Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2020 Jan;23(1):35-48. 10.5223/pghn.2020.23.1.35.
Risk and Protective Factors for Gastrointestinal Symptoms associated with Antibiotic Treatment in Children: A Population Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric, Ospedale “F. Del Ponteâ€, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy. silvia.salvatore@uninsubria.it
- 2Department of Statistic, University of Padua, Padua, Italy.
- KMID: 2467892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2020.23.1.35
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Gastrointestinal symptoms are often related to antibiotic treatment. Their incidence, risk and protective conditions in children are not well defined and represent the aims of this study.
METHODS
We prospectively enrolled inpatient children submitted to antibiotic treatment. Indication, type, dose and duration of treatment, probiotic supplementation and gastrointestinal symptoms were recorded at recruitment, after two and four weeks. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) was defined as the presence of at least 3 loose/liquid stools within 14 days from antibiotic onset.
RESULTS
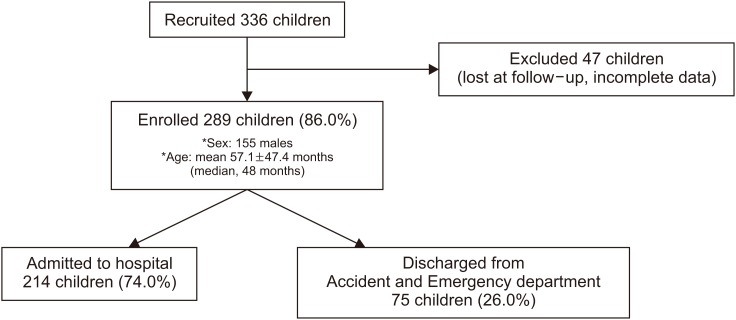
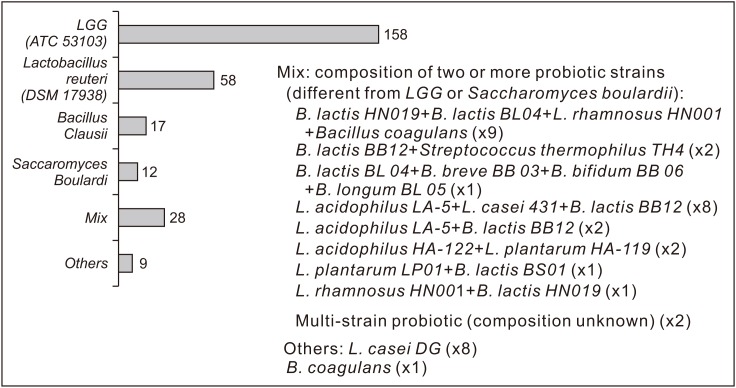
AAD occurred in 59/289 (20.4%) of patients, with increased risk in children younger than 3 years (relative risk [RR]=4.25), in lower respiratory (RR=2.11) and urinary infections (RR=3.67), intravenous administration (RR=1.81) and previous AAD episodes (RR=1.87). Abdominal pain occurred in 27/289 (9.3%), particularly in children >6 years (RR=4.15), with previous abdominal pain (RR=7.2) or constipation (RR=4.06). Constipation was recorded in 23/289 (8.0%), with increased risk in children having surgery (RR=2.56) or previous constipation (RR=7.38). Probiotic supplementation significantly reduced AAD (RR=0.30) and abdominal pain (RR=0.36). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) and L. reuteri significantly reduced AAD (RR=0.37 and 0.35) and abdominal pain (RR=0.37 and 0.24).
CONCLUSION
AAD occurred in 20.4% of children, with increased risk at younger age, lower respiratory and urinary tract infections, intravenous treatment and previous AAD. LGG and L. reuteri reduced both AAD and associated abdominal pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chai G, Governale L, McMahon AW, Trinidad JP, Staffa J, Murphy D. Trends of outpatient prescription drug utilization in US children, 2002-2010. Pediatrics. 2012; 130:23–31. PMID: 22711728.
Article2. Goldenberg JZ, Lytvyn L, Steurich J, Parkin P, Mahant S, Johnston BC. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015; (12):CD004827. PMID: 26695080.
Article3. Videlock EJ, Cremonini F. Meta-analysis: probiotics in antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 35:1355–1369. PMID: 22531096.
Article4. Reed DE, Vanner SJ. Emerging studies of human visceral nociceptors. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017; 312:G201–7. PMID: 28007748.
Article5. Szajewska H, Canani RB, Guarino A, Hojsak I, Indrio F, Kolacek S, et al. ESPGHAN Working Group for ProbioticsPrebiotics. Probiotics for the Prevention of Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea in Children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016; 62:495–506. PMID: 26756877.
Article6. World Health Organization. Diarrhoeal Disease Fact Sheet [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2017. cited 2019 Aug date. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diarrhoeal-disease.7. McFarland LV, Ozen M, Dinleyici EC, Goh S. Comparison of pediatric and adult antibiotic-associated diarrhea and Clostridium difficile infections. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:3078–3104. PMID: 27003987.8. Cai J, Zhao C, Du Y, Zhang Y, Zhao M, Zhao Q. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of probiotics for antibiotic-associated diarrhea: systematic review with network meta-analysis. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018; 6:169–180.
Article9. Reyes H, Guiscafré H, Muñoz O, Pérez-Cuevas R, Martinez H, Gutiérrez G. Antibiotic noncompliance and waste in upper respiratory infections and acute diarrhea. J Clin Epidemiol. 1997; 50:1297–1304. PMID: 9393386.
Article10. McFarland LV. [Risk factor for antibiotic-associated diarrhea. A review of the literature]. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1998; 149:261–266. French. PMID: 9791558.11. McFarland LV, Goh S. Preventing pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea and Clostridium difficile infections with probiotics: a meta-analysis. World J Meta-Anal. 2013; 1:102–120.12. Turck D, Bernet JP, Marx J, Kempf H, Giard P, Walbaum O, et al. Incidence and risk factors of oral antibiotic-associated diarrhea in an outpatient pediatric population. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003; 37:22–26. PMID: 12827001.
Article13. Erdeve O, Tiras U, Dallar Y. The probiotic effect of Saccharomyces boulardii in a pediatric age group. J Trop Pediatr. 2004; 50:234–236. PMID: 15357564.
Article14. Murphy JL, Fenn N, Pyle L, Heizer H, Hughes S, Nomura Y, et al. Adverse events in pediatric patients receiving long-term oral and intravenous antibiotics. Hosp Pediatr. 2016; 6:330–338. PMID: 27220835.
Article15. Li N, Zheng B, Cai HF, Chen YH, Qiu MQ, Liu MB. Cost-effectiveness analysis of oral probiotics for the prevention of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea in children and adolescents. J Hosp Infect. 2018; 99:469–474. PMID: 29678466.
Article16. Hyams JS, Di Lorenzo C, Saps M, Shulman RJ, Staiano A, van Tilburg M. Functional disorders: children and adolescents. Gastroenterology. 2016; DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.015. [Epub ahead of print].17. Benninga MA, Faure C, Hyman PE, St James Roberts I, Schechter NL, Nurko S. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: neonate/toddler. Gastroenterology. 2016; DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.016. [Epub ahead of print].
Article18. Tabbers MM, DiLorenzo C, Berger MY, Faure C, Langendam MW, Nurko S, et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology. Evaluation and treatment of functional constipation in infants and children: evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014; 58:258–274. PMID: 24345831.19. Patro-Golab B, Shamir R, Szajewska H. Yogurt for treating antibiotic-associated diarrhea: systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition. 2015; 31:796–800. PMID: 25933485.
Article20. Akobeng AK. Communicating the benefits and harms of treatments. Arch Dis Child. 2008; 93:710–713. PMID: 18456681.
Article21. Guo B, Yuan Y. A comparative review of methods for comparing means using partially paired data. Stat Methods Med Res. 2017; 26:1323–1340. PMID: 25834090.
Article22. Johnston BC, Shamseer L, da Costa BR, Tsuyuki RT, Vohra S. Measurement issues in trials of pediatric acute diarrheal diseases: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2010; 126:e222–31. PMID: 20566617.
Article23. Castelluzzo MA, Tarsitano F, Pensabene F. Approccio al bambino con disturbi funzionali gastrointestinali. Prosp in Ped. 2016; 46:276–289.24. Robinson CJ, Young VB. Antibiotic administration alters the community structure of the gastrointestinal micobiota. Gut Microbes. 2010; 1:279–284. PMID: 20953272.25. Haran JP, Hayward G, Skinner S, Merritt C, Hoaglin DC, Hibberd PL, et al. Factors influencing the development of antibiotic associated diarrhea in ED patients discharged home: risk of administering IV antibiotics. Am J Emerg Med. 2014; 32:1195–1199. PMID: 25149599.
Article26. Szajewska H. What are the indications for using probiotics in children? Arch Dis Child. 2016; 101:398–403. PMID: 26347386.
Article27. Urbańska M, Gieruszczak-Białek D, Szajewska H. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 for diarrhoeal diseases in children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016; 43:1025–1034. PMID: 26991503.28. Uusijärvi A, Bergström A, Simrén M, Ludvigsson JF, Kull I, Wickman M, et al. Use of antibiotics in infancy and childhood and risk of recurrent abdominal pain--a Swedish birth cohort study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014; 26:841–850. PMID: 24708246.
Article29. Pensabene L, Talarico V, Concolino D, Ciliberto D, Campanozzi A, Gentile T, et al. Post-Infectious Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Study Group of Italian Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. Postinfectious functional gastrointestinal disorders in children: a multicenter prospective study. J Pediatr. 2015; 166:903–907.e1. PMID: 25661403.
Article30. Saps M, Pensabene L, Di Martino L, Staiano A, Wechsler J, Zheng X, et al. Post-infectious functional gastrointestinal disorders in children. J Pediatr. 2008; 152:812–816.e1. PMID: 18492522.
Article31. Saps M, Pensabene L, Turco R, Staiano A, Cupuro D, Di Lorenzo C. Rotavirus gastroenteritis: precursor of functional gastrointestinal disorders? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009; 49:580–583. PMID: 19633576.
Article32. Salvatore S, Pensabene L, Borrelli O, Saps M, Thapar N, Concolino D, et al. Mind the gut: probiotics in paediatric neurogastroenterology. Benef Microbes. 2018; 9:883–898. PMID: 30198327.
Article33. Smith JT, Smith MS. Does a preoperative bowel preparation reduce bowel morbidity and length of stay after scoliosis surgery? A randomized prospective study. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33:e69–71. PMID: 23812136.
Article34. Korterink JJ, Ockeloen L, Benninga MA, Tabbers MM, Hilbink M, Deckers-Kocken JM. Probiotics for childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2014; 103:365–372. PMID: 24236577.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on Children's Mental Health of Mothers with Mental Illness
- Which Alarm Symptoms Are Associated With Abnormal Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Among Thai Children?
- Prevalence, risk factors, and treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in children
- Equivalence model: A new graphical model for causal inference
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes