Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Oct;51(4):1420-1429. 10.4143/crt.2018.638.
MiR-1246 Promotes Metastasis and Invasion of A549 cells by Targeting GSK-3β‒Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Second People's Hospital of China Three Gorges University, Yichang, China.
- 2Hubei Key Laboratory of Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapy, Yichang, China. zyjzyq@163.com
- 3Medical College of Three Gorges University, Yichang, China.
- 4The Institute of Infection and Inflammation, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, China.
- KMID: 2460591
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.638
Abstract
- PURPOSE
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of small non-coding RNAs involved in different cancers, including lung cancer. Here, we aim to investigate the expression profiles of circulating miRNAs and their roles contributed to the progress of lung cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
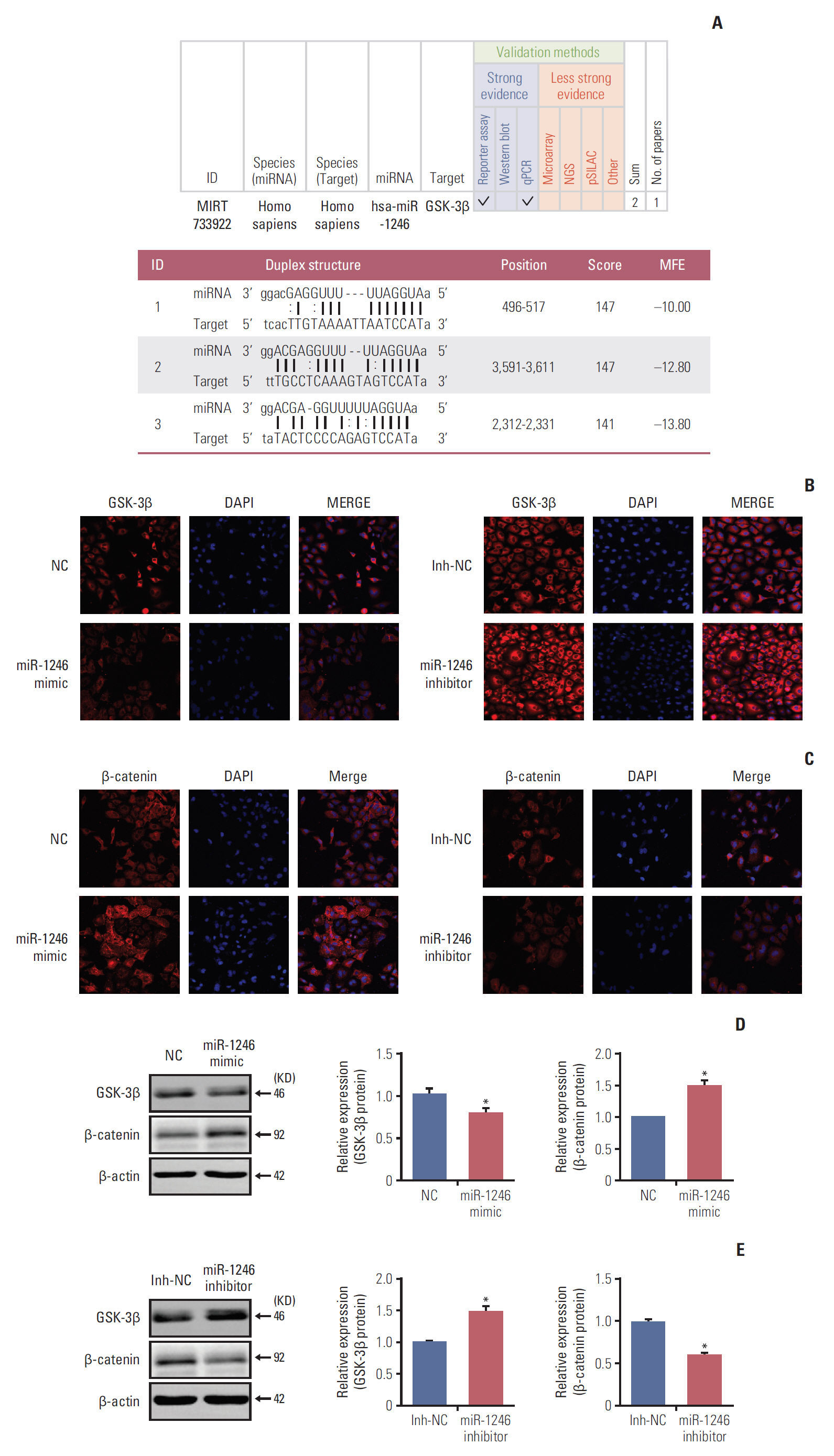
The levels of circulating miRNA in lung cancer patients were investigated by miRNAs assay. Then we predicted the target genes of aberrantly expressing miRNAs by searching genetic databases. Based on the A549 cells transfected with miR-1246 mimics or miR-1246 inhibitor,we further measured the roles of miR-1246 involving in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration and invasion capacities of lung cancer cells in vitro. Finally, we detected the effects of miR-1246 on glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β)/β-catenin pathway by immunofluorescence and Western blot, respectively.
