Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Apr;51(2):737-747. 10.4143/crt.2018.342.
Discordance of the PAM50 Intrinsic Subtypes Compared with Immunohistochemistry-Based Surrogate in Breast Cancer Patients: Potential Implication of Genomic Alterations of Discordance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yhparkhmo@skku.edu
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 3Samsung Genome Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jonghan.yu@samsung.com
- KMID: 2464419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.342
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We aimed to analyze the discordance between immunohistochemistry (IHC)-based surrogate subtyping and PAM50 intrinsic subtypes and to assess overall survival (OS) according to discordance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 607 patients were analyzed. Hormone receptor (HR) expression was evaluated by IHC, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression was analyzed by IHC and/or fluorescence in situ hybridization. PAM50 intrinsic subtypes were determined according to 50 cancer genes using the NanoString nCounter Analysis System. We matched concordant tumor as luminal A and HR+/HER2-, luminal B and HR+/HER2+, HR-/HER2+ and HER2-enriched, and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and normal- or basal-like. We used Ion Ampliseq Cancer Panel v2 was used to identify the genomic alteration related with discordance. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate OS.
RESULTS
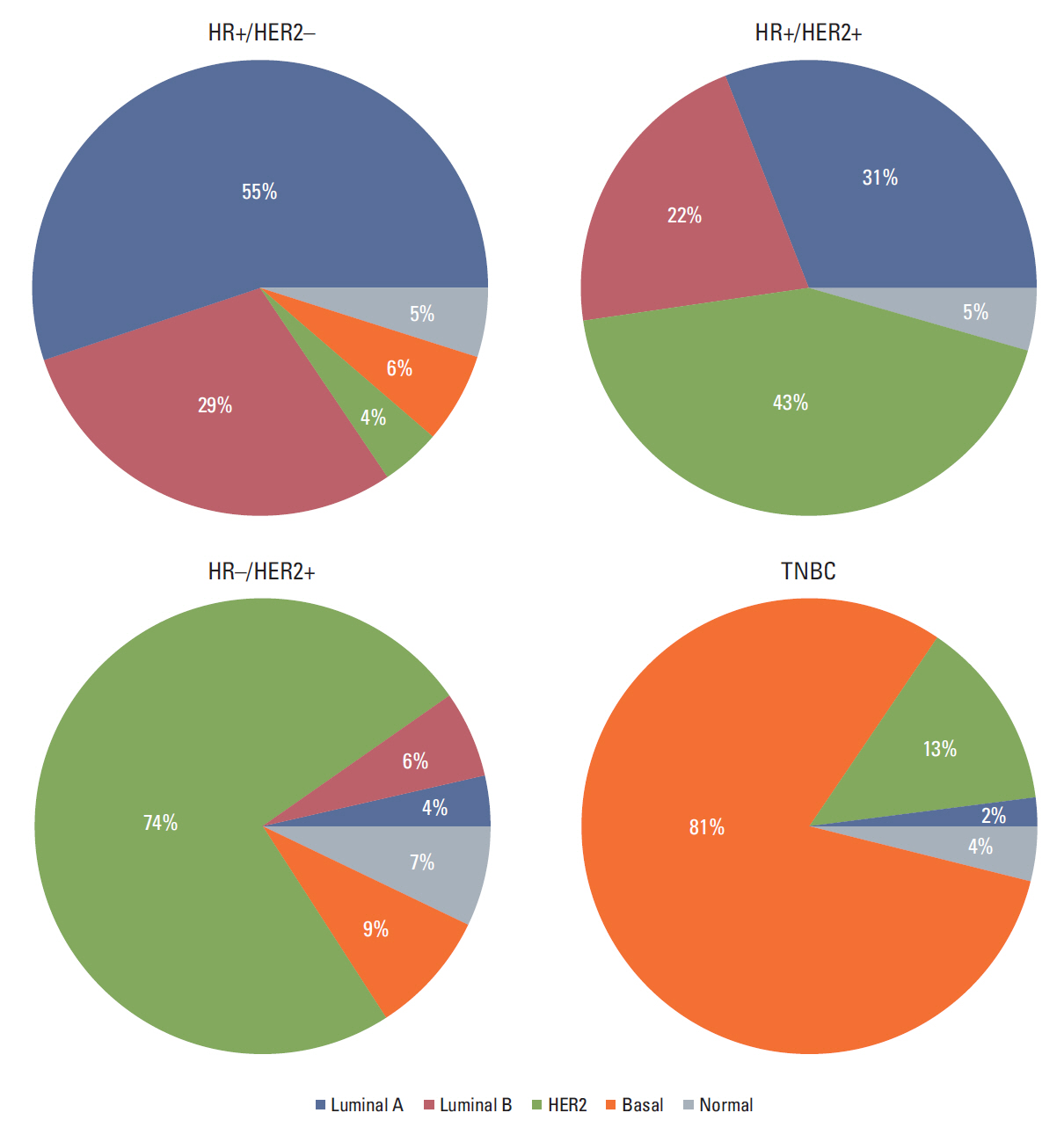
