J Bone Metab.
2020 Feb;27(1):71-75. 10.11005/jbm.2020.27.1.71.
Paget's Disease of Bone Affecting Peripheral Limb: Difficulties in Diagnosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. raisondetre@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2471316
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2020.27.1.71
Abstract
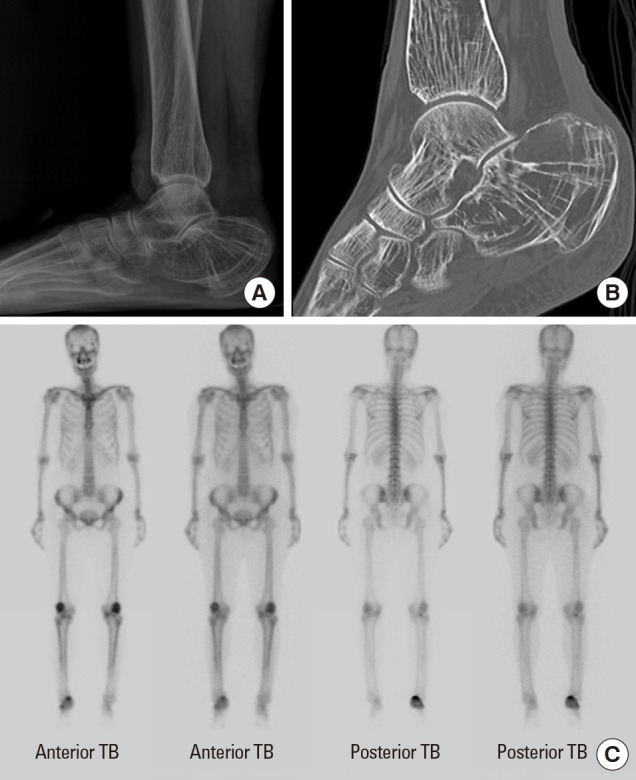
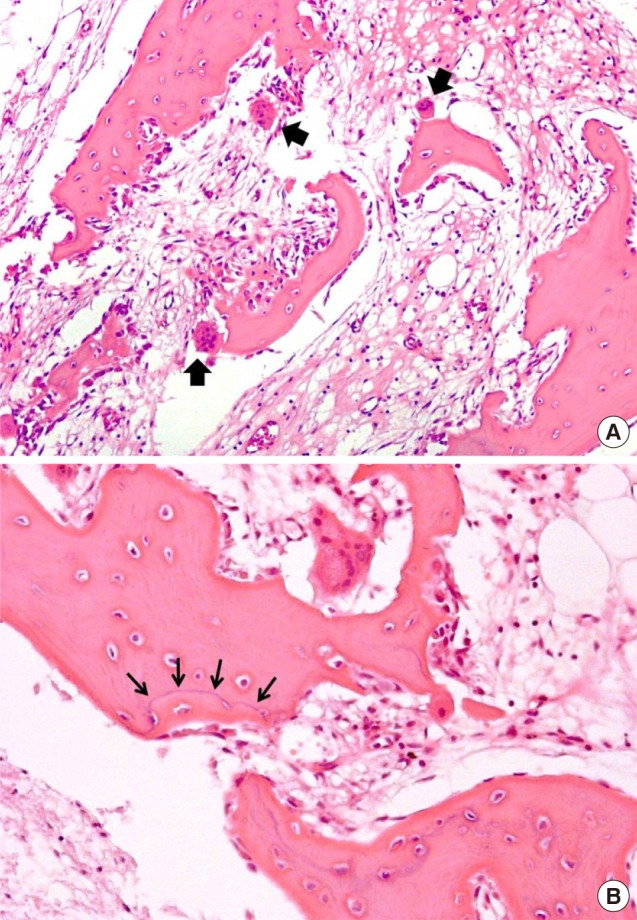
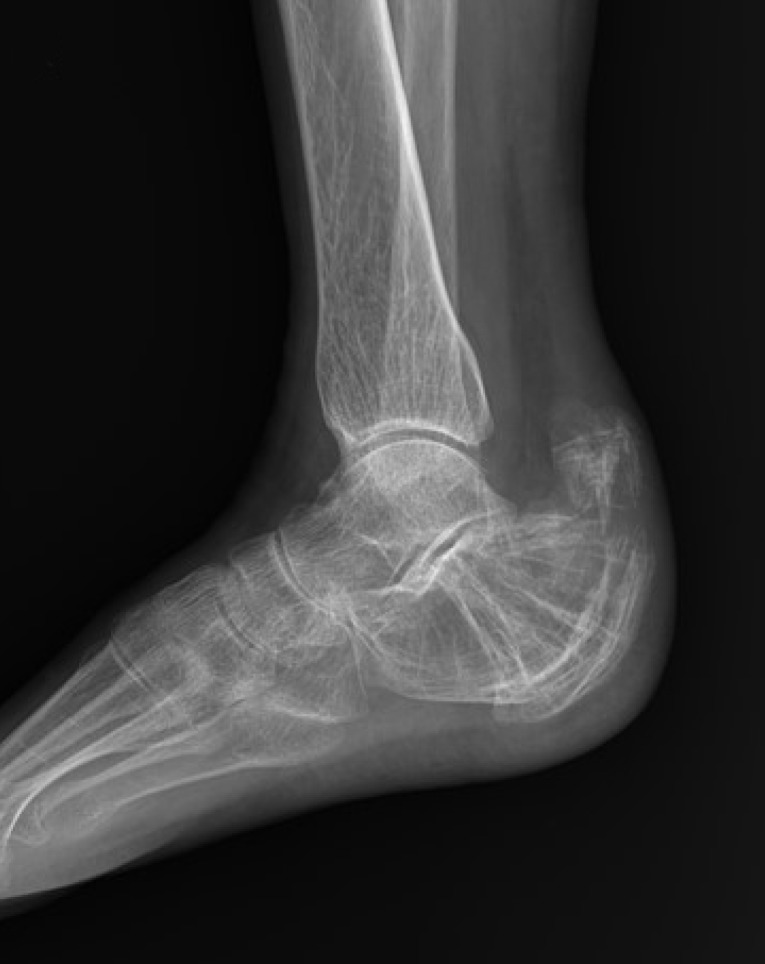
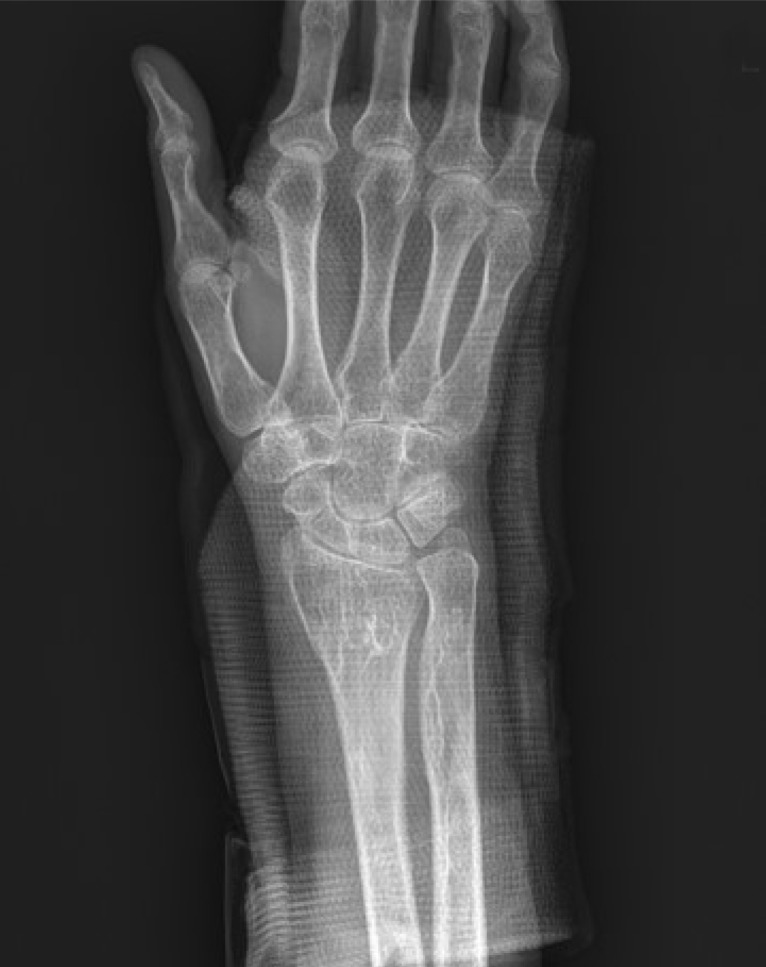
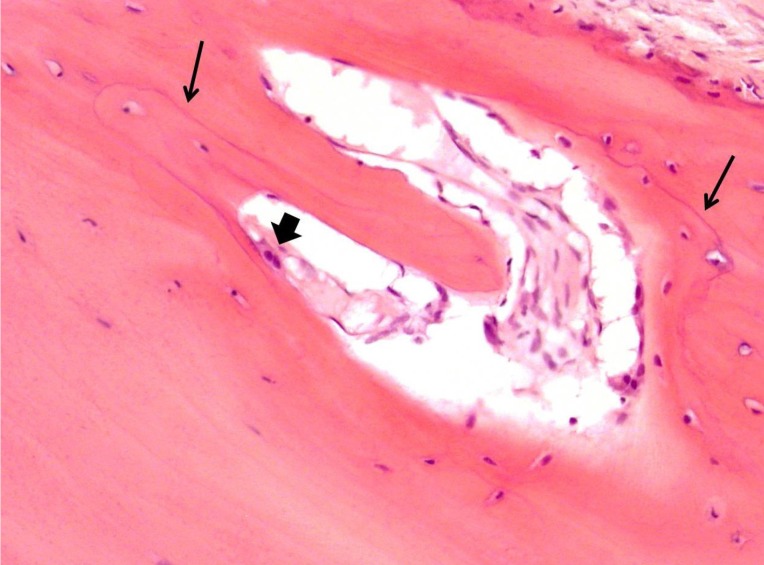
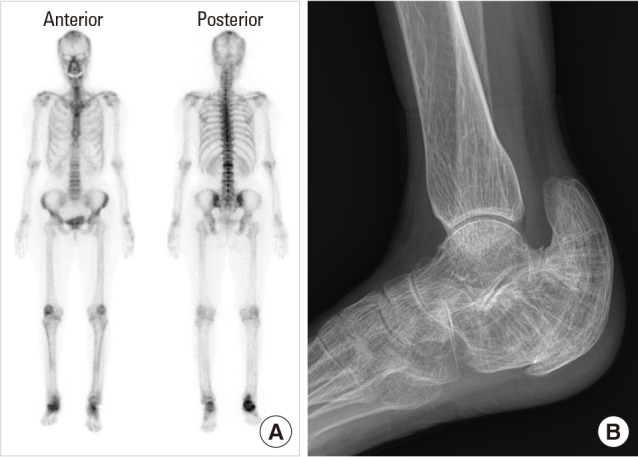
- In terms of management of Paget's disease of bone (PDB), early diagnosis and proper management achieving remission is essential with lifelong specialist follow-up. We present the case of a 40-year-old woman with PDB affecting mainly the distal extremities (ankle and wrist). The patient visited our hospital in 2012 with heel pain. Plain radiography revealed osteoporosis, and a bone scan revealed hot uptake. Initial laboratory investigations showed normal serum calcium, 25-hydroxy-vitamin D, and parathyroid hormone levels; however, osteocalcin, C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen, and bone alkaline phosphatase levels were elevated. A bone mineral density scan showed T- and Z-scores of −2.5 and −2.7, respectively, and bisphosphonate treatment was initiated. Biopsy performed on the calcaneal lateral wall revealed inconclusive findings. Follow-up biopsy on the left distal radius was performed 7 years later to investigate wrist pain, and this examination led to a final diagnosis as PDB. We suggest inconclusive biopsy result during the early phase of PDB and highly recommend follow-up evaluation in osteoporosis with atypical behavior.