Nat Prod Sci.
2019 Dec;25(4):311-316. 10.20307/nps.2019.25.4.311.
Synergistic Effect of Flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllus Heartwoods on Anticancer Activity of Cisplatin Against H460 and MCF-7 Cell Lines
- Affiliations
-
- 1Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Sultan Zainal Abidin, Jalan Sultan Mahmud 20400, Kuala Terengganu, Terengganu, Malaysia. nordinsimbak@unisza.edu.my
- 2Research Center for Chemistry, Indonesian Institute of Sciences, Kawasan PUSPIPTEK Serpong, Tangerang Selatan, Banten 15314, Indonesia. abdiwiraseptama@gmail.com
- 3Faculty of Medicine, UPN Veteran, Jl. Rs. Fatmawati, Pondok Labu, Jakarta Selatan, 12450, Indonesia.
- KMID: 2468064
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2019.25.4.311
Abstract
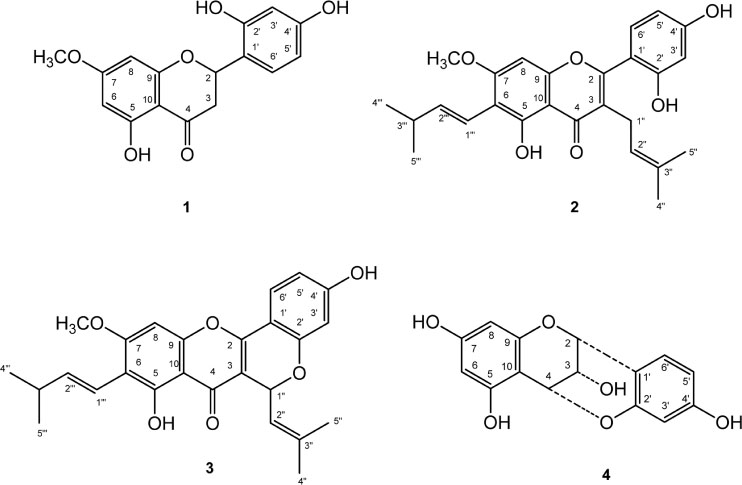
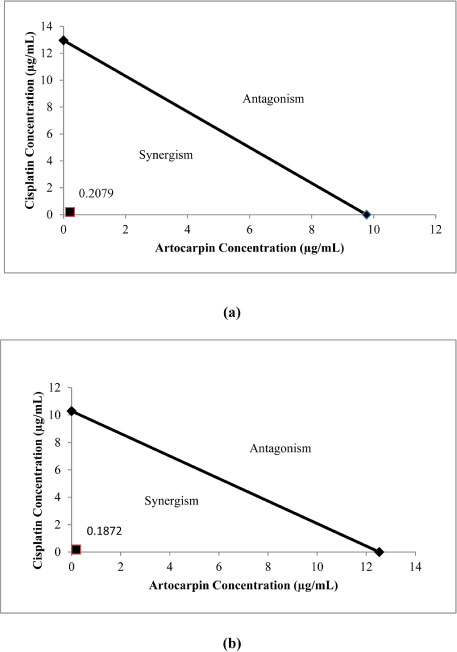
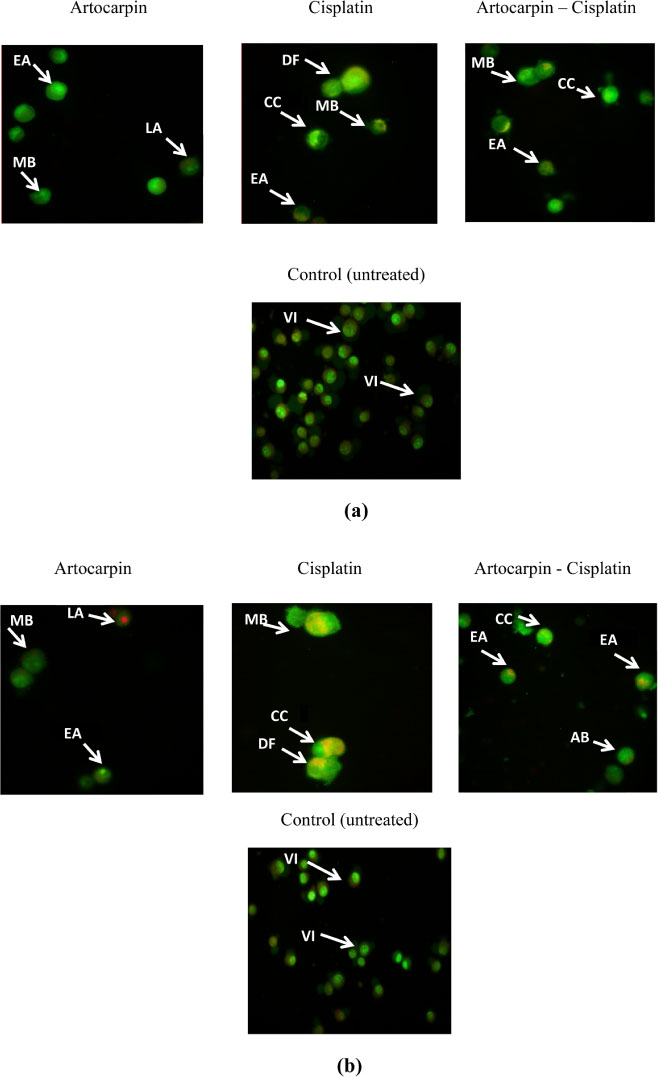
- Artocarpus heterophyllus has been used as traditional medicine. This plant is one of the sources of flavonoid. Flavonoid compounds possessed a wide range of biological properties including anticancer. This study was performed to investigate the cytotoxic effect of flavonoids from A. heterophyllus on H460 and MCF-7 cell lines. The interaction of flavonoids and cisplatin against tested cancer cells was also evaluated. MTT assay was used to determine the cytotoxic effect of flavonoid. Isobologram analysis was selected to evaluate the synergistic effect between flavonoid and cisplatin, their interaction was then confirmed using AO/PI staining method. Amongst of flavonoid compounds, artocarpin exhibited strong cytotoxic effect on both MCF-7 and H460 cell lines with ICâ‚…â‚€ values of 12.53 µg/mL (28.73 µM) and 9.77 µg/mL (22.40 µM), respectively. This compound enhanced anticancer activity of cisplatin against H460 and MCF-7. The combination produced a synergistic effect on H460 and MCF-7 cell lines with a combination index (CI) values of 0.2 and 0.18, respectively. The AO/PI stained demonstrated that the combination of artocarpin and cisplatin caused morphological changes that indicated apoptosis. Moreover, artocarpanone also significantly increased cytotoxic effect of cisplatin compared to its single concentration with CI below than 1. This result suggested the potency of flavonoid named artocarpin to enhance the anticancer activity of cisplatin on H460 and MCF-7 cell lines.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108.2. Oser MG, Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Engelman JA. The Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:e165–e172.3. Tao Z, Shi A, Lu C, Song T, Zhang Z, Zhao J. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015; 72:333–338.4. Borghei YS, Hosseini M, Dadmehr M, Hosseinkhani S, Ganjali MR, Sheikhnejad R. Anal Chim Acta. 2016; 904:92–97.5. Ahmad M, Khan MA, Marwat KS, Zafar M, Khan MA, Hassan TU, Sultana S. American-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci. 2009; 5:126–140.6. Cai Y, Luo Q, Sun M, Corke H. Life Sci. 2004; 74:2157–2184.7. Salguero CP. A traditional recipes for health and harmony; Findhor. Scotland: Findhorn press;2003. p. 119.8. Arung ET, Yoshikawa K, Shimizu K, Kondo R. Fitoterapia. 2010; 81:120–123.9. Septama AW, Panichayupakaranant P. Pharm Biol. 2015; 53:1608–1613.10. Septama AW, Panichayupakaranant P. Pharm Biol. 2016; 54:686–691.11. Sato M, Fujiwara S, Tsuchiya H, Fujii T, Iinuma M, Tosa H, Ohkawa Y. J Ethnopharmacol. 1996; 54:171–176.12. Septama AW, Jantan I, Panichayupakaranant P. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2018; 70:1242–1252.13. Ko FN, Cheng ZJ, Lin CN, Teng CM. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998; 25:160–168.14. Zheng ZP, Chen S, Wang S, Cheng KW, Wu JJ, Yang D, Wang M. . J Agric Food Chem. 2009; 57:6649–6655.15. Oladimenji P, Cui H, Zhang C, Chen T. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016; 12:997–1010.16. Li P, Yang S, Dou M, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhao X. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014; 140:2065–2075.17. Zhang Z, Guo S, Liu X, Gao X. Drug Res. 2015; 65:214–218.18. Goh SH, Mohamed Alitheen NB, Md Yussoff F, Yap SK, Loh SP. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014; 10:1–8.19. Arung ET, Wicaksono BD, Handoko YA, Kusuma IW, Shimizu K, Yulia D, Sandra F. J Nat Med. 2010; 64:423–429.20. Tsai MH, Liu JF, Chiang YC, Hu SC, Hsu LF, Lin YC, Lin ZC, Lee HC, Chen MC, Huang CL, Lee CW. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:28342–28358.21. Chan EWC, Wong SK, Tangah J, Chan HT. Sys Rev Pharm. 2018; 9:58–63.22. Amable L. Pharmacol Res. 2016; 106:27–36.23. Yang Y, Zhang Z, Li S, Ye X, Li X, He K. Fitoterapia. 2014; 92:133–147.24. Solomon M, Wofford J, Johnson C, Regan D, Creer MH. Transfusion. 2010; 50:820–830.25. Chan LL, Wilkinson AR, Paradis BD, Lai N. J Fluoresc. 2012; 22:1301–1311.26. Chan LL, Laverty DJ, Smith T, Nejad P, Hei H, Gandhi R, Kuksin D, Qiu J. J Immunol Methods. 2013; 388:25–32.27. Chan LL, Kuksin D, Laverty DJ, Saldi S, Qiu J. Cytotechnology. 2015; 67:461–473.28. Stankovic MS, Curcic MG, Zizic JB, Topuzovic MD, Solujic SR, Markovic SD. Int J Mol Sci. 2011; 12:4190–4205.29. Alabsi AM, Ali R, Ali AM, Al-Dubai SA, Harun H, Abu Kasim NH, Alsalahi A. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2002; 13:5131–5136.30. Li CJ, Chu CY, Huang LH, Wang MH, Sheu LF, Yeh JI, Hsu HY. Cancer Lett. 2012; 319:203–213.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Simultaneous HPLC Analysis of Three Flavonoids in the Extracts of Artocarpus heterophyllus Heartwoods
- Inhibition of Melanoma Cell Lines Using Antisense Sequence Expressing Adenovirus and Cisplatin
- Effects of genistein on anti-tumor activity of cisplatin in human cervical cancer cell lines
- In Vitro Interaction of Taxol with Other Antitumor Drugs in the Established Choriocarcinoma Cell Lines
- Differential Effects of Tautomycetin and Its Derivatives on Protein Phosphatase Inhibition, Immunosuppressive Function and Antitumor Activity