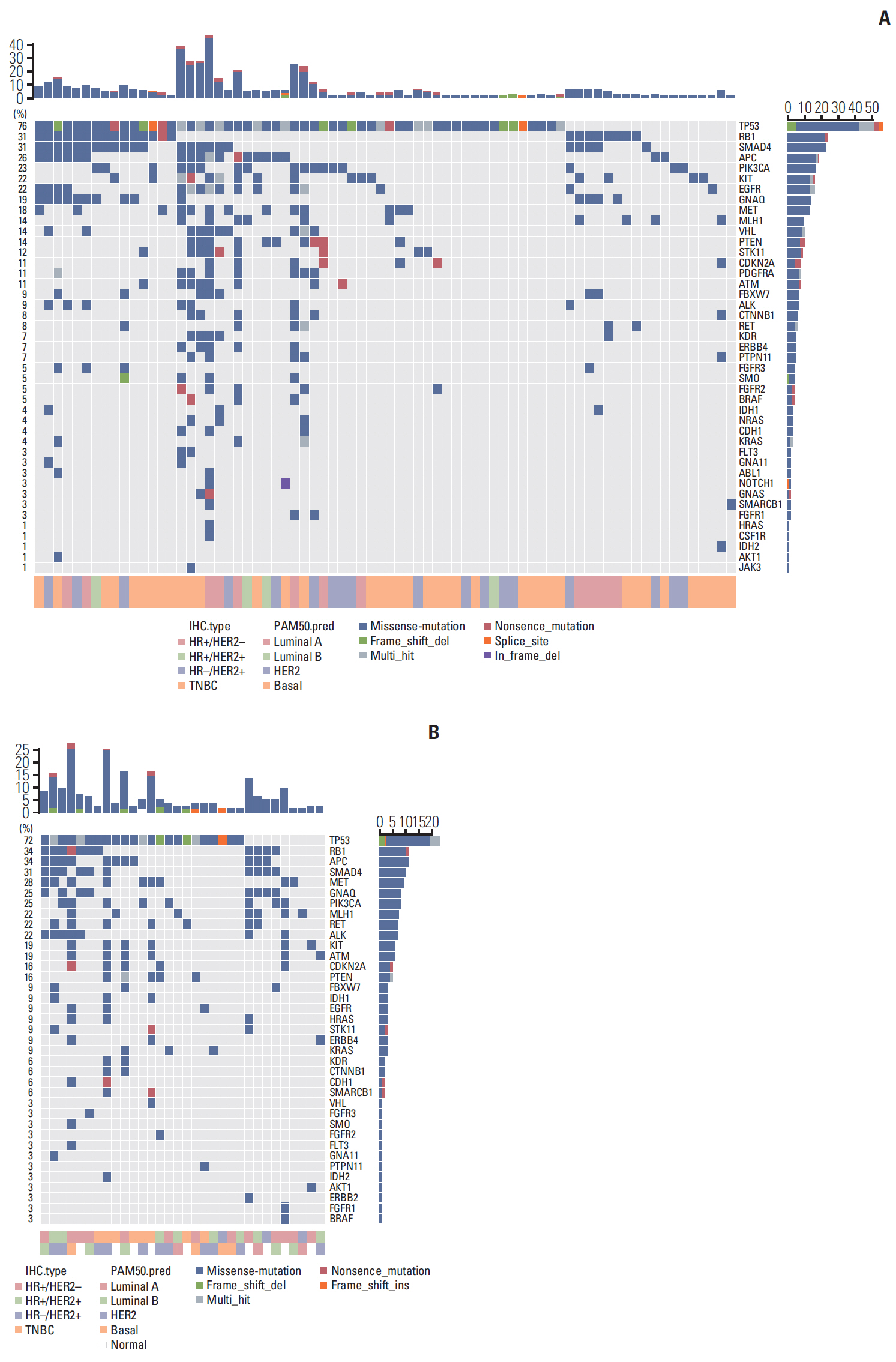
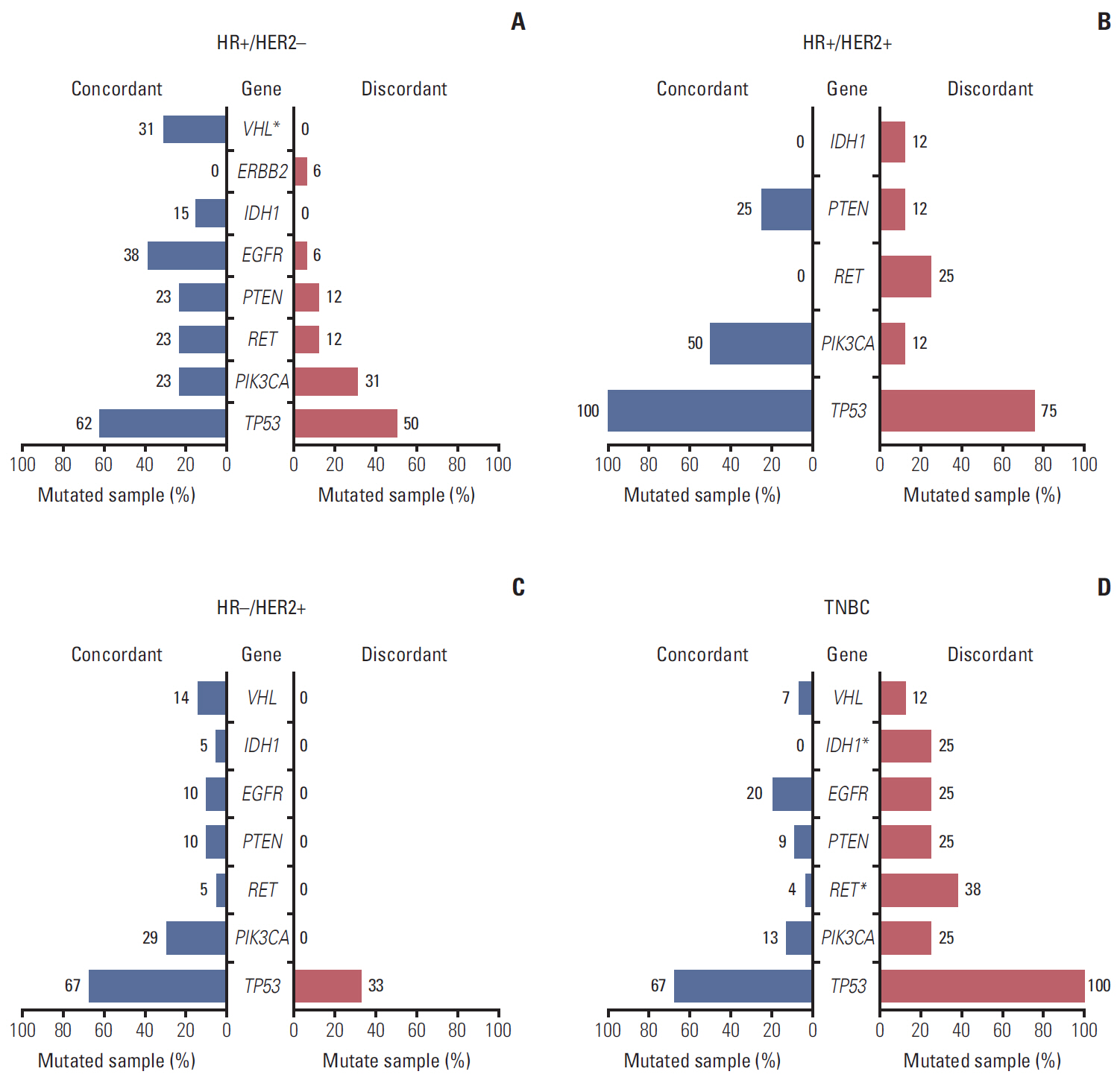
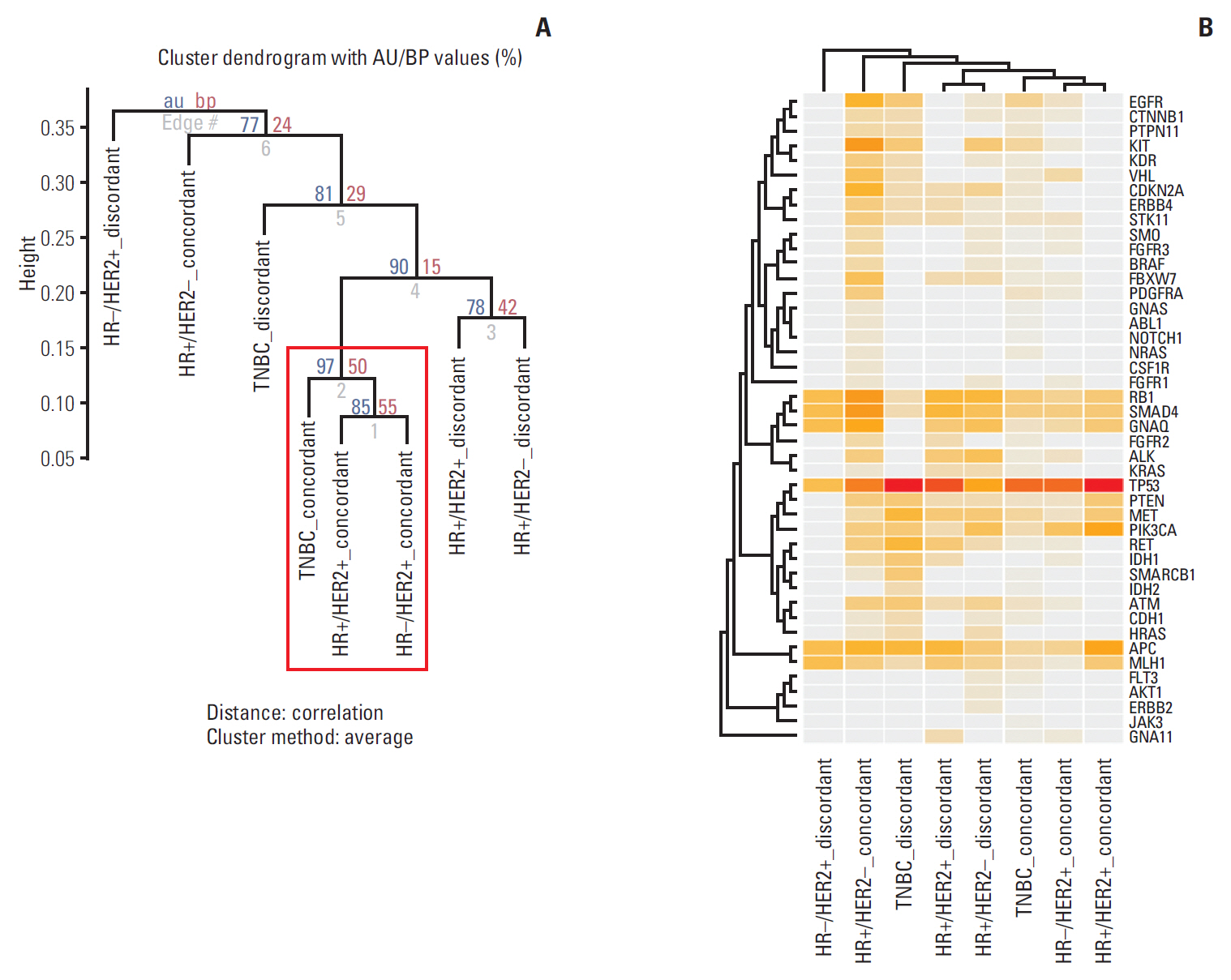
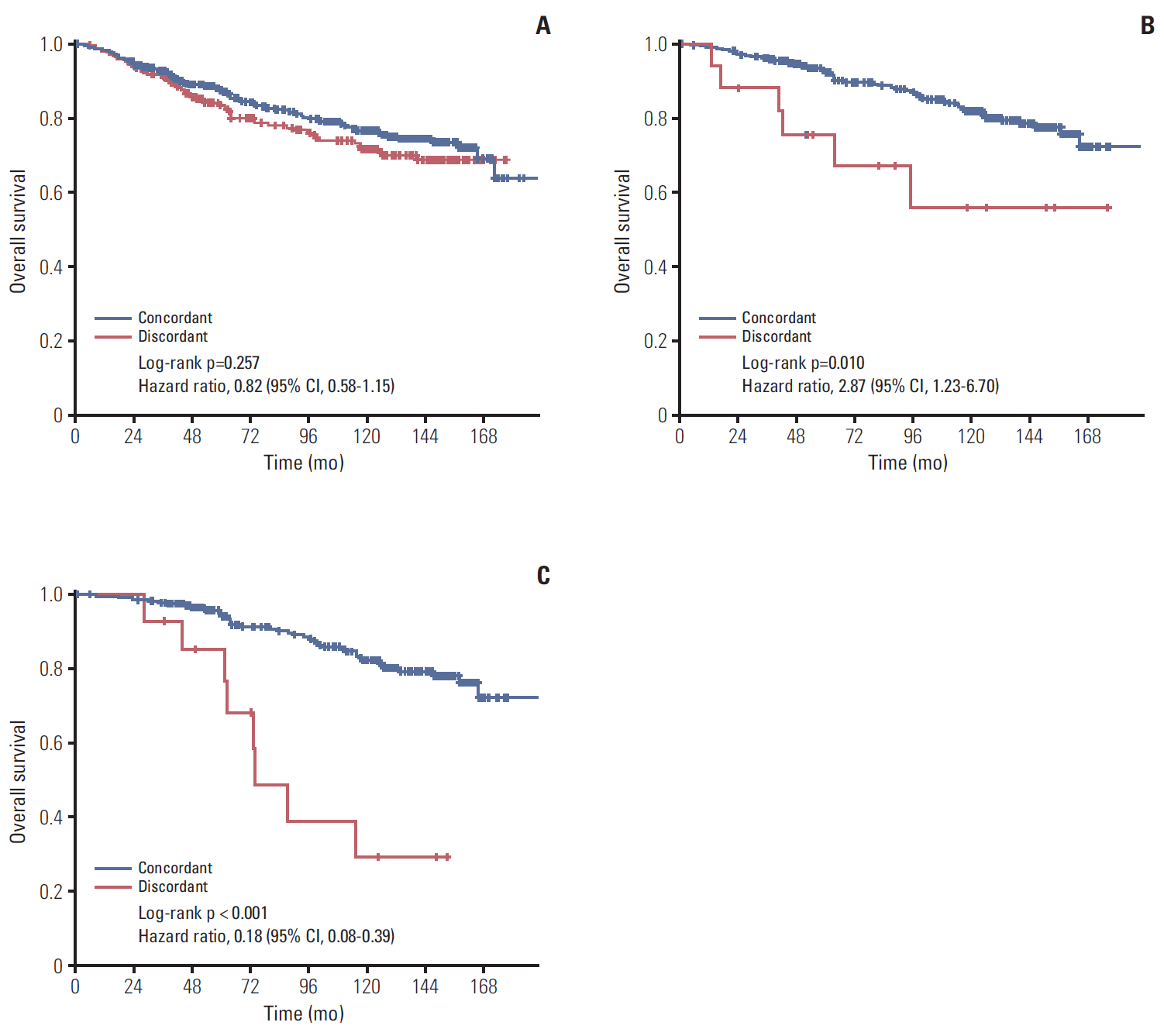
In total, 233 patients (38.4%) were discordant between IHC-based subtype and PAM50 intrinsic subtype. Using targeted sequencing, we detected somatic mutation-related discordant breast cancer including the VHL gene in the HR+/HER2- group (31% in concordant group, 0% in discordant group, p=0.03) and the IDH and RET genes (7% vs. 12%, p=0.02 and 0% vs. 25%, p=0.02, respectively) in the TNBC group. Among the luminal A/B patients with a discordant result had significantly worse OS (median OS, 73.6 months vs. not reached; p < 0.001), and among the patients with HR positivity, the basal-like group as determined