RESULTS
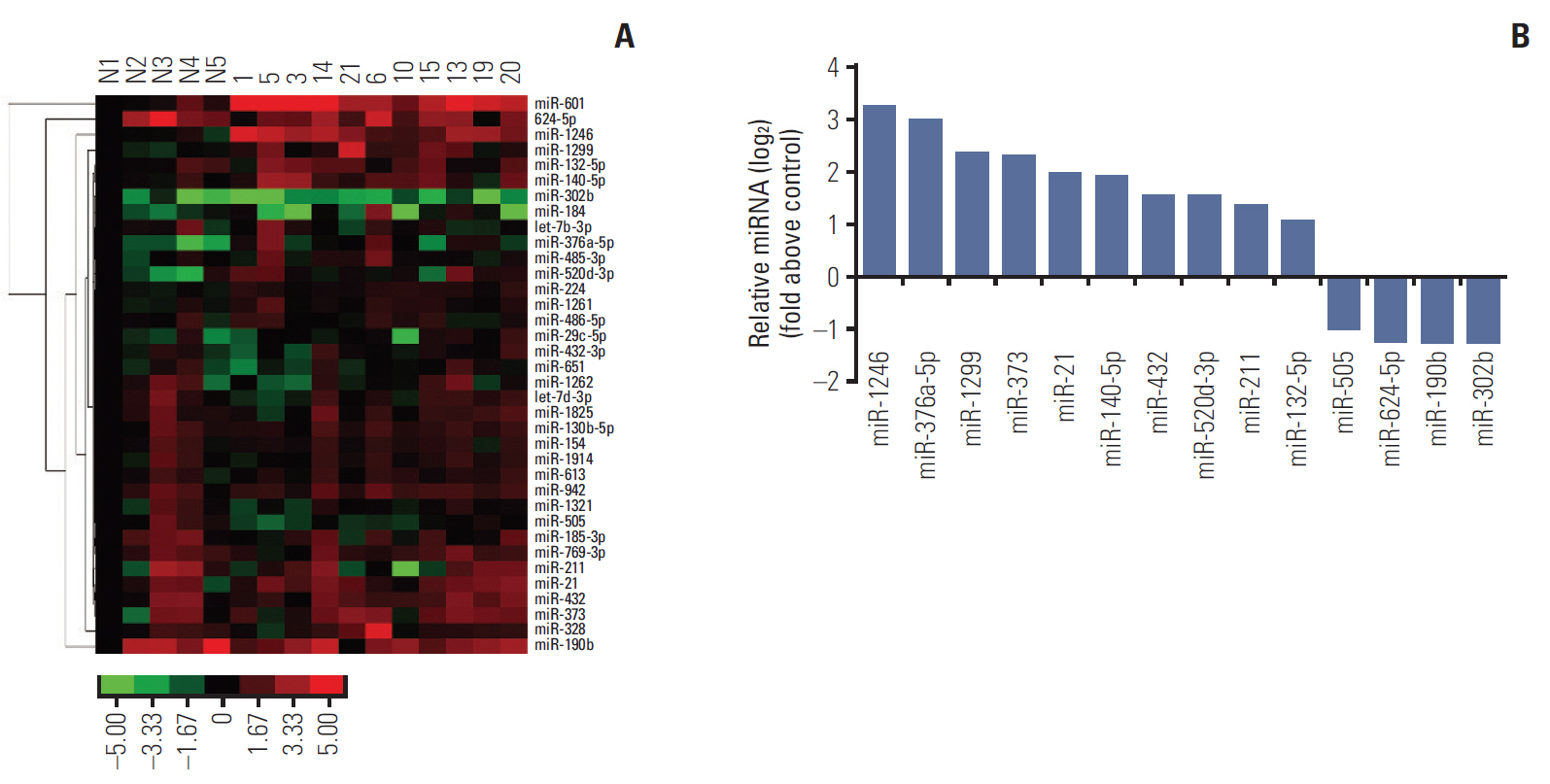
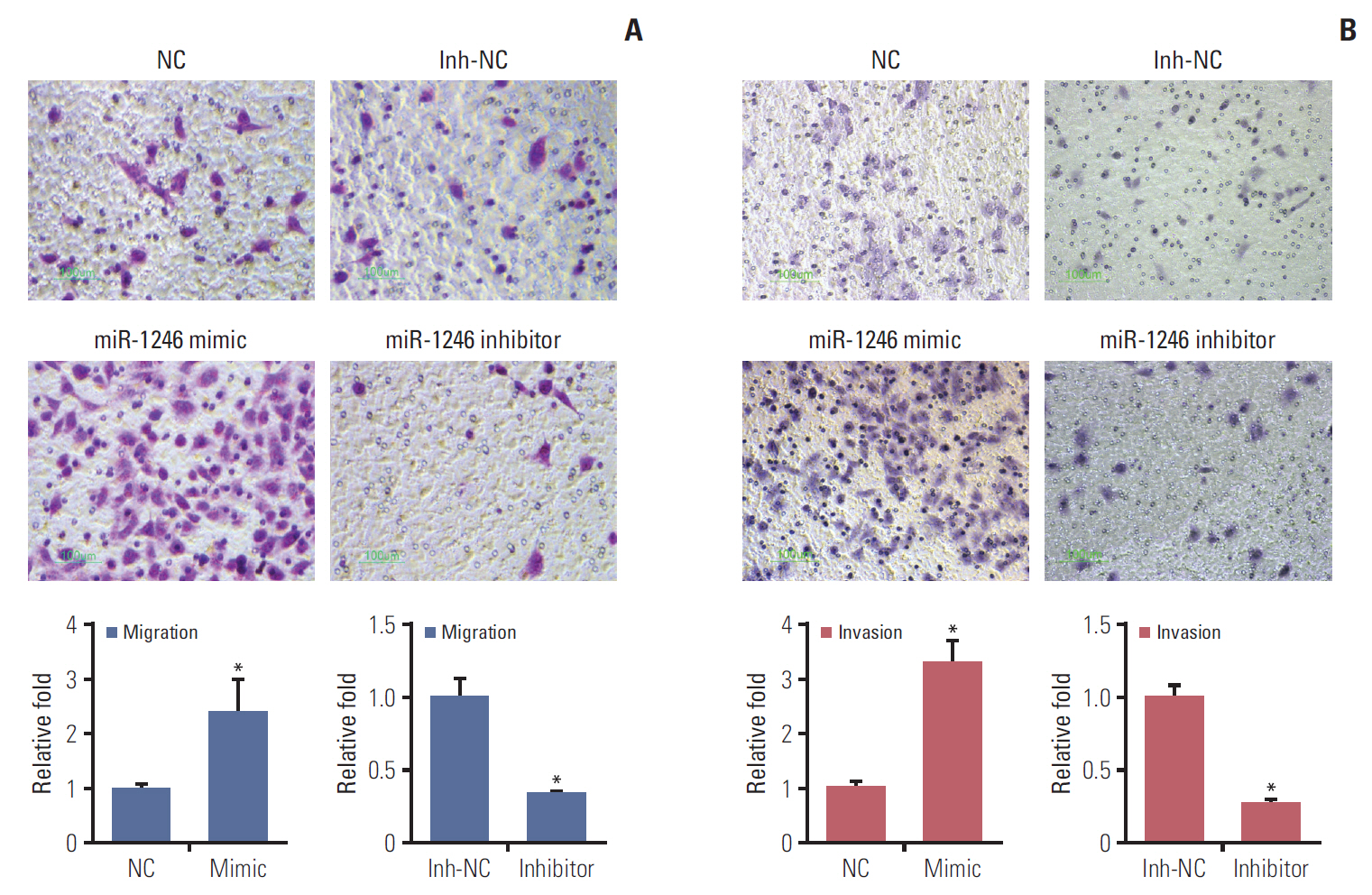
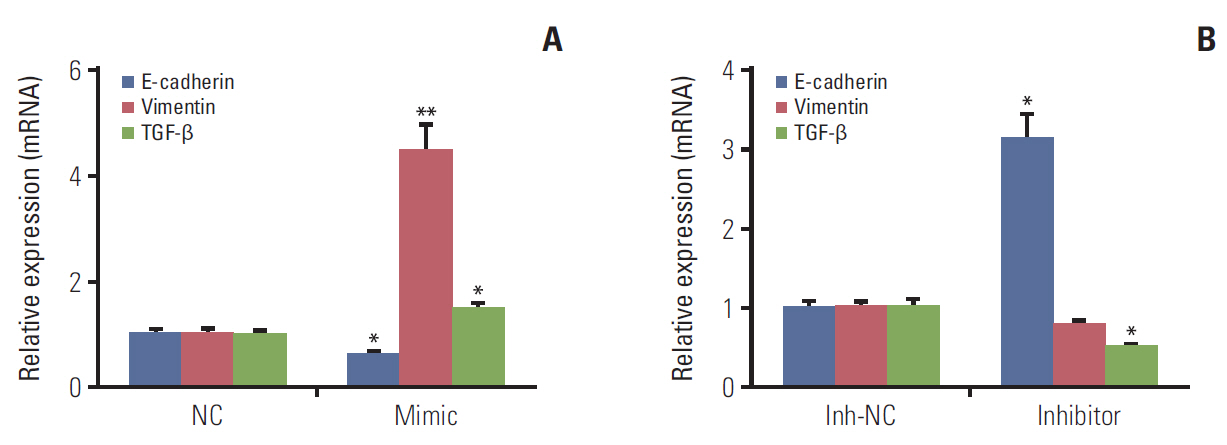
We identified that 14 miRNAs were aberrantly expressed in the serum of lung cancer patients. Among them, miR-1246 was the most up-regulated. The cell assays indicated that miR-1246 significantly increased the migration and invasion capabilities of A549 lung cancer cells. Meanwhile, immunofluorescence analysis revealed that miR-1246 promoted EMT process of A549 cells accompanying with decreasing E-cadherin expression, while increasing vimentin and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) expression. Furthermore, an online tool predicated that miR-1246 might bind to 3"²-untranslated region of GSK-3β, which was confirmed by overexpression and knockdown of miR-1246 assays.
CONCLUSION
