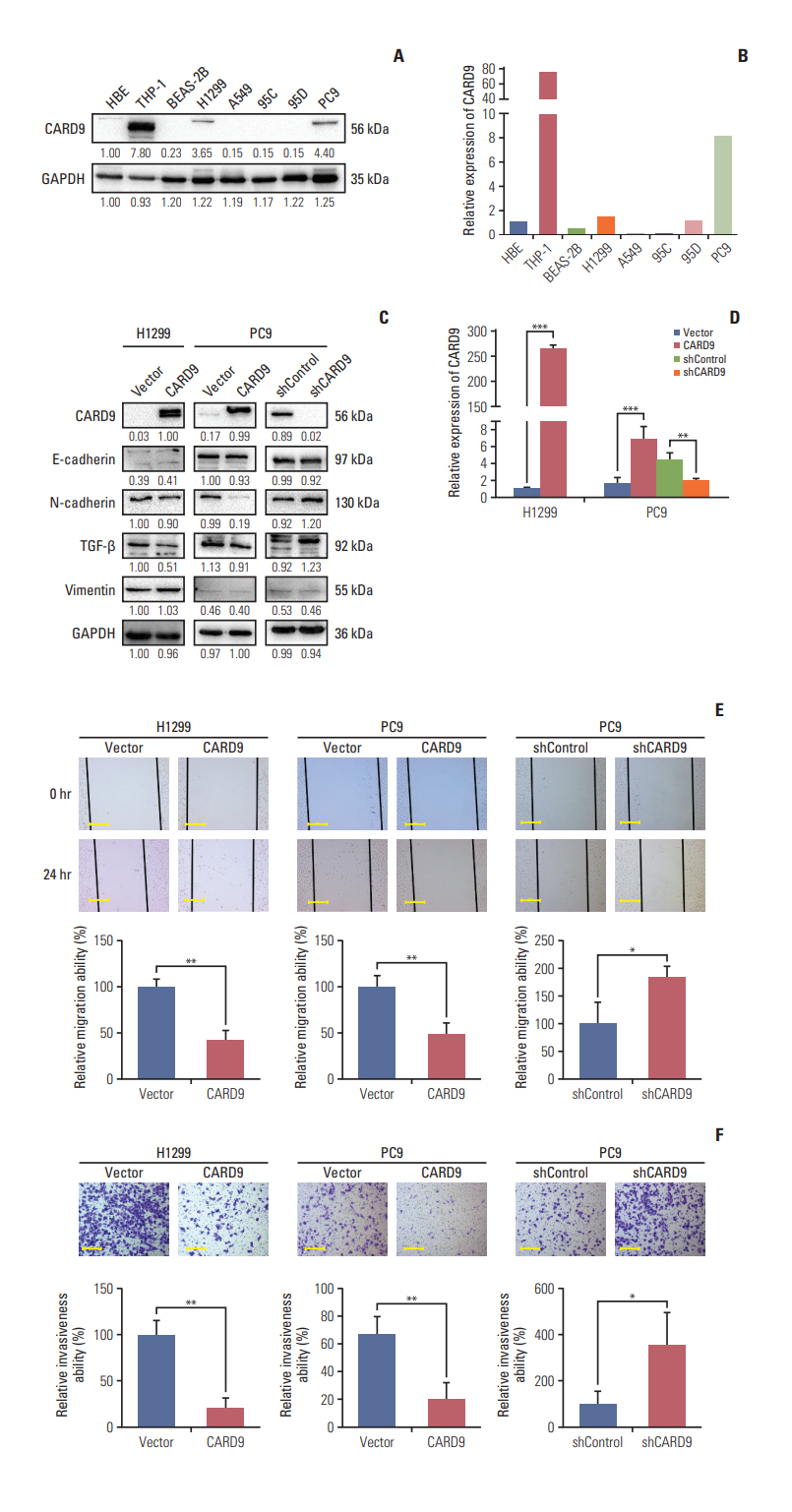
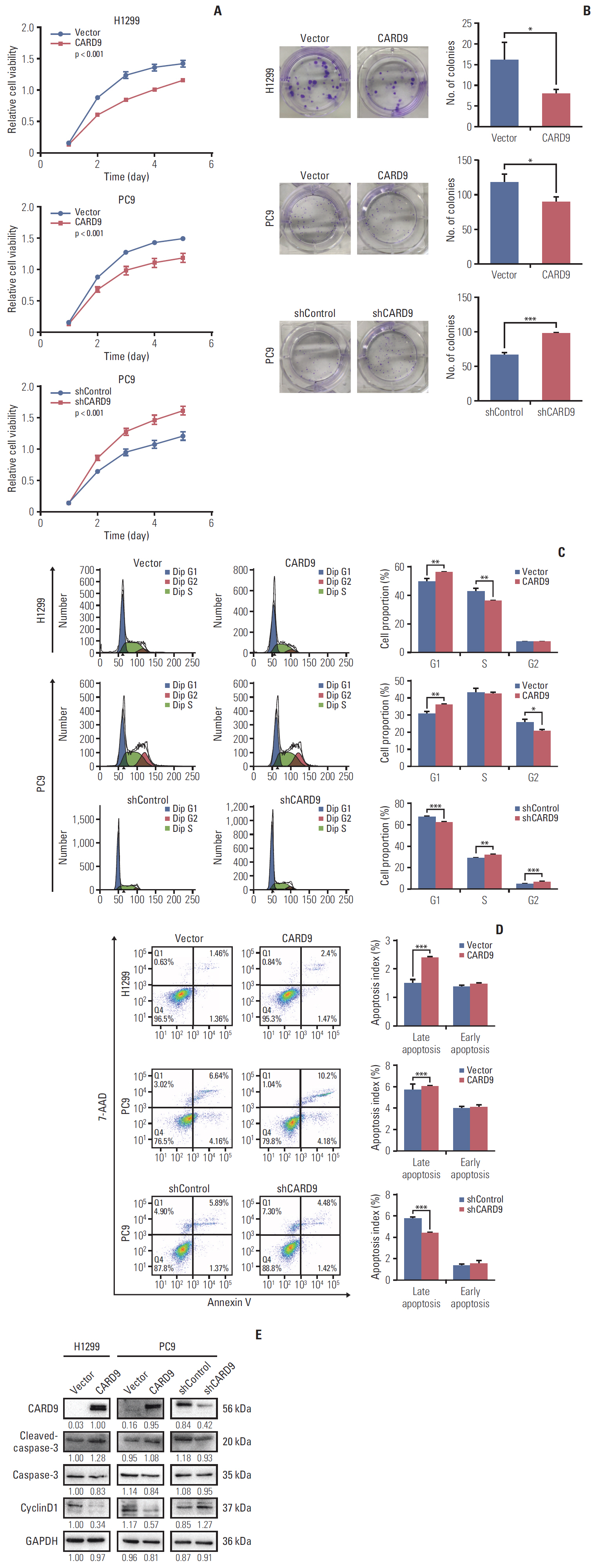
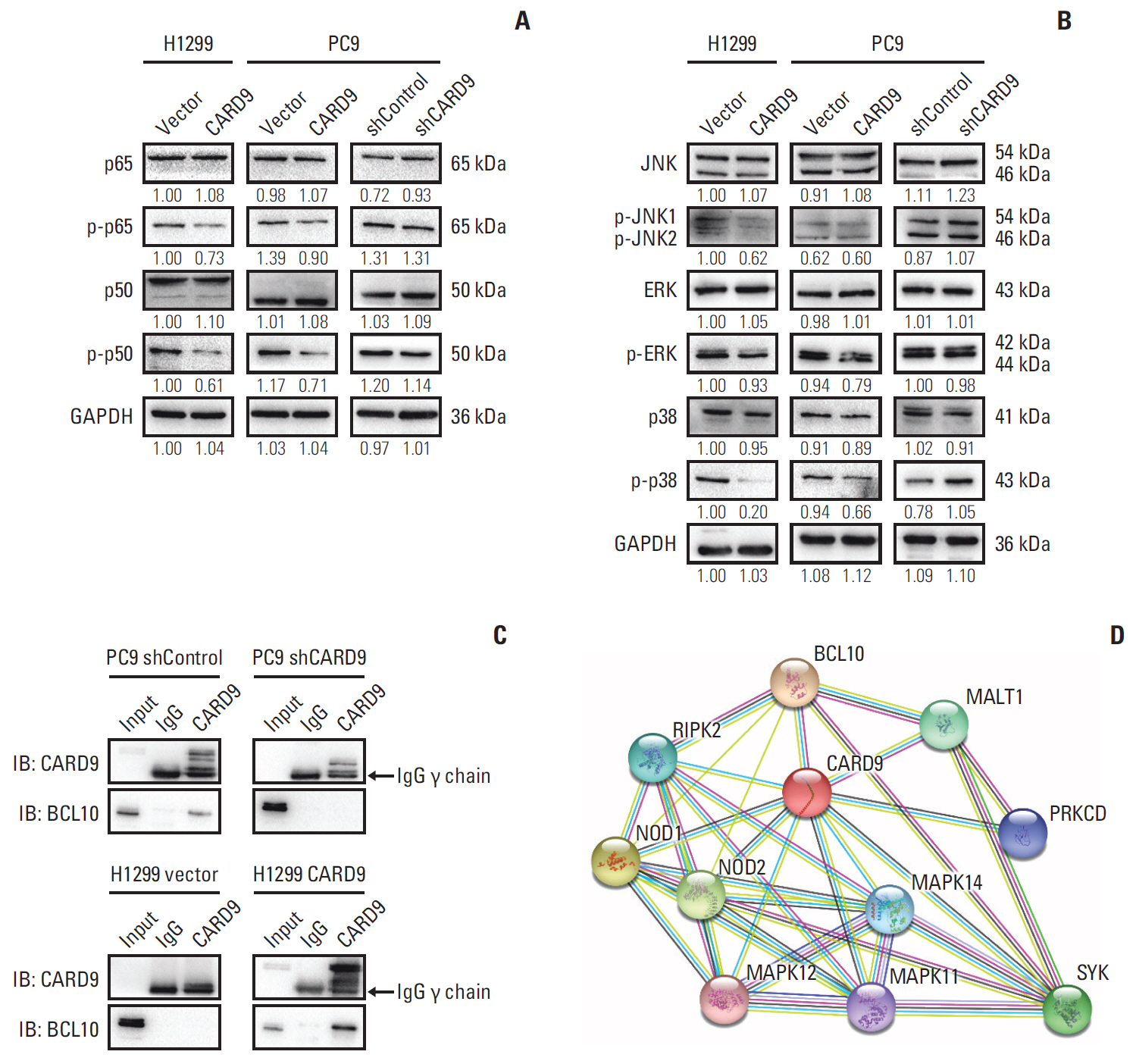
Immunohistochemistry, western blot, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction were used to detect the expression of CARD9 in specimens of NSCLC patients. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) databasewas also used to analyze the expression of CARD9 in NSCLC and its predicting value for prognosis. Immunofluorescence was used for CARD9 cellular location. Cell growth assay, clonal formation assay, wound healing assay, matrigel invasion assay, and flow cytometry were used to test cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and cycle progression of NSCLC cells with CARD9 knockdown or CARD9 overexpression. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to identify the interaction between CARD9 and B-cell lymphoma 10 (BCL10). SB203580 was used to inhibit p38 activation.
Results
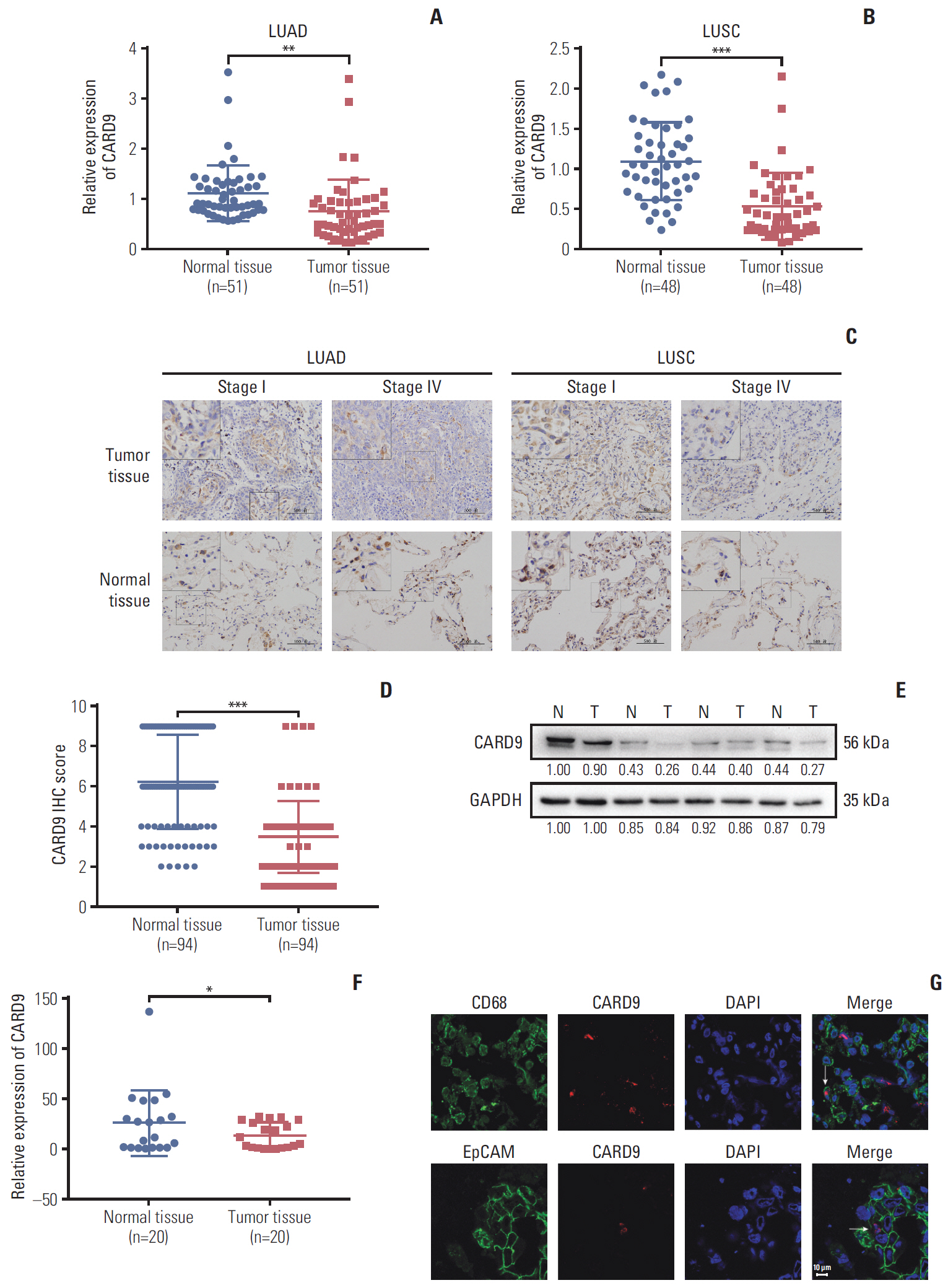
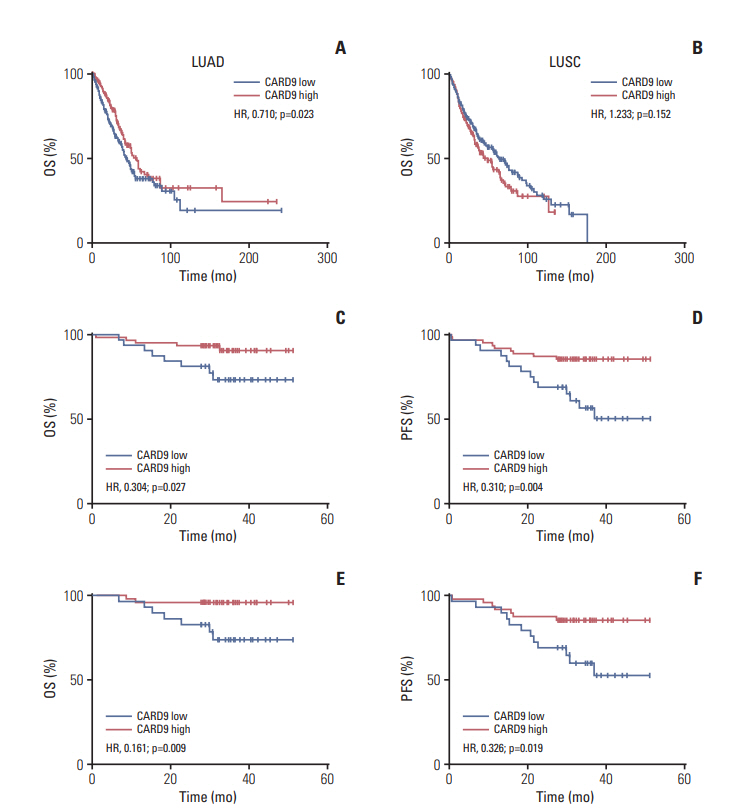
CARD9 was decreased in NSCLC tissues compared with normal tissues; low CARD9 expression was associated with poor survival. CARD9 was expressed both in tumor cells and macrophages. Downregulation of CARD9 in NSCLC cells enhanced the abilities of proliferation, invasion and migration via activated MAPK/p38 signaling, while overexpression of CARD9 presented antitumor effects. BCL10 was identified to interact with CARD9.
Conclusion
We demonstrate that CARD9 is an independent prognostic factor in NSCLC patients and inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion by suppressing MAPK/p38 pathway in NSCLC cells.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424.
Article2. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2019 [Internet]. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society;2019. [cited 2019 Jun 10]. Available from: http://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancerorg/research/cancer-factsand-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-andfigures/2019/cancer-facts-andfigures-2019.pdf.3. Hsu YM, Zhang Y, You Y, Wang D, Li H, Duramad O, et al. The adaptor protein CARD9 is required for innate immune responses to intracellular pathogens. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:198–205.
Article4. Yang H, Minamishima YA, Yan Q, Schlisio S, Ebert BL, Zhang X, et al. pVHL acts as an adaptor to promote the inhibitory phosphorylation of the NF-kappaB agonist Card9 by CK2. Mol Cell. 2007; 28:15–27.5. Cao Z, Conway KL, Heath RJ, Rush JS, Leshchiner ES, Ramirez-Ortiz ZG, et al. Ubiquitin ligase TRIM62 regulates CARD9-mediated anti-fungal immunity and intestinal inflammation. Immunity. 2015; 43:715–26.
Article6. Nakamura S, Nakamura S, Matsumoto T, Yada S, Hirahashi M, Suekane H, et al. Overexpression of caspase recruitment domain (CARD) membrane-associated guanylate kinase 1 (CARMA1) and CARD9 in primary gastric B-cell lymphoma. Cancer. 2005; 104:1885–93.
Article7. Leo VI, Tan SH, Bergmann H, Cheah PY, Chew MH, Lim KH, et al. CARD9 promotes sex-biased colon tumors in the APCmin mouse model. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015; 3:721–6.
Article8. Tan W, Hildebrandt MA, Pu X, Huang M, Lin J, Matin SF, et al. Role of inflammatory related gene expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma development and clinical outcomes. J Urol. 2011; 186:2071–7.
Article9. Li H, Tang Z, Zhu H, Ge H, Cui S, Jiang W. Proteomic study of benign and malignant pleural effusion. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016; 142:1191–200.
Article10. Qu J, Liu L, Xu Q, Ren J, Xu Z, Dou H, et al. CARD9 prevents lung cancer development by suppressing the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and IDO production. Int J Cancer. 2019; 145:2225–37.
Article11. Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M, Wyder S, Simonovic M, et al. The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45:D362–8.
Article12. Cai J, Xia L, Li J, Ni S, Song H, Wu X. Tumor-associated macrophages derived TGF-beta induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells through Smad2, 3-4/Snail signaling pathway. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:252–66.13. Hara H, Ishihara C, Takeuchi A, Imanishi T, Xue L, Morris SW, et al. The adaptor protein CARD9 is essential for the activation of myeloid cells through ITAM-associated and Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:619–29.
Article14. Saijo S, Ikeda S, Yamabe K, Kakuta S, Ishigame H, Akitsu A, et al. Dectin-2 recognition of alpha-mannans and induction of Th17 cell differentiation is essential for host defense against Candida albicans. Immunity. 2010; 32:681–91.15. Robinson MJ, Osorio F, Rosas M, Freitas RP, Schweighoffer E, Gross O, et al. Dectin-2 is a Syk-coupled pattern recognition receptor crucial for Th17 responses to fungal infection. J Exp Med. 2009; 206:2037–51.
Article16. Yang M, Shao JH, Miao YJ, Cui W, Qi YF, Han JH, et al. Tumor cell-activated CARD9 signaling contributes to metastasis-associated macrophage polarization. Cell Death Differ. 2014; 21:1290–302.
Article17. Bergmann H, Roth S, Pechloff K, Kiss EA, Kuhn S, Heikenwalder M, et al. Card9-dependent IL-1beta regulates IL-22 production from group 3 innate lymphoid cells and promotes colitis-associated cancer. Eur J Immunol. 2017; 47:1342–53.18. Liu M, Luo F, Ding C, Albeituni S, Hu X, Ma Y, et al. Dectin-1 activation by a natural product beta-glucan converts immunosuppressive macrophages into an M1-like phenotype. J Immunol. 2015; 195:5055–65.19. Haas T, Heidegger S, Wintges A, Bscheider M, Bek S, Fischer JC, et al. Card9 controls Dectin-1-induced T-cell cytotoxicity and tumor growth in mice. Eur J Immunol. 2017; 47:872–9.
Article20. Qian BZ, Pollard JW. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell. 2010; 141:39–51.
Article21. An J, Liu H, Magyar CE, Guo Y, Veena MS, Srivatsan ES, et al. Hyperactivated JNK is a therapeutic target in pVHL-deficient renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2013; 73:1374–85.
Article22. LeibundGut-Landmann S, Gross O, Robinson MJ, Osorio F, Slack EC, Tsoni SV, et al. Syk- and CARD9-dependent coupling of innate immunity to the induction of T helper cells that produce interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:630–8.
Article23. Pereira M, Tourlomousis P, Wright J, Monie TP, Bryant CE. CARD9 negatively regulates NLRP3-induced IL-1beta production on Salmonella infection of macrophages. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:12874.
Article24. Chen Z, Liu F, Zhang N, Cao D, Liu M, Tan Y, et al. p38beta, A novel regulatory target of Pokemon in hepatic cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14:13511–24.25. Tomas-Loba A, Manieri E, Gonzalez-Teran B, Mora A, Leiva-Vega L, Santamans AM, et al. p38gamma is essential for cell cycle progression and liver tumorigenesis. Nature. 2019; 568:557–60.26. Malik A, Sharma D, Malireddi RK, Guy CS, Chang TC, Olsen SR, et al. SYK-CARD9 signaling axis promotes gut fungimediated inflammasome activation to restrict colitis and colon cancer. Immunity. 2018; 49:515–30.
Article27. Wang T, Fan C, Yao A, Xu X, Zheng G, You Y, et al. The adaptor protein CARD9 protects against colon cancer by restricting mycobiota-mediated expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Immunity. 2018; 49:504–14.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Quercetin induces cell death by caspase-dependent and p38 MAPK pathway in EGFR mutant lung cancer cells
- The effect of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-ribonucleoside was mediated by p38 mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathway in FRO thyroid cancer cells
- Recombinant Human Thioredoxin-1 Protects Macrophages from Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Foam Cell Formation and Cell Apoptosis
- Cathepsin C Interacts with TNF-α/p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Promote Proliferation and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- MiR-152 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells by inhibiting FGF2