by PAM50 showed significantly inferior OS compared to other intrinsic subtypes (5-year OS rate, 92.2% vs. 75.6%; p=0.01).
CONCLUSION
A substantial portion of patients showed discrepancy between IHC subtype and PAM50 intrinsic subtype in our study. The survival analysis demonstrated that current IHC-based classification could mislead the treatment and result in poor outcome. Current guidelines for IHC might be updated accordingly.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015; 65:87–108.
Article2. Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012; 490:61–70.3. Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000; 406:747–52.
Article4. Prat A, Parker JS, Fan C, Perou CM. PAM50 assay and the three-gene model for identifying the major and clinically relevant molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 135:301–6.
Article5. Sotiriou C, Pusztai L. Gene-expression signatures in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:790–800.
Article6. Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J, Cronin M, et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:2817–26.
Article7. Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, Leung S, Voduc D, Vickery T, et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:1160–7.
Article8. Prat A, Perou CM. Deconstructing the molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2011; 5:5–23.
Article9. Gnant M, Filipits M, Greil R, Stoeger H, Rudas M, Bago-Horvath Z, et al. Predicting distant recurrence in receptor-positive breast cancer patients with limited clinicopathological risk: using the PAM50 Risk of Recurrence score in 1478 postmenopausal patients of the ABCSG-8 trial treated with adjuvant endocrine therapy alone. Ann Oncol. 2014; 25:339–45.
Article10. Dowsett M, Sestak I, Lopez-Knowles E, Sidhu K, Dunbier AK, Cowens JW, et al. Comparison of PAM50 risk of recurrence score with oncotype DX and IHC4 for predicting risk of distant recurrence after endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:2783–90.
Article11. Nielsen TO, Parker JS, Leung S, Voduc D, Ebbert M, Vickery T, et al. A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16:5222–32.
Article12. Leong SP, Shen ZZ, Liu TJ, Agarwal G, Tajima T, Paik NS, et al. Is breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western countries? World J Surg. 2010; 34:2308–24.