Taken together, the study illustrates that miR-1246 regulates Wnt/β-catenin pathway through targeting GSK-3β/β-catenin, which partly contributing to tumor metastasis. MiR-1246 may play an essential role in the diagnosis and therapeutic of lung cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Blotting, Western
Cadherins
Databases, Genetic
Diagnosis
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Fluorescent Antibody Technique
Glycogen Synthase
Humans
In Vitro Techniques
Lung Neoplasms
MicroRNAs
Neoplasm Metastasis*
RNA, Small Untranslated
Transforming Growth Factors
Vimentin
Cadherins
Glycogen Synthase
MicroRNAs
RNA, Small Untranslated
Transforming Growth Factors
Vimentin
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Uddin A, Chakraborty S. Role of miRNAs in lung cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2018; Apr. 20. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26607.
Article2. Lin G, Liu B, Meng Z, Liu Y, Li X, Wu X, et al. MiR-26a enhances invasive capacity by suppressing GSK3beta in human lung cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2017; 352:364–74.3. Jiang W, Wei K, Pan C, Li H, Cao J, Han X, et al. MicroRNA-1258 suppresses tumour progression via GRB2/Ras/Erk pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cell Prolif. 2018; 51:e12502.
Article4. Wu KL, Tsai MJ, Yang CJ, Chang WA, Hung JY, Yen CJ, et al. Liver metastasis predicts poorer prognosis in stage IV lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving first-line gefitinib. Lung Cancer. 2015; 88:187–94.
Article5. Reck M, Popat S, Reinmuth N, De Ruysscher D, Kerr KM, Peters S, et al. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014; 25 Suppl 3:iii27–39.
Article6. Bica-Pop C, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Magdo L, Raduly L, Gulei D, Berindan-Neagoe I. Overview upon miR-21 in lung cancer: focus on NSCLC. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018; 75:3539–51.
