Use of Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Two COVID-19 Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2509617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e149
Abstract
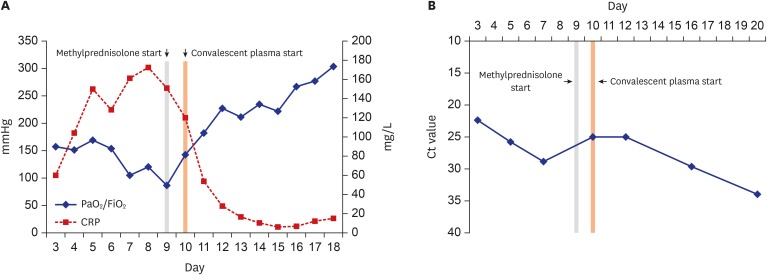
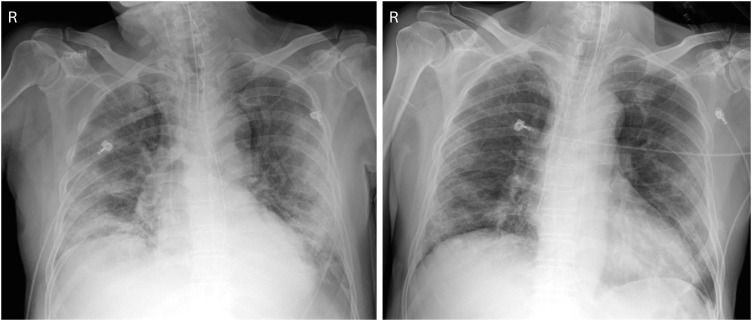
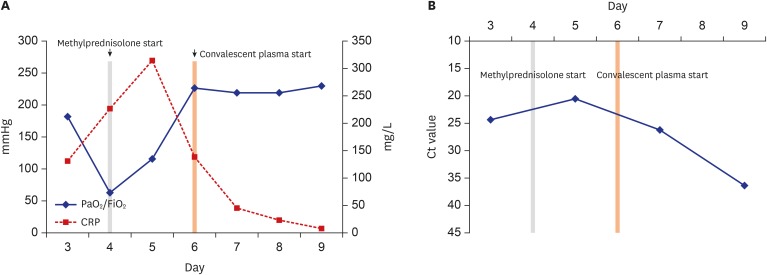
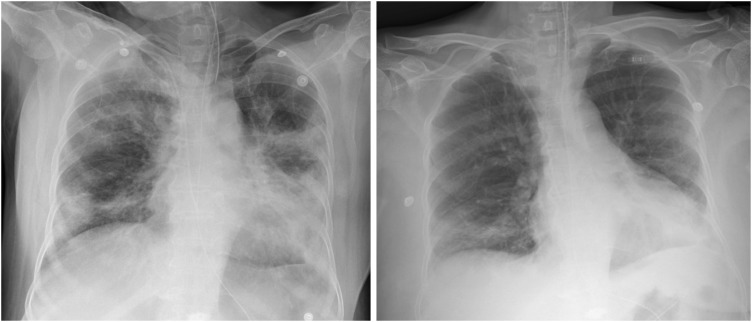
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 not yet has established its treatment, but convalescent plasma has been expected to increase survival rates as in the case with other emerging viral infections. We describe two cases of COVID-19 treated with convalescent plasma infusion. Both patients presented severe pneumonia with acute respiratory distress syndrome and showed a favorable outcome after the use of convalescent plasma in addition to systemic corticosteroid. To our knowledge, this is the first report of the use of convalescent plasma therapy for COVID-19 in Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Corona Virus Disease 2019: a Long Way to Go but Worth Trying
Jin-Hong Yoo
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(14):e150. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e150.Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Coronavirus Disease 2019: a Case Report and Suggestions to Overcome Obstacles
Jae Hyoung Im, Chung Hyun Nahm, Ji Hyeon Baek, Hea Yoon Kwon, Jin-Soo Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(26):e239. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e239.Clinical and Virologic Effectiveness of Remdesivir Treatment for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea: a Nationwide Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Eun-Jeong Joo, Jae-Hoon Ko, Seong Eun Kim, Seung-Ji Kang, Ji Hyeon Baek, Eun Young Heo, Hye Jin Shi, Joong Sik Eom, Pyoeng Gyun Choe, Seongman Bae, Sang Hyun Ra, Da Young Kim, Baek-Nam Kim, Yu Min Kang, Ji Yeon Kim, Jin-Won Chung, Hyun-Ha Chang, Sohyun Bae, Shinhyea Cheon, Yoonseon Park, Heun Choi, Eunjung Lee, Bo young Lee, Jung Wan Park, Yujin Sohn, Jung Yeon Heo, Sung-Han Kim, Kyong Ran Peck
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(11):e83. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e83.Analysis of PubMed and KoreaMed Indexed Korean Publications on COVID-19
Jong-Min Kim, Jin-Hong Yoo, Hae Kyung Cho, Sung-Tae Hong
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(49):e345. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e345.
Reference
-
1. Mair-Jenkins J, Saavedra-Campos M, Baillie JK, Cleary P, Khaw FM, Lim WS, et al. The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2015; 211(1):80–90. PMID: 25030060.
Article2. Marano G, Vaglio S, Pupella S, Facco G, Catalano L, Liumbruno GM, et al. Convalescent plasma: new evidence for an old therapeutic tool? Blood Transfus. 2016; 14(2):152–157. PMID: 26674811.3. Burnouf T, Seghatchian J. Ebola virus convalescent blood products: where we are now and where we may need to go. Transfus Apheresis Sci. 2014; 51(2):120–125.
Article4. Public Health England I. Treatment of MERS-CoV: information for clinicians. Updated 2017. Accessed February 2, 2020. http://www.hpa.org.uk/webc/HPAwebFile/HPAweb_C/1317139281416.5. Hung IF, To KK, Lee CK, Lee KL, Chan K, Yan WW, et al. Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52(4):447–456. PMID: 21248066.
Article6. Soo YO, Cheng Y, Wong R, Hui DS, Lee CK, Tsang KK, et al. Retrospective comparison of convalescent plasma with continuing high-dose methylprednisolone treatment in SARS patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004; 10(7):676–678. PMID: 15214887.
Article7. Russell CD, Millar JE, Baillie JK. Clinical evidence does not support corticosteroid treatment for 2019-nCoV lung injury. Lancet. 2020; 395(10223):473–475. PMID: 32043983.
Article8. World Health Organization. Geneva: World Health Organization;2020. 1. 28. Updated 2020. Accessed February 2, 2020. https://www.who.int/publications-detail/clinical-management-of-severe-acute-respiratory-infection-when-novel-coronavirus-(ncov)-infection-is-suspected.9. Hanley B, Lucas SB, Youd E, Swift B, Osborn M. Autopsy in suspected COVID-19 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2020.
Article10. Wong VW, Dai D, Wu AK, Sung JJ. Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome with convalescent plasma. Hong Kong Med J. 2003; 9(3):199–201. PMID: 12777656.11. Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S, et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern Med. 2020.
Article12. Arabi YM, Mandourah Y, Al-Hameed F, Sindi AA, Almekhlafi GA, Hussein MA, et al. Corticosteroid therapy for critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197(6):757–767. PMID: 29161116.
Article13. Lee N, Allen Chan KC, Hui DS, Ng EK, Wu A, Chiu RW, et al. Effects of early corticosteroid treatment on plasma SARS-associated Coronavirus RNA concentrations in adult patients. J Clin Virol. 2004; 31(4):304–309. PMID: 15494274.
Article14. Chen L, Xiong J, Bao L, Shi Y. Convalescent plasma as a potential therapy for COVID-19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20(4):398–400. PMID: 32113510.
Article15. Lu CL, Murakowski DK, Bournazos S, Schoofs T, Sarkar D, Halper-Stromberg A, et al. Enhanced clearance of HIV-1-infected cells by broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1 in vivo. Science. 2016; 352(6288):1001–1004. PMID: 27199430.
Article16. Liu Y, Yan LM, Wan L, Xiang TX, Le A, Liu JM, et al. Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020.
Article17. Zou L, Ruan F, Huang M, Liang L, Huang H, Hong Z, et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(12):1177–1179. PMID: 32074444.
Article18. Gu J, Gong E, Zhang B, Zheng J, Gao Z, Zhong Y, et al. Multiple organ infection and the pathogenesis of SARS. J Exp Med. 2005; 202(3):415–424. PMID: 16043521.
Article19. Li T, Qiu Z, Zhang L, Han Y, He W, Liu Z, et al. Significant changes of peripheral T lymphocyte subsets in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. J Infect Dis. 2004; 189(4):648–651. PMID: 14767818.
Article20. Choe PG, Perera RA, Park WB, Song KH, Bang JH, Kim ES, et al. MERS-CoV Antibody Responses 1 Year after Symptom Onset, South Korea, 2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017; 23(7):1079–1084.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Practical Considerations in Convalescent Plasma Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Korea
- Treatment Options for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, and Coronavirus Disease 2019: a Review of Clinical Evidence
- Convalescent plasma in COVID-19: renewed focus on the timing and effectiveness of an old therapy