Nat Prod Sci.
2019 Sep;25(3):238-243. 10.20307/nps.2019.25.3.238.
Quantification of the Bioactive Components of the Rhizomes of Curcuma wenyujin and Assessment of Its Anti-inflammatory Effect in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia-1 Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Herbal Medicine Research Division, Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, Daejeon 34054, Korea. hkshin@kiom.re.kr
- KMID: 2459966
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.20307/nps.2019.25.3.238
Abstract
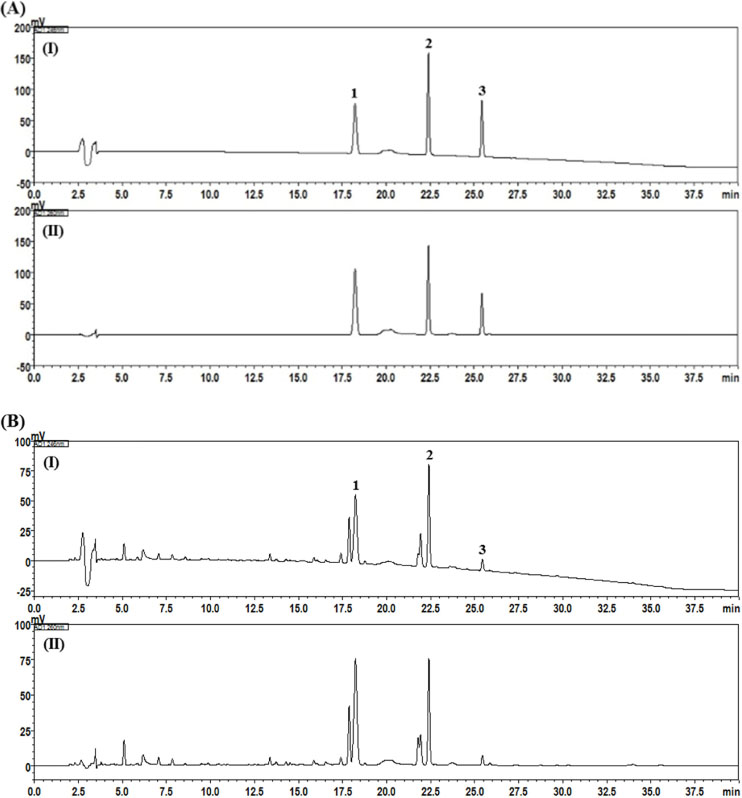
- In this study, the marker compounds of Curcumae Rhizoma (CR) were simultaneously quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography equipped with a photodiode array detector and the anti-inflammatory effects of CR extract and marker compounds in human benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial-1 (BPH-1) cell lines were investigated. The marker components (4S,5S)-(+)-germacrone-4,5-epoxide, furanodienone, and germacrone, were separated on Gemini Câ‚₈ columns (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) at 40 ℃ by using a gradient of two mobile phases eluting at 1.0 mL/min. Prostaglandin Eâ‚‚ (PGEâ‚‚) levels in Human BPH-1 cells were determined with an ELISA kit. The coefficients of determination in a calibration curve of each analyte were all 0.9997. The limits of detection and quantification of the three compounds were 0.10 - 0.32 µg/mL and 0.30 - 0.98 µg/mL, respectively. The content of three compounds, (4S,5S)-(+)-germacrone-4,5-epoxide, furanodienone, and germacrone, in the CR sample were found to be 5.79 - 5.92 mg/g, 4.72 - 4.86 mg/g, and 1.06 - 1.09 mg/g, respectively. Regarding pharmacological activity against benign prostatic hyperplasia, CR and its components significantly suppressed PGEâ‚‚ levels of BPH-1 cells. The established analysis method will help to improve quality assessment of CR samples and related products. In addition, CR and its components exhibit anti-inflammatory activity in BPH-1 cells, suggesting the inhibitory efficacy of these compounds against the pathogenesis of BPH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dong JY, Ma XY, Cai XQ, Yan PC, Yue L, Lin C, Shao WW. Phytochemistry. 2013; 85:122–128.2. An YW, Hu G, Yin GP, Zhu JJ, Zhang QW, Wang ZM, Peng J, Fan B. J Chromatogr Sci. 2014; 52:961–970.3. Korean Pharmacopoeia Committee. The Korean Pharmacopoeia. 11th eds. Seoul: Shinilbooks;2014. p. 1836.4. Yan J, Chen G, Tong S, Feng Y, Sheng L, Lou J. J Chromatogr A. 2005; 1070:207–210.5. Qiu G, Yan P, Shao W, Zhou J, Lin W, Fang L, Zhao X, Dong J. Chem Pharm Bull. 2013; 61:983–986.6. Zhou CX, Zhang LS, Chen FF, Wu HS, Mo JX, Gan LS. Fitoterapia. 2017; 121:141–145.7. Lou Y, Zhao F, He H, Peng KF, Chen LX, Qiu F. Chem Biodivers. 2010; 7:1245–1253.8. Dong J, Shao W, Yan P, Cai X, Fang L, Zhao X, Lin W, Cai Y. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015; 25:198–202.9. Ma ZJ, Meng ZK, Zhang P. Fitoterapia. 2009; 80:374–376.10. Park E, Lee MY, Seo CS, Jeon WY, Shin HK. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017; 209:230–235.11. Wang X, Jiang Y, Hu D. Chem Cent J. 2016; 10:32.12. Tohda C, Nakayama N, Hatanaka F, Komatsu K. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006; 3:255–260.13. Hou Y, Lu CL, Zeng QH, Jiang JG. EXCLI J. 2015; 14:706–713.14. Shacter E, Weitzman SA. Oncology (Williston Park). 2002; 16:217–226.15. Gual-Vaqués P, Jané-Salas E, Egido-Moreno S, Ayuso-Montero R, Marí-Roig A, López-López J. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017; 22:e36–e42.16. Robert G, Descazeaud A, Nicolaiew N, Terry S, Sirab N, Vacherot F, Maillé P, Allory Y, de la. Prostate. 2009; 69:1774–1780.17. Handisurya A, Steiner GE, Stix U, Ecker RC, Pfaffeneder-Mantai S, Langer D, Kramer G, Memaran-Dadgar N, Marberger M. Prostate. 2001; 49:251–262.18. Wu Q, Zhou Y, Chen L, Shi J, Wang CY, Miao L, Klocker H, Park I, Lee C, Zhang J. J Endocrinol. 2007; 195:89–94.19. Zhang YJ, Bai Q. Natl J Androl. 2014; 20:244–248.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Prominently Large Glans penis as a Possible sign of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Ethanol Extract of Chaenomeles sinensis Inhibits the Development of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Exhibiting Anti-oxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
- Antibiotic Components from the Rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria
- Inflammatory Responses in a Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Epithelial Cell Line (BPH-1) Infected with Trichomonas vaginalis
- The Effects of Abdominal Obesity on the Increased Prevalence Rate of Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Patients