Article7. Song L, Peng L, Hua S, Li X, Ma L, Jie J, et al. miR-144-5p enhances the radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via targeting ATF2. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:5109497.
Article8. Kim S, Kim TM, Kim DW, Kim S, Kim M, Ahn YO, et al. Acquired resistance of MET-amplified non-small cell lung cancer cells to the MET inhibitor capmatinib. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:951–62.
Article9. Nowrin K, Sohal SS, Peterson G, Patel R, Walters EH. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a fundamental underlying pathogenic process in COPD airways: fibrosis, remodeling and cancer. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2014; 8:547–59.
Article10. Sung WJ, Kim H, Park KK. The biological role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 2016; 36:1199–206.
Article11. Otsuki Y, Saya H, Arima Y. Prospects for new lung cancer treatments that target EMT signaling. Dev Dyn. 2018; 247:462–72.
Article12. Martinez-Rivera V, Negrete-Garcia MC, Avila-Moreno F, Ortiz-Quintero B. Secreted and tissue miRNAs as diagnosis biomarkers of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19:E195.13. Moshiri F, Salvi A, Gramantieri L, Sangiovanni A, Guerriero P, De Petro G, et al. Circulating miR-106b-3p, miR-101-3p and miR-1246 as diagnostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2018; 9:15350–64.
Article14. Li L, Sun Y, Feng M, Wang L, Liu J. Clinical significance of blood-based miRNAs as biomarkers of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15:8915–25.15. Yang Y, Sun Y, Wu Y, Tang D, Ding X, Xu W, et al. Downregulation of miR-3127-5p promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via FZD4 regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2018; 57:842–53.16. Baranwal S, Alahari SK. miRNA control of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 2010; 126:1283–90.
Article17. Skronska-Wasek W, Gosens R, Konigshoff M, Baarsma HA. WNT receptor signalling in lung physiology and pathology. Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 187:150–66.
Article18. Tanaka K, Kumano K, Ueno H. Intracellular signals of lung cancer cells as possible therapeutic targets. Cancer Sci. 2015; 106:489–96.
Article19. Krishnamurthy N, Kurzrock R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: update on effectors and inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018; 62:50–60.
Article20. Jia Z, Zhang Y, Xu Q, Guo W, Guo A. miR-126 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by targeting PI3K/AKT/Snail signaling of lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15:7369–75.
Article21. Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:10513–8.
Article22. Kodahl AR, Lyng MB, Binder H, Cold S, Gravgaard K, Knoop AS, et al. Novel circulating microRNA signature as a potential non-invasive multi-marker test in ER-positive early-stage breast cancer: a case control study. Mol Oncol. 2014; 8:874–83.
Article23. Ortiz-Quintero B. Cell-free microRNAs in blood and other body fluids, as cancer biomarkers. Cell Prolif. 2016; 49:281–303.
Article24. Zhang WC, Chin TM, Yang H, Nga ME, Lunny DP, Lim EK, et al. Tumour-initiating cell-specific miR-1246 and miR-1290 expression converge to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:11702.
Article25. Kim G, An HJ, Lee MJ, Song JY, Jeong JY, Lee JH, et al. HsamiR-1246 and hsa-miR-1290 are associated with stemness and invasiveness of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2016; 91:15–22.
Article26. Yuan D, Xu J, Wang J, Pan Y, Fu J, Bai Y, et al. Extracellular miR-1246 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and enhances radioresistance by directly targeting DR5. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:32707–22.
Article27. Chai S, Ng KY, Tong M, Lau EY, Lee TK, Chan KW, et al. Octamer 4/microRNA-1246 signaling axis drives Wnt/beta-catenin activation in liver cancer stem cells. Hepatology. 2016; 64:2062–76.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of microRNA-135a on the epithelial–mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by targeting GSK3β through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- The Long Non-Coding RNA CASC2 Suppresses Cell Viability, Migration, and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Directly Downregulating miR-183
- miR-34a Inhibitor May Effectively Protect against Sevoflurane-Induced Hippocampal Apoptosis through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Targeting Wnt1
- MiR-214 Regulates the Human Hair Follicle Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation by Targeting EZH2 and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Way In Vitro
- The Long Noncoding RNA NEAT1 Targets miR-34a-5p and Drives Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Progression via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling