J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Jul;35(26):e239. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e239.
Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Coronavirus Disease 2019: a Case Report and Suggestions to Overcome Obstacles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- KMID: 2503691
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e239
Abstract
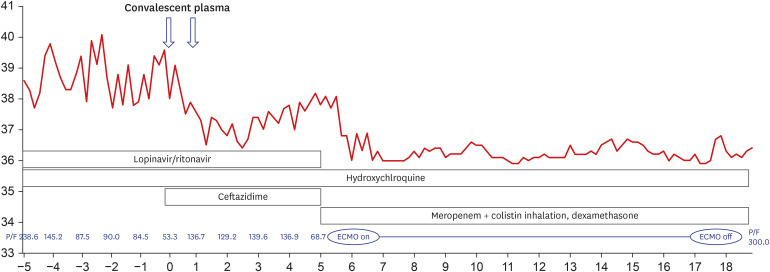
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is rapidly spreading around the world, causing much morbidity and mortality everywhere. However, effective treatments or vaccines are still not available. Although convalescent plasma (CP) therapy can be useful in the treatment of COVID-19, it has not been widely used in Korea because of the concerns about adverse effects and the difficulty in matching patients to donors. The use of ABO-incompatible plasma is not contraindicated in treatment, but can be hesitated due to the lack of experience of physicians. Here, we describe a 68-year old man with COVID-19 who was treated ABO-incompatible plasma therapy; additionally, we comment on the acute side effects associated with ABO mismatch transfusion. To overcome the obstacles of donor-recipient connections (schedule and distance), we propose the storage of frozen plasma, modification of the current Blood Management Law, and the establishment of a CP bank. We suggest that experience gained in CP therapy will be useful for not only the treatment of COVID-19, but also for coping with new emerging infectious diseases.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical and Virologic Effectiveness of Remdesivir Treatment for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea: a Nationwide Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Eun-Jeong Joo, Jae-Hoon Ko, Seong Eun Kim, Seung-Ji Kang, Ji Hyeon Baek, Eun Young Heo, Hye Jin Shi, Joong Sik Eom, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Seongman Bae, Sang Hyun Ra, Da Young Kim, Baek-Nam Kim, Yu Min Kang, Ji Yeon Kim, Jin-Won Chung, Hyun-Ha Chang, Sohyun Bae, Shinhyea Cheon, Yoonseon Park, Heun Choi, Eunjung Lee, Bo young Lee, Jung Wan Park, Yujin Sohn, Jung Yeon Heo, Sung-Han Kim, Kyong Ran Peck
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(11):e83. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e83.
Reference
-
1. Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(8):727–733. PMID: 31978945.
Article2. Cao B, Wang Y, Wen D, Liu W, Wang J, Fan G, et al. A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(19):1787–1799. PMID: 32187464.3. Taccone FS, Gorham J, Vincent JL. Hydroxychloroquine in the management of critically ill patients with COVID-19: the need for an evidence base. Lancet Respir Med. 2020; 8(6):539–541. PMID: 32304640.
Article4. Wang Y, Zhang D, Du G, Du R, Zhao J, Jin Y, et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet. 2020; 395(10236):1569–1578. PMID: 32423584.5. Yoo JH. Uncertainty about the efficacy of remdesivir on COVID-19. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(23):e221. PMID: 32537956.
Article6. Gasparyan AY, Misra DP, Yessirkepov M, Zimba O. Perspectives of immune therapy in coronavirus disease 2019. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(18):e176. PMID: 32383371.
Article7. Ingraham NE, Lotfi-Emran S, Thielen BK, Techar K, Morris RS, Holtan SG, et al. Immunomodulation in COVID-19. Lancet Respir Med. 2020; 8(6):544–546. PMID: 32380023.
Article8. Khailany RA, Safdar M, Ozaslan M. Genomic characterization of a novel SARS-CoV-2. Gene Rep. 2020; 19:100682.
Article9. Mair-Jenkins J, Saavedra-Campos M, Baillie JK, Cleary P, Khaw FM, Lim WS, et al. The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2015; 211(1):80–90. PMID: 25030060.
Article10. Casadevall A, Pirofski LA. The convalescent sera option for containing COVID-19. J Clin Invest. 2020; 130(4):1545–1548. PMID: 32167489.
Article11. Ahn JY, Sohn Y, Lee SH, Cho Y, Hyun JH, Baek YJ, et al. Use of convalescent plasma therapy in two COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(14):e149. PMID: 32281317.
Article12. Yoo JH. Convalescent plasma therapy for corona virus disease 2019: a long way to go but worth trying. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(14):e150. PMID: 32281318.
Article13. Kleinman S, Caulfield T, Chan P, Davenport R, McFarland J, McPhedran S, et al. Toward an understanding of transfusion-related acute lung injury: statement of a consensus panel. Transfusion. 2004; 44(12):1774–1789. PMID: 15584994.
Article14. Lee JH, Kang ES, Kim DW. Two cases of transfusion-related acute lung injury triggered by HLA and anti-HLA antibody reaction. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25(9):1398–1403. PMID: 20808691.
Article15. Chapman CE, Williamson LM. National blood service TRALI reduction policies: implementation and effect. Transfus Med Hemother. 2008; 35(2):93–96. PMID: 21512634.
Article16. Moore JB, June CH. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19. Science. 2020; 368(6490):473–474. PMID: 32303591.
Article17. Berséus O, Boman K, Nessen SC, Westerberg LA. Risks of hemolysis due to anti-A and anti-B caused by the transfusion of blood or blood components containing ABO-incompatible plasma. Transfusion. 2013; 53(Suppl 1):114S–123S. PMID: 23301963.
Article18. Ebert RV, Emerson CP Jr. A clinical study of transfusion reactions: the hemolytic effect of group-O blood and pooled plasma containing incompatible isoagglutinins. J Clin Invest. 1946; 25(4):627–638. PMID: 16695355.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Practical Considerations in Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Two COVID-19 Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Korea
- A Transient Effect of Convalescent Plasma Therapy in a Patient with Severe Covonavirus Disease 2019: A Case Report
- Convalescent plasma in COVID-19: renewed focus on the timing and effectiveness of an old therapy