Diabetes Metab J.
2020 Feb;44(1):78-90. 10.4093/dmj.2018.0265.
Efficacy and Safety of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients Treated with Statins for Residual Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 7Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 8Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- 10Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 13Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea.
- 14Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 15Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- 16Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 17Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea.
- 18Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- 19Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 20Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- 21Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju, Korea.
- 22Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 23Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 24Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 25Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 26Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Paul's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 27Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 28Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leemk@skku.edu
- KMID: 2470957
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0265
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Cardiovascular risk remains increased despite optimal low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level induced by intensive statin therapy. Therefore, recent guidelines recommend non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) as a secondary target for preventing cardiovascular events. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and tolerability of omega-3 fatty acids (OM3-FAs) in combination with atorvastatin compared to atorvastatin alone in patients with mixed dyslipidemia.
METHODS
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, and phase III multicenter study included adults with fasting triglyceride (TG) levels ≥200 and <500 mg/dL and LDL-C levels <110 mg/dL. Eligible subjects were randomized to ATOMEGA (OM3-FAs 4,000 mg plus atorvastatin calcium 20 mg) or atorvastatin 20 mg plus placebo groups. The primary efficacy endpoints were the percent changes in TG and non-HDL-C levels from baseline at the end of treatment.
RESULTS
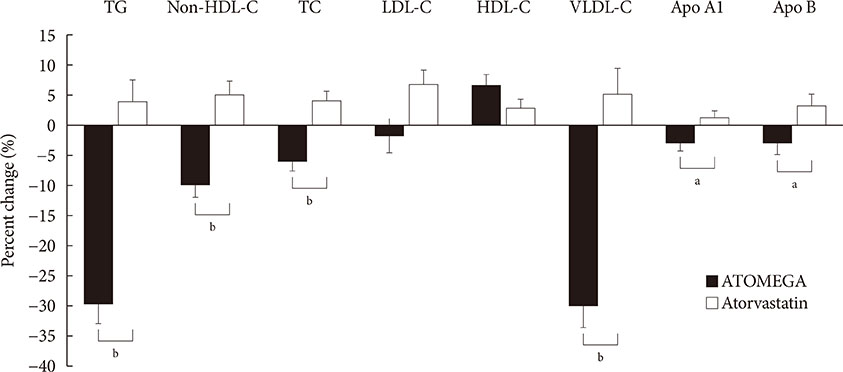
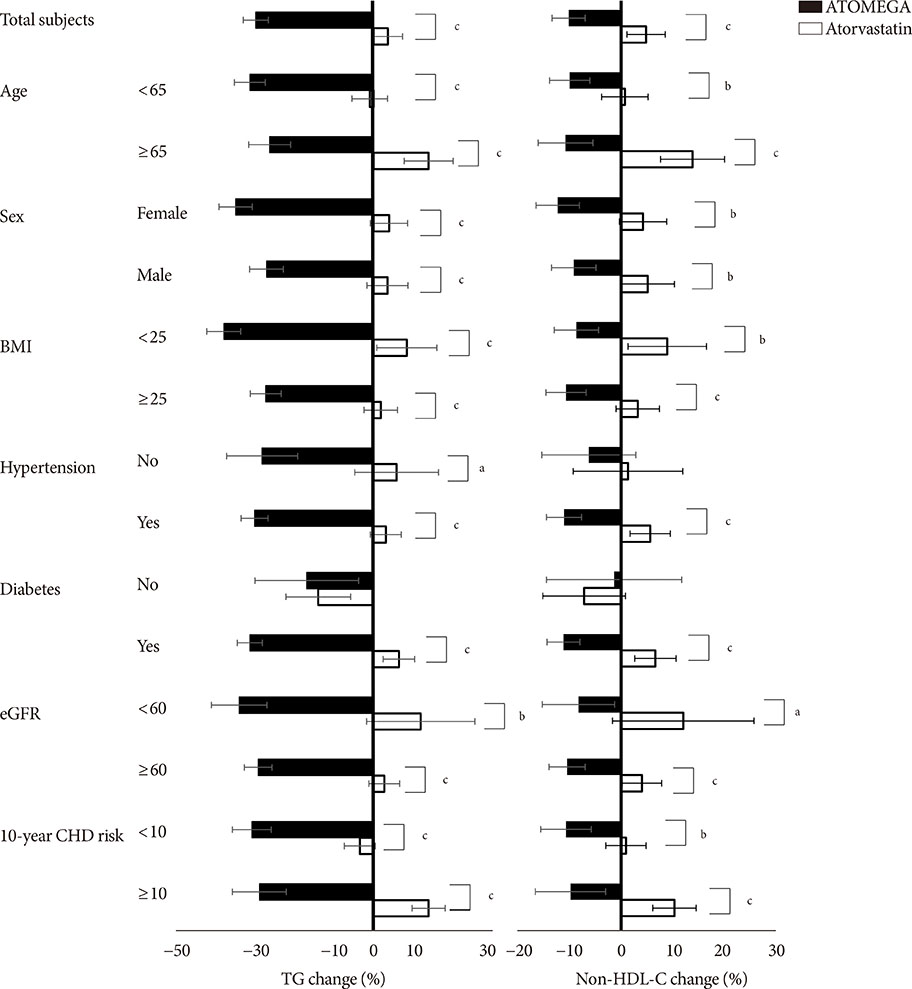
After 8 weeks of treatment, the percent changes from baseline in TG (−29.8% vs. 3.6%, P<0.001) and non-HDL-C (−10.1% vs. 4.9%, P<0.001) levels were significantly greater in the ATOMEGA group (n=97) than in the atorvastatin group (n=103). Moreover, the proportion of total subjects reaching TG target of <200 mg/dL in the ATOMEGA group was significantly higher than that in the atorvastatin group (62.9% vs. 22.3%, P<0.001). The incidence of adverse events did not differ between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