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Alkaline Phosphatase
Biopsy
Bone Density
Calcium
Collagen Type I
Diagnosis*
Diphosphonates
Early Diagnosis
Extremities*
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Heel
Humans
Osteitis Deformans*
Osteocalcin
Osteoporosis
Parathyroid Hormone
Radiography
Radius
Specialization
Wrist
Alkaline Phosphatase
Calcium
Collagen Type I
Diphosphonates
Osteocalcin
Parathyroid Hormone
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Updates on Paget’s Disease of Bone
Yong Jun Choi, Young Bae Sohn, Yoon-Sok Chung
Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):732-743. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1575.
Reference
-
1. Paul Tuck S, Layfield R, Walker J, et al. Adult Paget's disease of bone: a review. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017; 56:2050–2059. PMID: 28339664.
Article2. Sankaran S, Naot D, Grey A, et al. Paget's disease in patients of Asian descent in New Zealand. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27:223–226. PMID: 21932347.
Article3. Brandi ML. Current treatment approaches for Paget's Disease of Bone. Discov Med. 2010; 10:209–212. PMID: 20875342.4. Singer FR, Bone HG, 3rd , Hosking DJ, et al. Paget's disease of bone: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:4408–4422. PMID: 25406796.
Article5. Wat WZ. Current perspectives on bisphosphonate treatment in Paget's disease of bone. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014; 10:977–983. PMID: 25429226.6. Choy WS, Baek CH, Koh DH. Paget's disease of bone: one case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1991; 26:970–974.
Article7. Cho SH, Suk SI, Ahn GH. Paget's disease: One case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1982; 17:1031–1034.
Article8. Kang H, Park YC, Yang KH. Paget's disease: Skeletal manifestations and effect of bisphosphonates. J Bone Metab. 2017; 24:97–103. PMID: 28642853.
Article9. Siris ES, Roodman GD. Paget's disease of bone. In : Rosen CJ, editor. Primer on the metabolic bone diseases and disorders of mineral metabolism. 7th ed. Washington, DC: American Society for Bone and Mineral Research;2008. p. 335–343.10. Ralston SH, Layfield R. Pathogenesis of Paget disease of bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012; 91:97–113. PMID: 22543925.
Article11. Nebot Valenzuela E, Pietschmann P. Epidemiology and pathology of Paget's disease of bone - a review. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2017; 167:2–8.12. Zhang R, Zhang G, Wang R, et al. Paget disease in a radius. Korean J Intern Med. 2018; 33:647–648. PMID: 29551057.
Article13. Ralston SH, Corral-Gudino L, Cooper C, et al. Diagnosis and management of Paget's disease of bone in adults: A clinical guideline. J Bone Miner Res. 2019; 34:579–604. PMID: 30803025.
Article