Article13. Min SY, Kim Z, Hur MH, Yoon CS, Park EH, Jung KW, et al. The basic facts of Korean breast cancer in 2013: results of a nationwide survey and breast cancer registry database. J Breast Cancer. 2016; 19:1–7.
Article14. Park YH, Lee SJ, Jung HA, Kim SM, Kim MJ, Kil WH, et al. Prevalence and clinical outcomes of young breast cancer (YBC) patients according to intrinsic breast cancer subtypes: Single institutional experience in Korea. Breast. 2015; 24:213–7.
Article15. Harris LN, Ismaila N, McShane LM, Andre F, Collyar DE, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, et al. Use of biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant systemic therapy for women with early-stage invasive breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:1134–50.
Article16. Sohn I, Kim J, Jung SH, Park C. Gradient lasso for Cox proportional hazards model. Bioinformatics. 2009; 25:1775–81.
Article17. Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A. Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 2007; 8:118–27.
Article18. Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013; 24:2206–23.19. Krop I, Ismaila N, Andre F, Bast RC, Barlow W, Collyar DE, et al. Use of biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant systemic therapy for women with early-stage invasive breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:2838–47.
Article20. Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ, et al. Strategies for subtypes: dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011; 22:1736–47.21. Paquet ER, Hallett MT. Absolute assignment of breast cancer intrinsic molecular subtype. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015; 107:357.
Article22. Carey LA, Berry DA, Cirrincione CT, Barry WT, Pitcher BN, Harris LN, et al. Molecular heterogeneity and response to neoadjuvant human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 targeting in CALGB 40601, a randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel plus trastuzumab with or without lapatinib. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:542–9.
Article23. Ramaswamy S, Ross KN, Lander ES, Golub TR. A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors. Nat Genet. 2003; 33:49–54.
Article24. van 't Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 2002; 415:530–6.25. Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JC, Leary RJ, Angenendt P, et al. An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma multiforme. Science. 2008; 321:1807–12.
Article26. Combs SE, Rieken S, Wick W, Abdollahi A, von Deimling A, Debus J, et al. Prognostic significance of IDH-1 and MGMT in patients with glioblastoma: one step forward, and one step back? Radiat Oncol. 2011; 6:115.
Article27. Kan Z, Jaiswal BS, Stinson J, Janakiraman V, Bhatt D, Stern HM, et al. Diverse somatic mutation patterns and pathway alterations in human cancers. Nature. 2010; 466:869–73.
Article28. Plaza-Menacho I, Burzynski GM, de Groot JW, Eggen BJ, Hofstra RM. Current concepts in RET-related genetics, signaling and therapeutics. Trends Genet. 2006; 22:627–36.29. Esseghir S, Todd SK, Hunt T, Poulsom R, Plaza-Menacho I, Reis-Filho JS, et al. A role for glial cell derived neurotrophic factor induced expression by inflammatory cytokines and RET/GFR alpha 1 receptor up-regulation in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:11732–41.30. Tozlu S, Girault I, Vacher S, Vendrell J, Andrieu C, Spyratos F, et al. Identification of novel genes that co-cluster with estrogen receptor alpha in breast tumor biopsy specimens, using a large-scale real-time reverse transcription-PCR approach. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006; 13:1109–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between MR Image-Based Radiomics Features and Risk Scores Associated with Gene Expression Profiles in Breast Cancer
- Comparative Analysis of T-Score Discordance between a Registry-Based Korean Population and Atypical Femoral Fracture Patients of a Single Institution
- Different Pattern of T-Score Discordance between Patients with Atypical Femoral Fracture and Femur Neck Fracture
- Comparative Study Between Radioisotope Uptake and Fluorescence Intensity of Indocyanine Green for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer
- Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion to Identify Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer with Different Vascular Normalization Gene Expression