Lab Med Online.
2020 Jan;10(1):88-91. 10.3343/lmo.2020.10.1.88.
A Case of Donor Cell Leukemia after Allogenic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with PML-RARA
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea. rpark@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2466771
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2020.10.1.88
Abstract
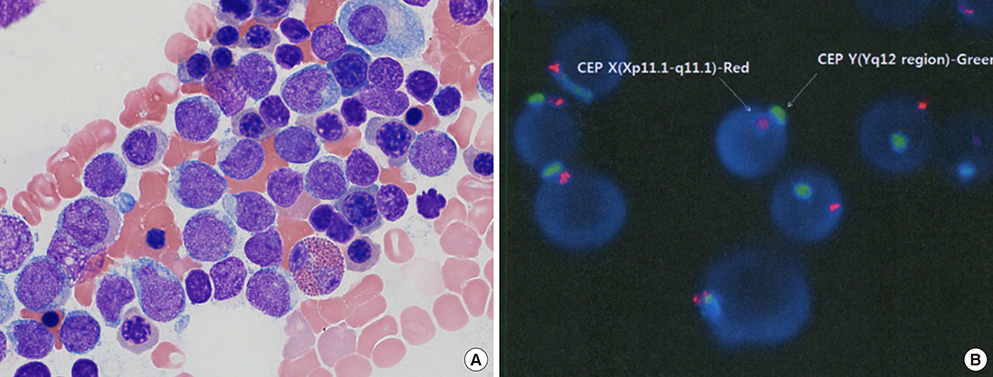
- Donor cell leukemia (DCL), a rare but fatal complication arising from allogenic stem cell transplantation, is a complex disease associated with multiple pathophysiological processes. Specific diagnosis of DCL distinct from relapsed leukemia is important owing to its implications in setting up therapeutic approaches. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), short tandem repeat (STR), variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) tests, or informative single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis can be used to confirm the origin of leukemic cells from donor cells. Here, we report a case of DCL in a female patient after allogeneic peripheral stem cell transplantation from a male donor for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) with PML-RARA. DCL developed 6 years after stem cell transplantation and leukemic cells of donor origin were confirmed by the presence of Y chromosome on the X/Y FISH analysis of bone marrow aspirate specimen. This is the first case of DCL reported in an APL patient in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hertenstein B, Hambach L, Bacigalupo A, Schmitz N, McCann S, Slavin S, et al. Chronic Leukaemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Development of leukemia in donor cells after allogeneic stem cell transplantation-a survey of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Haematologica. 2005; 90:969–975.2. Wang E, Hutchison CB, Huang Q, Lu CM, Crow J, Wang FF, et al. Donor cell-derived leukemias/myelodysplastic neoplasms in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: A clinicopathologic study of 10 cases and a comprehensive review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 135:525–540.
Article3. Kim EJ, Kim YS, Lee HS, Lee EM, Park IC, Lee WH, et al. A case of donor cell leukemia after allogenic bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Korean J Med. 2014; 86:510–514.
Article4. Rashidi A. FISH-negative, cytogenetically cryptic acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2015; 5:e320.
Article5. Wiseman DH. Donor cell leukemia: A review. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011; 17:771–789.
Article6. Ruiz-Delgado GJ, Hernández-Reyes J, González-Ramírez MP, Martagón-Herrera NÁ, Garcés-Eisele J, Ruiz-Argüelles A, et al. Donor cell leukemia (DCL): A prospective study of its identification and treatment. Gac Med Mex. 2015; 151:582–587.7. Niederwieser DW, Appelbaum FR, Gastl G, Gersdorf E, Meister B, Gei-ssler D, et al. Inadvertent transmission of a donor’s acute myeloid leukemia in bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:1794–1796.
Article8. Yasuda T, Ueno T, Fukumura K, Yamato A, Ando M, Yamaguchi H, et al. Leukemic evolution of donor-derived cells harboring IDH2 and DNMT3A mutations after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2014; 28:426–428.
Article9. Kobayashi S, Kobayashi A, Osawa Y, Nagao S, Takano K, Okada Y, et al. Donor cell leukemia arising from preleukemic clones with a novel germline DDX41 mutation after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2017; 31:1020–1022.
Article10. Comoli P, Basso S, Zecca M, Pagliara D, Baldanti F, Bernardo ME, et al. Preemptive therapy of EBV-related lymphoproliferative disease after pediatric haploidentical stem cell transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:1648–1655.
Article11. Wright EG. Ionizing radiation and leukaemia: more questions than answers. Hematol Oncol. 2005; 23:119–126.
Article12. Cooley LD, Sears DA, Udden MM, Harrison WR, Baker KR. Donor cell leukemia: report of a case occurring 11 years after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation and review of the literature. Am J Hematol. 2000; 63:46–53.
Article13. Flynn CM. Donor cell leukemia: insight into cancer stem cells and the stem cell niche. Blood. 2007; 109:2688–2692.
Article14. Curtis RE, Rowlings PA, Deeg HJ, Shriner DA, Socíe G, Travis LB, et al. Solid cancers after bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:897–904.
Article15. Wynn RF, Cross MA, Hatton C, Will AM, Lashford LS, Dexter TM, et al. Accelerated telomere shortening in young recipients of allogeneic bone-marrow transplants. Lancet. 1998; 351:178–181.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Case Report of a Child with High-Risk Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Treated with Allogenic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
- A Case of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with Co-existence of BCR-ABL1 and PML-RARA Rearrangements Detected by PCR
- Utility of RARa Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for Follow-up in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: Comparison with PML/RARa Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
- The t (15;17) Breakpoint of the PML Gene in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
- Detection of PML/RARA Rearrangement by Reverse Transcriptase-PCR and Sequencing in a Case of Microgranular Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Lacking t(15;17) on Karyotype and FISH