Intest Res.
2020 Jan;18(1):45-55. 10.5217/ir.2019.00039.
Anti-MAdCAM-1 antibody (PF-00547659) for active refractory Crohn’s disease in Japanese and Korean patients: the OPERA study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Jikei University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Gastroenterology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- 6Institute of Gastroenterology and Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 7Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Keio University Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
- 9Department of Gastroenterology, Chiba University Hospital, Chiba, Japan
- 10Department of Gastroenterology and Hematology, National Hospital Organization, Hirosaki National Hospital, Hirosaki, Japan
- 11Clinical Research, Pfizer Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan
- 12Clinical Statistics, Pfizer Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan
- 13Clinical Pharmacology, Development Japan, Pfizer Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan
- 14Clinical Statistics, Pfizer Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA
- 15Gastroenterology, Pfizer Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA
- 16Early Clinical Research and Development, Pfizer Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA
- 17Biotherapeutics Clinical R&D, Pfizer Inc., Collegeville, PA, USA
- 18Gastroenterology, Clinical Programs, Pfizer Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA
- 19Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan
- 20Center for Advanced IBD Research and Treatment, Kitasato Institute Hospital, Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan
- KMID: 2501366
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2019.00039
Abstract
- Background/Aims
PF-00547659 is a monoclonal antibody against human mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) that prevents the binding of α4β7+ lymphocytes to MAdCAM-expressing sites in the gastrointestinal tract with high affinity and selectivity, and is being developed for the treatment of Crohn’s disease (CD).
Methods
OPERA is a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to investigate the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of PF-00547659 following subcutaneous administration in subjects with active CD, a history of failure or intolerance to anti-tumor necrosis factor and/or immunosuppressants, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein > 3.0 mg/L, and ulcers on colonoscopy. The primary endpoint was Crohn’s Disease Activity Index-70 response at week 8 or 12. Subpopulation analyses for Asian subjects were performed as some differences are observed in genetics and clinical phenotypes in Asian CD patients compared with Western patients.
Results
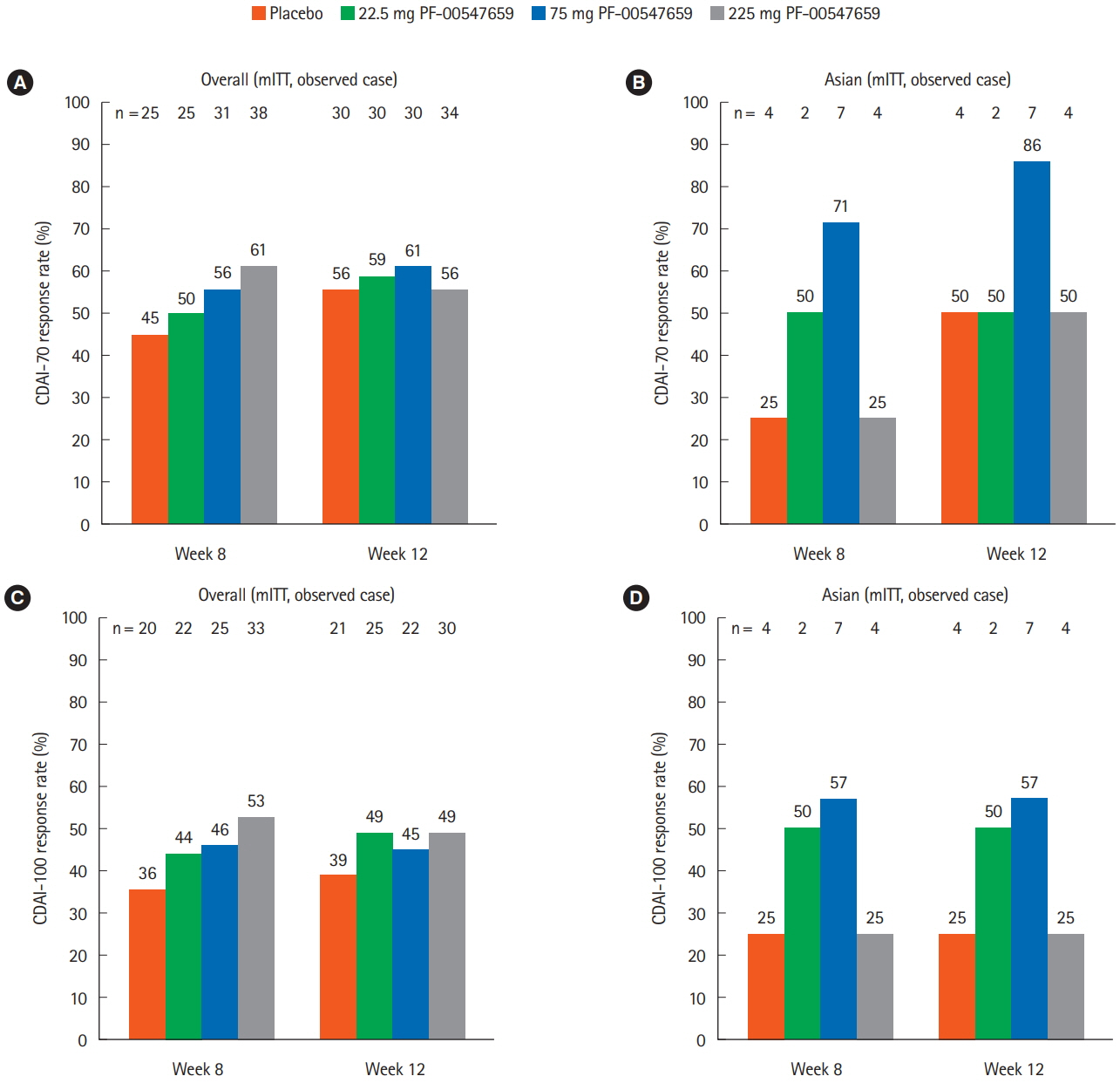
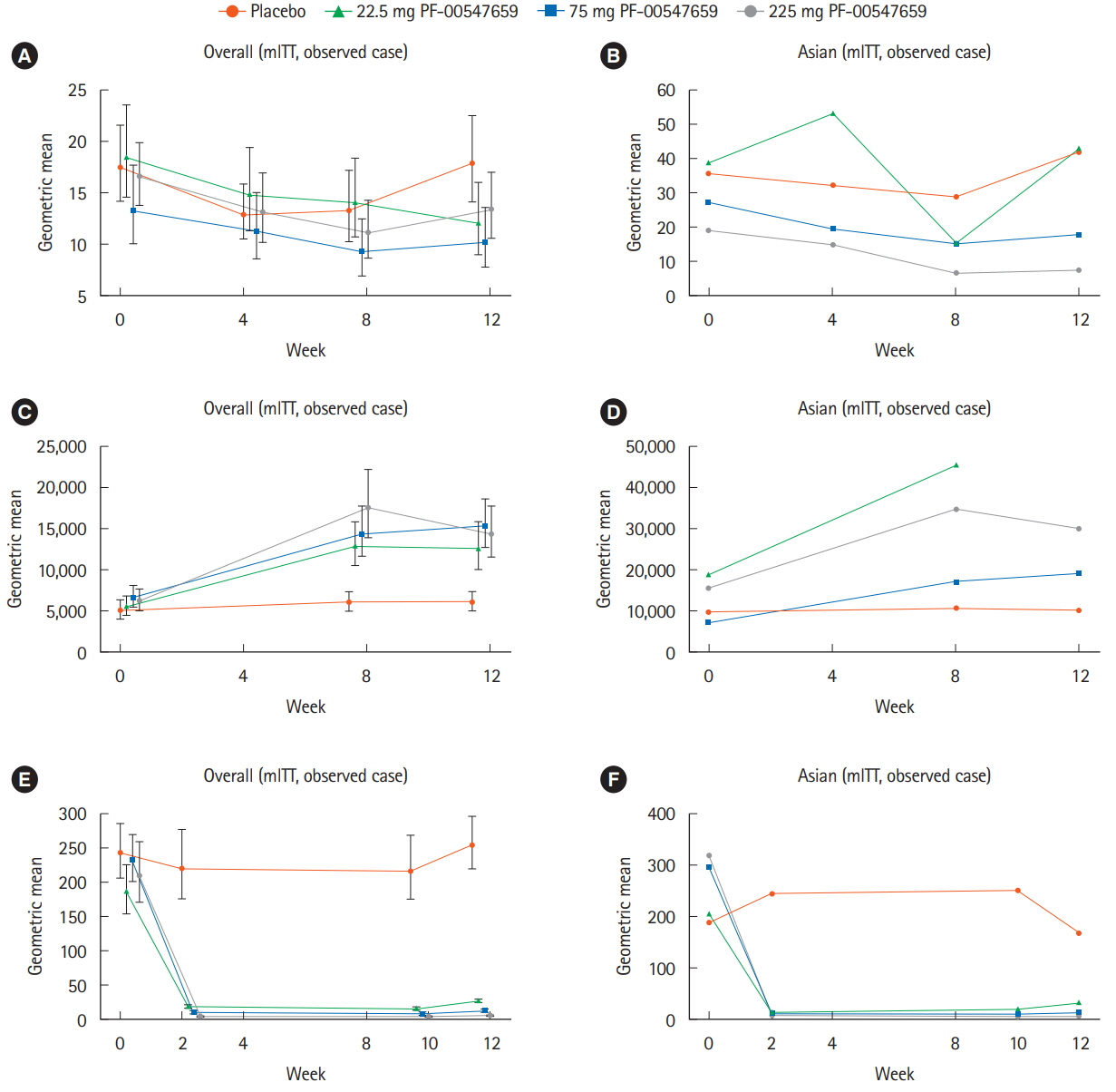
In this study, 265 CD subjects were randomized, with a subpopulation of 21 subjects (8 Japanese and 13 Korean) defined as the Asian population. In the overall and Asian populations; PF-00547659 was pharmacologically active as evidenced by soluble MAdCAM and circulating β7+ central memory CD4+ T-lymphocytes, although no clear evidence of efficacy was observed in any clinical endpoints; pharmacokinetics of PF-00547659 in the Asian subpopulation was generally comparable to the overall population; and the safety profile of PF-00547659 appeared acceptable up to 12 weeks of treatment.