The addition of OM3-FAs to atorvastatin improved TG and non-HDL-C levels to a significant extent compared to atorvastatin alone in subjects with residual hypertriglyceridemia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. LaRosa JC, Grundy SM, Waters DD, Shear C, Barter P, Fruchart JC, Gotto AM, Greten H, Kastelein JJ, Shepherd J, Wenger NK. Treating to New Targets (TNT) Investigators. Intensive lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1425–1435.
Article2. Lee MH, Kim HC, Ahn SV, Hur NW, Choi DP, Park CG, Suh I. Prevalence of dyslipidemia among Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey 1998-2005. Diabetes Metab J. 2012; 36:43–55.
Article3. Hegele RA, Ginsberg HN, Chapman MJ, Nordestgaard BG, Kuivenhoven JA, Averna M, Boren J, Bruckert E, Catapano AL, Descamps OS, Hovingh GK, Humphries SE, Kovanen PT, Masana L, Pajukanta P, Parhofer KG, Raal FJ, Ray KK, Santos RD, Stalenhoef AF, Stroes E, Taskinen MR, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Watts GF, Wiklund O. European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. The polygenic nature of hypertriglyceridaemia: implications for definition, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:655–666.
Article4. Tirosh A, Rudich A, Shochat T, Tekes-Manova D, Israeli E, Henkin Y, Kochba I, Shai I. Changes in triglyceride levels and risk for coronary heart disease in young men. Ann Intern Med. 2007; 147:377–385.
Article5. Miller M, Cannon CP, Murphy SA, Qin J, Ray KK, Braunwald E. PROVE IT-TIMI 22 Investigators. Impact of triglyceride levels beyond low-density lipoprotein cholesterol after acute coronary syndrome in the PROVE IT-TIMI 22 trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:724–730.
Article6. Scott R, O'Brien R, Fulcher G, Pardy C, D'Emden M, Tse D, Taskinen MR, Ehnholm C, Keech A. Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes (FIELD) Study Investigators. Effects of fenofibrate treatment on cardiovascular disease risk in 9,795 individuals with type 2 diabetes and various components of the metabolic syndrome: the Fenofibrate Intervention and Event Lowering in Diabetes (FIELD) study. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:493–498.
Article7. Elam M, Lovato L, Ginsberg H. The ACCORD-Lipid study: implications for treatment of dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Lipidol. 2011; 6:9–20.
Article8. Catapano AL, Graham I, De Backer G, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ, Drexel H, Hoes AW, Jennings CS, Landmesser U, Pedersen TR, Reiner Z, Riccardi G, Taskinen MR, Tokgozoglu L, Verschuren WMM, Vlachopoulos C, Wood DA, Zamorano JL, Cooney MT. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2016 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:2999–3058.
Article9. Singh AK, Singh R. Triglyceride and cardiovascular risk: a critical appraisal. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 20:418–428.
Article10. Jellinger PS, Handelsman Y, Rosenblit PD, Bloomgarden ZT, Fonseca VA, Garber AJ, Grunberger G, Guerin CK, Bell DSH, Mechanick JI, Pessah-Pollack R, Wyne K, Smith D, Brinton EA, Fazio S, Davidson M. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology guidelines for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Endocr Pract. 2017; 23:1–87.
Article11. Davidson MH, Stein EA, Bays HE, Maki KC, Doyle RT, Shalwitz RA, Ballantyne CM, Ginsberg HN. COMBination of prescription Omega-3 with Simvastatin (COMBOS) Investigators. Efficacy and tolerability of adding prescription omega-3 fatty acids 4 g/d to simvastatin 40 mg/d in hypertriglyceridemic patients: an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Ther. 2007; 29:1354–1367.
Article12. Kim CH, Han KA, Yu J, Lee SH, Jeon HK, Kim SH, Kim SY, Han KH, Won K, Kim DB, Lee KJ, Min K, Byun DW, Lim SW, Ahn CW, Kim S, Hong YJ, Sung J, Hur SH, Hong SJ, Lim HS, Park IB, Kim IJ, Lee H, Kim HS. Efficacy and safety of adding omega-3 fatty acids in statin-treated patients with residual hypertriglyceridemia: ROMANTIC (Rosuvastatin-OMAcor iN residual hyperTrIglyCeridemia), a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. Clin Ther. 2018; 40:83–94.
Article13. Dunbar RL, Nicholls SJ, Maki KC, Roth EM, Orloff DG, Curcio D, Johnson J, Kling D, Davidson MH. Effects of omega-3 carboxylic acids on lipoprotein particles and other cardiovascular risk markers in high-risk statin-treated patients with residual hypertriglyceridemia: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Lipids Health Dis. 2015; 14:98.
Article14. Wilson PW, D’Agostino RB, Levy D, Belanger AM, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB. Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation. 1998; 97:1837–1847.
Article15. Wong ND, Zhao Y, Quek RGW, Blumenthal RS, Budoff MJ, Cushman M, Garg P, Sandfort V, Tsai M, Lopez JAG. Residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in statin-treated adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J Clin Lipidol. 2017; 11:1223–1233.
Article16. Davidson MH, Maki KC, Pearson TA, Pasternak RC, Deedwania PC, McKenney JM, Fonarow GC, Maron DJ, Ansell BJ, Clark LT, Ballantyne CM. Results of the National Cholesterol Education (NCEP) Program Evaluation ProjecT Utilizing Novel E-Technology (NEPTUNE) II survey and implications for treatment under the recent NCEP Writing Group recommendations. Am J Cardiol. 2005; 96:556–563.
Article17. Puri R, Nissen SE, Shao M, Elshazly MB, Kataoka Y, Kapadia SR, Tuzcu EM, Nicholls SJ. Non-HDL cholesterol and triglycerides: implications for coronary atheroma progression and clinical events. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016; 36:2220–2228.18. Robinson JG, Wang S, Smith BJ, Jacobson TA. Meta-analysis of the relationship between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction and coronary heart disease risk. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 53:316–322.
Article19. Kastelein JJ, Maki KC, Susekov A, Ezhov M, Nordestgaard BG, Machielse BN, Kling D, Davidson MH. Omega-3 free fatty acids for the treatment of severe hypertriglyceridemia: the EpanoVa fOr Lowering Very high triglyceridEs (EVOLVE) trial. J Clin Lipidol. 2014; 8:94–106.
Article20. Ng TW, Ooi EM, Watts GF, Chan DC, Barrett PH. Atorvastatin plus omega-3 fatty acid ethyl ester decreases very-low-density lipoprotein triglyceride production in insulin resistant obese men. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:519–526.
Article21. Ballantyne CM, Bays HE, Kastelein JJ, Stein E, Isaacsohn JL, Braeckman RA, Soni PN. Efficacy and safety of eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (AMR101) therapy in statin-treated patients with persistent high triglycerides (from the ANCHOR study). Am J Cardiol. 2012; 110:984–992.
Article22. Skulas-Ray AC, West SG, Davidson MH, Kris-Etherton PM. Omega-3 fatty acid concentrates in the treatment of moderate hypertriglyceridemia. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008; 9:1237–1248.
Article23. Lee MW, Park JK, Hong JW, Kim KJ, Shin DY, Ahn CW, Song YD, Cho HK, Park SW, Lee EJ. Beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids on low density lipoprotein particle size in patients with type 2 diabetes already under statin therapy. Diabetes Metab J. 2013; 37:207–211.
Article24. Haffner SM, Stern MP, Hazuda HP, Mitchell BD, Patterson JK. Cardiovascular risk factors in confirmed prediabetic individuals. Does the clock for coronary heart disease start ticking before the onset of clinical diabetes? JAMA. 1990; 263:2893–2898.
Article25. Yang K, Zeng L, Bao T, Ge J. Effectiveness of omega-3 fatty acid for polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018; 16:27.
Article26. Yan JH, Guan BJ, Gao HY, Peng XE. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e12271.27. Jacobo-Cejudo MG, Valdes-Ramos R, Guadarrama-Lopez AL, Pardo-Morales RV, Martinez-Carrillo BE, Harbige LS. Effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Nutrients. 2017; 9:E573.
Article28. Lepretti M, Martucciello S, Burgos Aceves MA, Putti R, Lionetti L. Omega-3 fatty acids and insulin resistance: focus on the regulation of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nutrients. 2018; 10:E350.
Article29. Chen C, Yu X, Shao S. Effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on glucose control and lipid levels in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0139565.
Article30. Maki KC, Dicklin MR, Lawless A, Reeves MS. Omega-3 fatty acids for the treatment of elevated triglycerides. Clin Lipidol. 2009; 4:425–437.
Article31. Chan DC, Watts GF, Barrett PH, Beilin LJ, Redgrave TG, Mori TA. Regulatory effects of HMG CoA reductase inhibitor and fish oils on apolipoprotein B-100 kinetics in insulin-resistant obese male subjects with dyslipidemia. Diabetes. 2002; 51:2377–2386.
Article32. Notarnicola M, Messa C, Refolo MG, Tutino V, Miccolis A, Caruso MG. Synergic effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and lovastatin on gene expression of HMGCoA reductase and LDL receptor in cultured HepG2 cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2010; 9:135.
Article33. Davidson MH. Omega-3 fatty acids: new insights into the pharmacology and biology of docosahexaenoic acid, docosapentaenoic acid, and eicosapentaenoic acid. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2013; 24:467–474.34. Yuki T, Ii M, Nagatsuka T, Fujisaka T, Takeda Y, Hoshiga M, Imagawa A. Synergistic favorable effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and statin on atherosclerosis. Biomed Res. 2018; 29:2147–2152.
Article35. Bowen KJ, Harris WS, Kris-Etherton PM. Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: are there benefits? Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2016; 18:69.
Article36. Yokoyama M, Origasa H, Matsuzaki M, Matsuzawa Y, Saito Y, Ishikawa Y, Oikawa S, Sasaki J, Hishida H, Itakura H, Kita T, Kitabatake A, Nakaya N, Sakata T, Shimada K, Shirato K. Japan EPA lipid intervention study (JELIS) Investigators. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on major coronary events in hypercholesterolaemic patients (JELIS): a randomised open-label, blinded endpoint analysis. Lancet. 2007; 369:1090–1098.
Article37. Bhatt DL, Steg PG, Miller M, Brinton EA, Jacobson TA, Ketchum SB, Doyle RT Jr, Juliano RA, Jiao L, Granowitz C, Tardif JC, Ballantyne CM. REDUCE-IT Investigators. Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:11–22.
Article38. Nosaka K, Miyoshi T, Iwamoto M, Kajiya M, Okawa K, Tsukuda S, Yokohama F, Sogo M, Nishibe T, Matsuo N, Hirohata S, Ito H, Doi M. Early initiation of eicosapentaenoic acid and statin treatment is associated with better clinical outcomes than statin alone in patients with acute coronary syndromes: 1-year outcomes of a randomized controlled study. Int J Cardiol. 2017; 228:173–179.
Article39. Eussen SR, Geleijnse JM, Giltay EJ, Rompelberg CJ, Klungel OH, Kromhout D. Effects of n-3 fatty acids on major cardiovascular events in statin users and non-users with a history of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33:1582–1588.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy and Safety of Prescription Omega-3 Fatty Acids Added to Stable Statin Therapy in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertriglyceridemia: a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Omega 3 fatty acids as a host modulator in chronic periodontitis patients: a randomised, double-blind, palcebo-controlled, clinical trial
- Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Low Density Lipoprotein Subfraction, Adiponectin and Apolipoprotein B in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Hypertriglyceridemia and Cardiovascular Diseases: Revisited
- An Update on Hypertriglyceridemia-Induced Acute Pancreatitis