Conclusions
In the overall and Asian populations, efficacy of PF-00547659 could not be demonstrated using any clinical endpoints compared with placebo. Pharmacokinetics and safety of PF-00547659 were generally comparable. Further studies with larger numbers of patients are required to confirm our results. (Trial Registration Number: NCT01276509)
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fiocchi C. Inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: where are we? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 30 Suppl 1:12–18.2. Streeter PR, Berg EL, Rouse BT, Bargatze RF, Butcher EC. A tissue-specific endothelial cell molecule involved in lymphocyte homing. Nature. 1988; 331:41–46.3. Nakache M, Berg EL, Streeter PR, Butcher EC. The mucosal vascular addressin is a tissue-specific endothelial cell adhesion molecule for circulating lymphocytes. Nature. 1989; 337:179–181.4. Briskin M, Winsor-Hines D, Shyjan A, et al. Human mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 is preferentially expressed in intestinal tract and associated lymphoid tissue. Am J Pathol. 1997; 151:97–110.5. Pullen N, Molloy E, Carter D, et al. Pharmacological characterization of PF-00547659, an anti-human MAdCAM monoclonal antibody. Br J Pharmacol. 2009; 157:281–293.6. Sandborn WJ, Lee SD, Tarabar D, et al. Phase II evaluation of anti-MAdCAM antibody PF-00547659 in the treatment of Crohn’s disease: report of the OPERA study. Gut. 2018; 67:1824–1835.7. Ng SC. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: focus on Asia. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2014; 28:363–372.8. Sands BE, Katz S, Wolf DC, et al. A randomised, double-blind, sham-controlled study of granulocyte/monocyte apheresis for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2013; 62:1288–1294.9. Park SC, Jeen YT. Genetic studies of inflammatory bowel disease-focusing on Asian patients. Cells. 2019; 8:E404.10. Introductory guide MedDRA version 18.1, 2015. MedDRA Web site. https://www.meddra.org/sites/default/files/guidance/file/intguide_18_1_english.pdf. Accessed Jan 16, 2020.11. Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:711–721.12. Schreiber S, Rutgeerts P, Fedorak RN, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of certolizumab pegol (CDP870) for treatment of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129:807–818.13. Targan SR, Feagan BG, Fedorak RN, et al. Natalizumab for the treatment of active Crohn’s disease: results of the ENCORE Trial. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:1672–1683.14. Sandborn WJ, Schreiber S, Feagan BG, et al. Certolizumab pegol for active Crohn’s disease: a placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 9:670–678.15. Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Reinisch W, et al. Infliximab, azathioprine, or combination therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1383–1395.16. Mager DE. Target-mediated drug disposition and dynamics. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006; 72:1–10.17. Wang DD, Zhang S, Zhao H, Men AY, Parivar K. Fixed dosing versus body size-based dosing of monoclonal antibodies in adult clinical trials. J Clin Pharmacol. 2009; 49:1012–1024.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Natural Course of Crohn's Disease and Novel Treatment Drugs
- A Case of Refractory Pediatric Crohn's Disease with a Successful Treatment by Infliximab Therapy
- Old and New Biologics and Small Molecules in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Anti Integrins
- Exclusive enteral nutrition for induction of remission in anti-tumor necrosis factor refractory adult Crohn’s disease: the Indian experience
- Recent Trends of Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease